The Milky Way: Spiral galaxies:
... •! We can perform a bulge/disk decomposition. •! And calculate bulge to disk and bulge to total ratios (by integrating exponential and r1/4-laws as in the problem set!) •! We find that B/D decreases along the Hubble ...
... •! We can perform a bulge/disk decomposition. •! And calculate bulge to disk and bulge to total ratios (by integrating exponential and r1/4-laws as in the problem set!) •! We find that B/D decreases along the Hubble ...
Binary Star Systems
... Classification of Binary Star Systems • Eclipsing binary Example - Algol – Q: Why is the eclipse of the B8 star deeper than the eclipse of the K2 star? • Smaller blue star emits more light per unit surface area than the larger red star ...
... Classification of Binary Star Systems • Eclipsing binary Example - Algol – Q: Why is the eclipse of the B8 star deeper than the eclipse of the K2 star? • Smaller blue star emits more light per unit surface area than the larger red star ...
Can we determine the grain composition of the Interstellar Medium with
... Vital to our understanding of the universe dust a primary respository of the ISM chemical evolution of stars, planets, life ` We are stardust ’ - Joni Mitchell, Woodstock (Ladies of the Canyon) - 1970 ...
... Vital to our understanding of the universe dust a primary respository of the ISM chemical evolution of stars, planets, life ` We are stardust ’ - Joni Mitchell, Woodstock (Ladies of the Canyon) - 1970 ...
The Milky Way Model - University of Chicago
... Galaxy should be visible in the distribution of objects - this was intended to be so. The number of Milky Way arms is still a hot topic of astronomical research and under some debate. The current convention is that there are 5: Orion, Perseus, Sagittarius, Scutum-Crux and Norma - in that order from ...
... Galaxy should be visible in the distribution of objects - this was intended to be so. The number of Milky Way arms is still a hot topic of astronomical research and under some debate. The current convention is that there are 5: Orion, Perseus, Sagittarius, Scutum-Crux and Norma - in that order from ...
The Pistol Star - Emmi
... The Pistol Star • The Pistol star is located near the center of the Milky way galaxy. • It was discovered by the Hubble Space telescope in the early 1900s. • It is 10 million times more brighter than the Sun. • The Pistol Star is 4 million years old. ...
... The Pistol Star • The Pistol star is located near the center of the Milky way galaxy. • It was discovered by the Hubble Space telescope in the early 1900s. • It is 10 million times more brighter than the Sun. • The Pistol Star is 4 million years old. ...
The Sun: the Solar Atmosphere, Nuclear Fusion
... The gas is heated by the motion through it of long lines of magnetic force, which act like whips. The gas is being “whipped”. ...
... The gas is heated by the motion through it of long lines of magnetic force, which act like whips. The gas is being “whipped”. ...
Determination of spiral orbits with constant tangential velocity
... established physics additional Dark Matter is postulated, whose nature is still unknown. The ECE theory is treading a different path instead. It is assumed that the stars do not circulate in nearly circular orbits around the center but move in a spiral path from their origin at the center to the out ...
... established physics additional Dark Matter is postulated, whose nature is still unknown. The ECE theory is treading a different path instead. It is assumed that the stars do not circulate in nearly circular orbits around the center but move in a spiral path from their origin at the center to the out ...
3D Reconstruction and Visualization of Spiral Galaxies
... heat. Thus, the dust transforms blue light into far infrared light and the absorption of starlight warms dust grains to ≈ 10K. At this temperature they radiate significantly at λ ≈ 200µm, and photons of this wavelength can escape. Figure 1 shows infrared images obtained by Spitzer’s infrared array c ...
... heat. Thus, the dust transforms blue light into far infrared light and the absorption of starlight warms dust grains to ≈ 10K. At this temperature they radiate significantly at λ ≈ 200µm, and photons of this wavelength can escape. Figure 1 shows infrared images obtained by Spitzer’s infrared array c ...
