Related Handout - Orange County Astronomers
... to capture the fainter or more scattered stars at the edges. Clusters like the Double Cluster in Perseus or M13 in Hercules are astonishingly beautiful when observed through a moderately sized scope. There are two types of star clusters: galactic or open clusters, and globular clusters. 4.2.1. Galac ...
... to capture the fainter or more scattered stars at the edges. Clusters like the Double Cluster in Perseus or M13 in Hercules are astonishingly beautiful when observed through a moderately sized scope. There are two types of star clusters: galactic or open clusters, and globular clusters. 4.2.1. Galac ...
GG_CERN_0707
... Either (i) determine mass profile from projected dispersion profile, with assumed isotropy, and smooth functional fit to the light profile Or (ii) assume a parameterised mass model M(r) and velocity dispersion anisotropy β(r) and fit dispersion profile to find best forms of these (for fixed light ...
... Either (i) determine mass profile from projected dispersion profile, with assumed isotropy, and smooth functional fit to the light profile Or (ii) assume a parameterised mass model M(r) and velocity dispersion anisotropy β(r) and fit dispersion profile to find best forms of these (for fixed light ...
The Bigger Picture - Astronomy and Astrophysics
... and evolution. In about a week we will follow through that history. • For now, we will use the H-R Diagram to determine one more property of stars. ...
... and evolution. In about a week we will follow through that history. • For now, we will use the H-R Diagram to determine one more property of stars. ...
Spectroscopy PPT
... Spectra (rainbows of diffracted light) can come from a (hot) glowing solid, a glowing liquid or a glowing gas (star). ...
... Spectra (rainbows of diffracted light) can come from a (hot) glowing solid, a glowing liquid or a glowing gas (star). ...
Recipe for a Star
... of mostly helium, then another shell of mostly hydrogen (see figure 5.19). The helium fusion in the core continues until helium is all used up in making carbon. Most of the red giants’s mass remains concentrated in the dense carbon core. These red giants are not hot enough to start carbon fusion. Th ...
... of mostly helium, then another shell of mostly hydrogen (see figure 5.19). The helium fusion in the core continues until helium is all used up in making carbon. Most of the red giants’s mass remains concentrated in the dense carbon core. These red giants are not hot enough to start carbon fusion. Th ...
Copyright 1995 Scientific American, Inc.
... should therefore disrupt the binary and nary phase. Since then, the discovery of at Harvard, Þrst measured the gravitasend the two neutron stars (the old three other neutron star binaries shows tional redshift, the loss of energy by one and the one that has just formed ) that other massive pairs hav ...
... should therefore disrupt the binary and nary phase. Since then, the discovery of at Harvard, Þrst measured the gravitasend the two neutron stars (the old three other neutron star binaries shows tional redshift, the loss of energy by one and the one that has just formed ) that other massive pairs hav ...
© Taganov I
... We see from Tadpole that stars form from planets in dense clumps of planets, not from gas clouds falling into merging, mythical, CDM halos. The first stars formed gently at 0.3 Myr from white-hot planet-mass clouds soon after plasma-gas recombination to form present day old globular clusters (OGCs), ...
... We see from Tadpole that stars form from planets in dense clumps of planets, not from gas clouds falling into merging, mythical, CDM halos. The first stars formed gently at 0.3 Myr from white-hot planet-mass clouds soon after plasma-gas recombination to form present day old globular clusters (OGCs), ...
Essential Questions
... (What is acceptable evidence to show desired results (rubrics, exam, etc.)? Attach Copy During the Smart Notebook lesson designed to introduce concepts, students will be continually questioned on these concepts using a combination of class work/homework questions and the SMART Response system. Class ...
... (What is acceptable evidence to show desired results (rubrics, exam, etc.)? Attach Copy During the Smart Notebook lesson designed to introduce concepts, students will be continually questioned on these concepts using a combination of class work/homework questions and the SMART Response system. Class ...
