Complete Lecture Notes (pdf file)
... • Individual stars • Binary systems • Star clusters....these reveal how stars evolve with time • Nuclear physics...energy source, synthesis of heavy elements No direct information about physical conditions in stellar interiors (except from helioseismology and solar neutrinos) No direct evidence for ...
... • Individual stars • Binary systems • Star clusters....these reveal how stars evolve with time • Nuclear physics...energy source, synthesis of heavy elements No direct information about physical conditions in stellar interiors (except from helioseismology and solar neutrinos) No direct evidence for ...
EarthComm_c1s3
... There are arguments against the steady-state theory. They include the discovery of the cosmic background radiation. As you read earlier, this radiation indicates that the universe did have a beginning. Just after the big bang, all that existed in the universe was energy. As the universe expanded, it ...
... There are arguments against the steady-state theory. They include the discovery of the cosmic background radiation. As you read earlier, this radiation indicates that the universe did have a beginning. Just after the big bang, all that existed in the universe was energy. As the universe expanded, it ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... F) At what altitude would Polaris appear above the northern horizon? Polaris would appear above the northern horizon at 32° altitude. G) Would a star with a declination of +60 be circumpolar? Explain. A star with a declination of +60 be circumpolar. It would dip to 2° above the northern horizon. H ...
... F) At what altitude would Polaris appear above the northern horizon? Polaris would appear above the northern horizon at 32° altitude. G) Would a star with a declination of +60 be circumpolar? Explain. A star with a declination of +60 be circumpolar. It would dip to 2° above the northern horizon. H ...
Microlensing Studies in Crowded Fields
... observed. We use Baade’s window in the bulge of the Milky Way. • Only main sequence stars will interest us: giant stars are too big to give the microlensing effect we seek. ...
... observed. We use Baade’s window in the bulge of the Milky Way. • Only main sequence stars will interest us: giant stars are too big to give the microlensing effect we seek. ...
How is Light Made?
... enough to circle around the earth 7.5 times in 1 second. Its properties demonstrate both wave-like nature (like interference) and particle-like nature (like photo-electric effect.) ...
... enough to circle around the earth 7.5 times in 1 second. Its properties demonstrate both wave-like nature (like interference) and particle-like nature (like photo-electric effect.) ...
Rotation Curves:
... • Note that density wave theory does not explain flocculent spirals. Those can be explained by self-propagating star formation: – Star forming regions produce supernovae, which shocks the gas, which triggers more star formation, etc, etc, etc – Differential rotation stretches out the regions of star ...
... • Note that density wave theory does not explain flocculent spirals. Those can be explained by self-propagating star formation: – Star forming regions produce supernovae, which shocks the gas, which triggers more star formation, etc, etc, etc – Differential rotation stretches out the regions of star ...
Star Maps and Constellations (pdf 3.7 Megs)
... magnitude, so numbers "less" than 1 have to be used. For example, Vega has a magnitude of 0, meaning it is brighter than a first magnitude star. The brightest star is Sirius, with a magnitude of 1.5, even brighter than Vega. The moon on this scale is -12.5, the sun -26.8 (see Table SC-VI). Polaris w ...
... magnitude, so numbers "less" than 1 have to be used. For example, Vega has a magnitude of 0, meaning it is brighter than a first magnitude star. The brightest star is Sirius, with a magnitude of 1.5, even brighter than Vega. The moon on this scale is -12.5, the sun -26.8 (see Table SC-VI). Polaris w ...
Capturing Heaven - Communicating Astronomy with the Public Journal
... Simply put, how does one draw space? To answer this question, it is necessary to move beyond the details of “How do I do such and such in Photoshop?” I’ll say this right up front: this article is not going anywhere near the raw techniques needed to create celestial art. I’ve discussed this with a nu ...
... Simply put, how does one draw space? To answer this question, it is necessary to move beyond the details of “How do I do such and such in Photoshop?” I’ll say this right up front: this article is not going anywhere near the raw techniques needed to create celestial art. I’ve discussed this with a nu ...
Chapter 17 Star Stuff Agenda How does a star`s mass affect nuclear
... • Fusion progresses no further in a low-mass star because the core temperature never grows hot enough for fusion of heavier elements (some He fuses to C to make oxygen) • Degeneracy pressure supports the white dwarf against gravity ...
... • Fusion progresses no further in a low-mass star because the core temperature never grows hot enough for fusion of heavier elements (some He fuses to C to make oxygen) • Degeneracy pressure supports the white dwarf against gravity ...
