Top 10
... there are observed to be layers where there are mass extinctions, when up to 95 percent of life on Earth became extinct. One such mass extinction period occurred 65 million years ago, and coincides with the independently determined extinction era for dinosaur species. This time is well before the ea ...
... there are observed to be layers where there are mass extinctions, when up to 95 percent of life on Earth became extinct. One such mass extinction period occurred 65 million years ago, and coincides with the independently determined extinction era for dinosaur species. This time is well before the ea ...
Cartwheel Galaxy - Chandra X
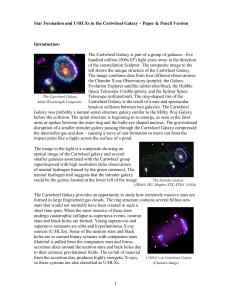
... 8. Is there an X-ray candidate for an active galactic nucleus (AGN) in Arp 147? Explain. 9. Why might there not be new star formation in the elliptical galaxy on the left? 10. A study of ULXs has determined that very few X-ray sources with luminosity greater than 1040 erg s−1 remain after ~15 Myr a ...
... 8. Is there an X-ray candidate for an active galactic nucleus (AGN) in Arp 147? Explain. 9. Why might there not be new star formation in the elliptical galaxy on the left? 10. A study of ULXs has determined that very few X-ray sources with luminosity greater than 1040 erg s−1 remain after ~15 Myr a ...
Galaxy interaction and transformation
... progenitors are more tilted relative to the orbital angular momentum. Highly flattened remnants can be produced in prograte and retrograde encounters. 2. The remnant of a major merger generally rotates slowly in the inner region but fast in the outer part. This happens because dynamic friction can t ...
... progenitors are more tilted relative to the orbital angular momentum. Highly flattened remnants can be produced in prograte and retrograde encounters. 2. The remnant of a major merger generally rotates slowly in the inner region but fast in the outer part. This happens because dynamic friction can t ...
DTU_9e_ch04 - University of San Diego Home Pages
... compositions of stars and interstellar clouds by studying the wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation that they absorb or emit how to tell whether an object in space is moving toward or away from Earth ...
... compositions of stars and interstellar clouds by studying the wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation that they absorb or emit how to tell whether an object in space is moving toward or away from Earth ...
Angular momentum evolution
... • Several thousands of rotational periods now available for solar-type and low-mass stars from ~1 Myr to a ~10 Gyr (0.2-1.2 Msun) • Kepler still expected to yield many more rotational periods for field stars • Several tens of vsini measurements available for VLM stars and brown dwarfs ...
... • Several thousands of rotational periods now available for solar-type and low-mass stars from ~1 Myr to a ~10 Gyr (0.2-1.2 Msun) • Kepler still expected to yield many more rotational periods for field stars • Several tens of vsini measurements available for VLM stars and brown dwarfs ...
Life Stages of High
... of objects with <0.08MSun before the core temperature becomes hot enough for fusion. • Starlike objects not massive enough to start fusion are brown dwarfs. ...
... of objects with <0.08MSun before the core temperature becomes hot enough for fusion. • Starlike objects not massive enough to start fusion are brown dwarfs. ...
HR Diagram Explorer Worksheet
... this equation to explain the results you found in the table of the previous question. Refer to the background material you have previously reviewed. ...
... this equation to explain the results you found in the table of the previous question. Refer to the background material you have previously reviewed. ...
Stellar Physics 1
... A. A hot dense gas produces a continuous spectrum with no spectral lines. B. A hot diffuse gas produces bright spectral lines – an emission spectrum. C. A cool dense gas produces a continuous spectrum with no spectral lines. y D. A cool diffuse gas in front of a source of continuous spectrum produce ...
... A. A hot dense gas produces a continuous spectrum with no spectral lines. B. A hot diffuse gas produces bright spectral lines – an emission spectrum. C. A cool dense gas produces a continuous spectrum with no spectral lines. y D. A cool diffuse gas in front of a source of continuous spectrum produce ...
powerpoint
... than a proton that would not emit much light. • Possible, but probably ruled out. • Then there is the other possibility – does dark matter really exist? ...
... than a proton that would not emit much light. • Possible, but probably ruled out. • Then there is the other possibility – does dark matter really exist? ...
Ayres-Kepler-ASC
... fast rotating stars, but also root of magnetic braking, which ultimately quenches activity. ...
... fast rotating stars, but also root of magnetic braking, which ultimately quenches activity. ...
Red Giants - Faculty Web Pages
... Most blue stars are Main Sequence stars. But whereas some red stars in the list are simply tiny, cool Main Sequence stars, other red stars of the exact same color are huge Red Giants! Telling the difference between the Main Sequence red stars and the Red Giant stars involves some complex measurement ...
... Most blue stars are Main Sequence stars. But whereas some red stars in the list are simply tiny, cool Main Sequence stars, other red stars of the exact same color are huge Red Giants! Telling the difference between the Main Sequence red stars and the Red Giant stars involves some complex measurement ...
Exoplanets - Mid-Pacific Institute
... They plan to detect exoplanets as they pass in front of their parent stars ...
... They plan to detect exoplanets as they pass in front of their parent stars ...
PPT
... higher brightness at left rim? Jacoby et al (2001) Conservation of momentum ΔM ≈ 0.05 M סּ 0.9 kms-1 ...
... higher brightness at left rim? Jacoby et al (2001) Conservation of momentum ΔM ≈ 0.05 M סּ 0.9 kms-1 ...
White Dwarfs and the age of the Universe
... diameter of Sirius B = 99% of the diameter of Earth (Sirius is 1.7 times bigger in diameter than Sun) ...
... diameter of Sirius B = 99% of the diameter of Earth (Sirius is 1.7 times bigger in diameter than Sun) ...
Student 1
... their cores and energy is generated at a slow rate through nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. These stars emit little light. In general, Red dwarfs less than 0.35 M☉ transport energy from the core to the surface by convection. Convection occurs because of opacity of the interior, which has a hi ...
... their cores and energy is generated at a slow rate through nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. These stars emit little light. In general, Red dwarfs less than 0.35 M☉ transport energy from the core to the surface by convection. Convection occurs because of opacity of the interior, which has a hi ...
Tuesday, October 28th "The Formation and Evolution of Galaxies"
... Raman Prinja is a Professor of Astrophysics at University College London, where he conducts research on massive stars in our Galaxy. The recipient of several awards, he has received the Royal Academy of Belgium’s Pol and Christiane Swings research prize and the faculty and departmental teaching awar ...
... Raman Prinja is a Professor of Astrophysics at University College London, where he conducts research on massive stars in our Galaxy. The recipient of several awards, he has received the Royal Academy of Belgium’s Pol and Christiane Swings research prize and the faculty and departmental teaching awar ...
Sco
... Be stars are rapidly rotating non-supergiant objects of spectral type B that sometimes show hydrogen emission lines in their spectra ...
... Be stars are rapidly rotating non-supergiant objects of spectral type B that sometimes show hydrogen emission lines in their spectra ...
Ch13_Lecture - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given luminosity, the larger the radiu ...
... • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given luminosity, the larger the radiu ...
Power-point slides for Lecture 5
... as we shall see. And the boundary pressure of the overlying silicon shell is not entirely negligible. ...
... as we shall see. And the boundary pressure of the overlying silicon shell is not entirely negligible. ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.