Supplementary notes on Binary Star Masses
... Here we have the sum of the masses, times sin3i, as a function of the three observables, P, K1, and K2. [Note: the book incorrectly has the velocities to the 2nd instead of 3rd power in Eqn 3.11] The advantage of this mass determination is that it is distance independent, unlike the case of visual b ...
... Here we have the sum of the masses, times sin3i, as a function of the three observables, P, K1, and K2. [Note: the book incorrectly has the velocities to the 2nd instead of 3rd power in Eqn 3.11] The advantage of this mass determination is that it is distance independent, unlike the case of visual b ...
b) How to Create Large Disks despite Major Mergers
... Therefore, disk galaxies must grow rather quiescently ...
... Therefore, disk galaxies must grow rather quiescently ...
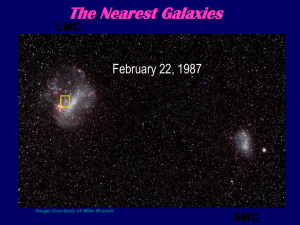
Galaxies - Mike Brotherton
... Ages of stellar population may pose a problem to the traditional theory of the history of the Milky Way. ...
... Ages of stellar population may pose a problem to the traditional theory of the history of the Milky Way. ...
Toys Watch the Sky - The Sun is a close star
... The Sun is a huge ball of glowing gases (mostly hydrogen and helium). It is the star at the centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In co ...
... The Sun is a huge ball of glowing gases (mostly hydrogen and helium). It is the star at the centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In co ...
Problem set 3 solution
... The derivation in the text assumes that the smaller star is hotter, i.e. that the primary eclipse is when the smaller star passes behind the larger. Can we back this up with the data? Assuming this is true, then in the primary eclipse we see only the larger star, which gives 100(m0 −mp )/5 = 100(5.4 ...
... The derivation in the text assumes that the smaller star is hotter, i.e. that the primary eclipse is when the smaller star passes behind the larger. Can we back this up with the data? Assuming this is true, then in the primary eclipse we see only the larger star, which gives 100(m0 −mp )/5 = 100(5.4 ...
X-ray Emission from Massive Stars
... X-rays from shock-heating in linedriven winds The Doppler desaturation that’s so helpful in driving a flow via momentum transfer in spectral lines is inherently unstable The line-driven instability (LDI) arises when a parcel of wind material is accelerated above the local flow speed, which moves it ...
... X-rays from shock-heating in linedriven winds The Doppler desaturation that’s so helpful in driving a flow via momentum transfer in spectral lines is inherently unstable The line-driven instability (LDI) arises when a parcel of wind material is accelerated above the local flow speed, which moves it ...
ppt - Department of Physics & Astronomy at the University of Utah
... Neutrinos produced from photo-disintegration and electron capture Overlying material is so dense that not even neutrinos can easily escape---> Neutrino heating just behind the shock!!! This allows the shock to resume its march towards the surface….If this does not happen quickly enough the initially ...
... Neutrinos produced from photo-disintegration and electron capture Overlying material is so dense that not even neutrinos can easily escape---> Neutrino heating just behind the shock!!! This allows the shock to resume its march towards the surface….If this does not happen quickly enough the initially ...
ASTR 105 Intro Astronomy: The Solar System
... Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: • What does the universe look like from Earth? • Why do stars rise and set? • How does the sky change with latitude and over the year? ...
... Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: • What does the universe look like from Earth? • Why do stars rise and set? • How does the sky change with latitude and over the year? ...
Structure of Neutron Stars
... The closest millisecond PSR. MNS=1.76+/-0.2 solar. Hopefully, this value will not be reconsidered. 2. The case of PSR J0751+1807. Initially, it was announced that it has a mass ~2.1 solar [astro-ph/0508050]. However, then in 2007 at a conference the authors announced that the result was incorrect. A ...
... The closest millisecond PSR. MNS=1.76+/-0.2 solar. Hopefully, this value will not be reconsidered. 2. The case of PSR J0751+1807. Initially, it was announced that it has a mass ~2.1 solar [astro-ph/0508050]. However, then in 2007 at a conference the authors announced that the result was incorrect. A ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.