The Interstellar Medium in High Redshift Galaxies Comes of Age
... molecular interstellar medium in high redshift galaxies, the past years have brought great advances in our understanding of the actual physical properties of the gas, which set the conditions for star formation. Observations of the ground-state CO J = 1−0 line have furnished crucial information on t ...
... molecular interstellar medium in high redshift galaxies, the past years have brought great advances in our understanding of the actual physical properties of the gas, which set the conditions for star formation. Observations of the ground-state CO J = 1−0 line have furnished crucial information on t ...
observing the universe
... A galaxy is an assembly of between a billion (109) and a hundred billion (1011) stars. There is often a large amount of dust and gas intermingled, all held together by gravity. The Sun and Earth are in the Milky Way Galaxy. Galaxies have many different characteristics, but the easiest way to classif ...
... A galaxy is an assembly of between a billion (109) and a hundred billion (1011) stars. There is often a large amount of dust and gas intermingled, all held together by gravity. The Sun and Earth are in the Milky Way Galaxy. Galaxies have many different characteristics, but the easiest way to classif ...
What is the minimum size of a star that will go supernova? A. Half
... A. Very polite motion from a star B. Angular change in position by a star as seen from Earth C. The correct motion of a star Answer: B. The angular change in position by a star as seen from Earth. Stars appear to have fixed positions on the sky. That’s one reason why the constellations are ...
... A. Very polite motion from a star B. Angular change in position by a star as seen from Earth C. The correct motion of a star Answer: B. The angular change in position by a star as seen from Earth. Stars appear to have fixed positions on the sky. That’s one reason why the constellations are ...
Physics 50 Problem set for the week of ______ Chapter 10: angular
... Physics 50 Problem set for the week of ____________ Chapter 10: angular momentum and torque 1. A solid sphere with a mass of 5.15 kg and radius of 0.34 m starts from rest and rolls down an inclined plane. Find its velocity when it gets to the bottom if the ball starts at a height of 2.1 m above the ...
... Physics 50 Problem set for the week of ____________ Chapter 10: angular momentum and torque 1. A solid sphere with a mass of 5.15 kg and radius of 0.34 m starts from rest and rolls down an inclined plane. Find its velocity when it gets to the bottom if the ball starts at a height of 2.1 m above the ...
Asteroseismic constraints on Asymmetric Dark Matter: Light particles
... for which astrometric observations are also available, for example stars observed by both Kepler and Hipparcos [52]. Thus, the ideal candidate is an object with highly constrained fundamental properties and a large number of detected oscillation modes. Binary stars are also very interesting since so ...
... for which astrometric observations are also available, for example stars observed by both Kepler and Hipparcos [52]. Thus, the ideal candidate is an object with highly constrained fundamental properties and a large number of detected oscillation modes. Binary stars are also very interesting since so ...
Globular Clusters
... At the distance of globular clusters, a star like our sun would be magnitude 18-20, far to dim to see in anything but a large professional telescope. But globular clusters often contain hundreds of thousands of these Yellow Dwarf stars, and their combined light is barely visible as a smooth backgrou ...
... At the distance of globular clusters, a star like our sun would be magnitude 18-20, far to dim to see in anything but a large professional telescope. But globular clusters often contain hundreds of thousands of these Yellow Dwarf stars, and their combined light is barely visible as a smooth backgrou ...
acta 20 - Pontifical Academy of Sciences
... smudges of light. Each smudge is actually an entire galaxy, which appears so small and faint because of its huge distance. The light from these remote galaxies set out as much as 10 billion years ago. They are being viewed when they have only recently formed. Some consist mainly of glowing diffuse g ...
... smudges of light. Each smudge is actually an entire galaxy, which appears so small and faint because of its huge distance. The light from these remote galaxies set out as much as 10 billion years ago. They are being viewed when they have only recently formed. Some consist mainly of glowing diffuse g ...
Document
... astronomers can carry out look-back studies to assess empirically when and how galaxies formed. The distant universe became a prominent field of astronomical research during the final decade of the twentieth century. At that time the Lyman break technique in combination with the new generation of 8- ...
... astronomers can carry out look-back studies to assess empirically when and how galaxies formed. The distant universe became a prominent field of astronomical research during the final decade of the twentieth century. At that time the Lyman break technique in combination with the new generation of 8- ...
Tyler Gray - Angelfire
... observers of the Ferguson Observatory near Kenwood, CA have photographed G1 and four fainter M31 globulars. The astrophotographer is even better off, as he can gather the fainter light of the fine detail in the spiral arms, as in our image: Amateurs can obtain most striking pictures even with inexp ...
... observers of the Ferguson Observatory near Kenwood, CA have photographed G1 and four fainter M31 globulars. The astrophotographer is even better off, as he can gather the fainter light of the fine detail in the spiral arms, as in our image: Amateurs can obtain most striking pictures even with inexp ...
Detection of isolated population III stars with the James Webb Space
... Greif et al. (2009) find that bremsstrahlung is very unlikely to be detected in the near future but the cumulative 21cm radiation might be strong enough to be within reach of the upcoming Square Kilometer Array. Direct observation of pair instability supernovae (PISN) could also be used to infer the ...
... Greif et al. (2009) find that bremsstrahlung is very unlikely to be detected in the near future but the cumulative 21cm radiation might be strong enough to be within reach of the upcoming Square Kilometer Array. Direct observation of pair instability supernovae (PISN) could also be used to infer the ...
Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard What is a white dwarf
... fusion on the surface lead to X-ray bursts Matter falling toward a neutron star forms an accretion disk, just as in a white-dwarf binary ...
... fusion on the surface lead to X-ray bursts Matter falling toward a neutron star forms an accretion disk, just as in a white-dwarf binary ...
The Structure of White Dwarf and Neutron Stars∗ Abstract
... The structure of stars, their evolution from birth to death, and the remnants they leave behind are central problems in astrophysics. The basics of star formation are well described in a number of introductory astronomy texts, and the reader may wish to consult one of these to “set the stage” [6]. H ...
... The structure of stars, their evolution from birth to death, and the remnants they leave behind are central problems in astrophysics. The basics of star formation are well described in a number of introductory astronomy texts, and the reader may wish to consult one of these to “set the stage” [6]. H ...
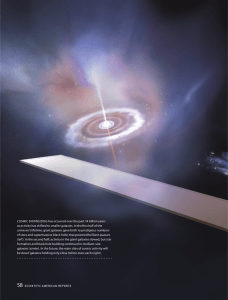
has occurred over the past 14 billion years COSMIC DOWNSIZING
... holes lurking in their cores. This research suggests that not all supermassive black holes were formed in the quasar era. These mighty objects have apparently been assembling from the earliest times until the present. The supermassive black holes that are still active, however, do not exhibit the sa ...
... holes lurking in their cores. This research suggests that not all supermassive black holes were formed in the quasar era. These mighty objects have apparently been assembling from the earliest times until the present. The supermassive black holes that are still active, however, do not exhibit the sa ...
SOUTHERN CONSTELLATION, SEXTANS Sextans constellation
... and is approximately 287 light years distant from Earth. It is the brightest star in Sextans. It is 122 times more luminous than the Sun and has a mass three times solar. The star is believed to be about 300 million years old. It is informally considered to be an “equator star,” currently located le ...
... and is approximately 287 light years distant from Earth. It is the brightest star in Sextans. It is 122 times more luminous than the Sun and has a mass three times solar. The star is believed to be about 300 million years old. It is informally considered to be an “equator star,” currently located le ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.