Neutron Stars
... Note: The shortest period pulsar is around 0.001 seconds (millisecond pulsar). ...
... Note: The shortest period pulsar is around 0.001 seconds (millisecond pulsar). ...
File
... To show that light is broken into many colors. Red light has a longer, more stretched-out wavelength. Galaxies that are moving away from us appear red. This shows that the universe is expanding, which supports the Big Bang theory. ...
... To show that light is broken into many colors. Red light has a longer, more stretched-out wavelength. Galaxies that are moving away from us appear red. This shows that the universe is expanding, which supports the Big Bang theory. ...
Stars and Galaxies
... millions to hundreds of millions of stars old! 6 to 13 billion years mostly red giants and dwarfs stars are clumped closely together, especially near the center of the cluster (densely) surround our disk as a halo ...
... millions to hundreds of millions of stars old! 6 to 13 billion years mostly red giants and dwarfs stars are clumped closely together, especially near the center of the cluster (densely) surround our disk as a halo ...
The LMC transition star R84 and the core of the LH 39 OB association
... the evolutionary sequence, between O and Wolf-Rayet (W-R) stars, is still far from being established. Of prime importance for this topic is the investigation of a very small family of objects, the so-called Ofpe/WN9 transition stars, which seems to hold the keys for better understanding the physical ...
... the evolutionary sequence, between O and Wolf-Rayet (W-R) stars, is still far from being established. Of prime importance for this topic is the investigation of a very small family of objects, the so-called Ofpe/WN9 transition stars, which seems to hold the keys for better understanding the physical ...
Nucleosynthesis in the Early Universe.
... but photodisintegration occurs at same rate as fusion. - When T falls further fusion occurs faster than photodisintegration then deuterons form. - This leads to formation of 4He - Process stops at this stage because there is no stable or long-lived isotope of elements Z = 5 or 8. Heavier elements ...
... but photodisintegration occurs at same rate as fusion. - When T falls further fusion occurs faster than photodisintegration then deuterons form. - This leads to formation of 4He - Process stops at this stage because there is no stable or long-lived isotope of elements Z = 5 or 8. Heavier elements ...
SUPERNOVA REMNANT SHOCKS IN AN INHOMOGENEOUS
... see Hollweg [1986].) Although this reduction in the viscosity occurs only perpendicular to t h e field, the full effect of the reduction is likely to occur in the problem at h a n d because the flow of the gas past the cloud will tend to drape the field lines along t h e boundary layer between the c ...
... see Hollweg [1986].) Although this reduction in the viscosity occurs only perpendicular to t h e field, the full effect of the reduction is likely to occur in the problem at h a n d because the flow of the gas past the cloud will tend to drape the field lines along t h e boundary layer between the c ...
Physical Properties of the Gas and Dust in the Orion B Molecular
... distinguish these units from the clumps described above, we call them dense “cores” (see Table 1). These cloud cores are, however, not the progenitors of individual stars. Their masses are, in general, much higher than the masses of the stars they form and their mass spectrum (LBS; Tatematsu et al. ...
... distinguish these units from the clumps described above, we call them dense “cores” (see Table 1). These cloud cores are, however, not the progenitors of individual stars. Their masses are, in general, much higher than the masses of the stars they form and their mass spectrum (LBS; Tatematsu et al. ...
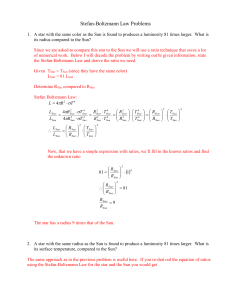
Stefan-Boltzmann Law Problems
... 1. A star with the same color as the Sun is found to produces a luminosity 81 times larger. What is its radius compared to the Sun? Since we are asked to compare this star to the Sun we will use a ratio technique that saves a lot of numerical work. Below I will decode the problem by writing out ht g ...
... 1. A star with the same color as the Sun is found to produces a luminosity 81 times larger. What is its radius compared to the Sun? Since we are asked to compare this star to the Sun we will use a ratio technique that saves a lot of numerical work. Below I will decode the problem by writing out ht g ...
Lecture 6: Multiple stars
... exactly where we see an excess. This is at least some evidence that our understanding of core collapse is correct. (A similar argument can be applied from disc fragmentation which should occur only at >100au.) ...
... exactly where we see an excess. This is at least some evidence that our understanding of core collapse is correct. (A similar argument can be applied from disc fragmentation which should occur only at >100au.) ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.