AAVSO: Mu Cephei, October 2002 Variable Star Of The Month
... classified as SRc or Lc. Mu Cephei is one of these and is listed in the General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) as a semiregular supergiant variable (type SRc) with a spectral type of M2eIa, a visual range of 3.43 - 5.1, and periods of 730 and 4400 days. The pulsations in Mu Cep, although relativ ...
... classified as SRc or Lc. Mu Cephei is one of these and is listed in the General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) as a semiregular supergiant variable (type SRc) with a spectral type of M2eIa, a visual range of 3.43 - 5.1, and periods of 730 and 4400 days. The pulsations in Mu Cep, although relativ ...
solar.gmu.edu
... •A quasar’s luminosity can be calculated from its apparent brightness and the distance using the inverse-square law •Even though small, the luminosity of a quasar (1038 to 1042 Watts) can be very larger, i.e., several thousand times more than the entire Milly Way Galaxies (1037). •A quasar has emiss ...
... •A quasar’s luminosity can be calculated from its apparent brightness and the distance using the inverse-square law •Even though small, the luminosity of a quasar (1038 to 1042 Watts) can be very larger, i.e., several thousand times more than the entire Milly Way Galaxies (1037). •A quasar has emiss ...
OORT CLOUD EXPLORER - DYNAMIC OCCULTATION
... In-situ observational measurements of the structure of the Oort cloud is exceedingly difficult, owing to the D−4 flux dependence. At this time there is very little, perhaps zero, direct observational measurement of this structure. The object 90377 (Senda) is a candidate for membership, but with a se ...
... In-situ observational measurements of the structure of the Oort cloud is exceedingly difficult, owing to the D−4 flux dependence. At this time there is very little, perhaps zero, direct observational measurement of this structure. The object 90377 (Senda) is a candidate for membership, but with a se ...
iaf2001_paper (doc - 1.8 MB)
... Figure 8 : The sky observed by COROT The field of view is 2.7° x 3.05°, half for seismology and half for exoplanets. The relative position (left/right) has been defined as the same time as the orbit plane, leading to a compromise between the two programs to set each half-field in the most favorable ...
... Figure 8 : The sky observed by COROT The field of view is 2.7° x 3.05°, half for seismology and half for exoplanets. The relative position (left/right) has been defined as the same time as the orbit plane, leading to a compromise between the two programs to set each half-field in the most favorable ...
Galaxies - senwiki
... -So what is a black hole? A black hole is a region of space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. -Why? Black holes have extremely strong gravitational pulls. They can pull in stars and accumulate the mass of the stars. -Where are black holes located? Astronomers belie ...
... -So what is a black hole? A black hole is a region of space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. -Why? Black holes have extremely strong gravitational pulls. They can pull in stars and accumulate the mass of the stars. -Where are black holes located? Astronomers belie ...
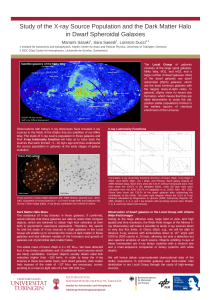
TF_final3 - Arecibo Observatory
... velocity width (W) of the lines is proportional to its luminosity (L) following an equation, L ∝ In a sample of 33 LIRGs the neutral hydrogen emission line width was measured. The luminosities of these galaxies from literature were found and a study was made of whether the Tully-Fisher law is mainta ...
... velocity width (W) of the lines is proportional to its luminosity (L) following an equation, L ∝ In a sample of 33 LIRGs the neutral hydrogen emission line width was measured. The luminosities of these galaxies from literature were found and a study was made of whether the Tully-Fisher law is mainta ...
Testing
... the interstellar medium, which slowly cools, making the molecular clouds where stars form. – Those stars will eventually return much of their matter to interstellar space. ...
... the interstellar medium, which slowly cools, making the molecular clouds where stars form. – Those stars will eventually return much of their matter to interstellar space. ...
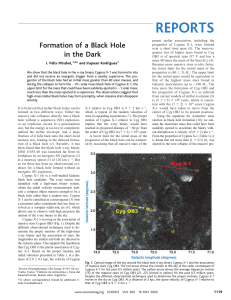
The role of black holes in galaxy formation and evolution
... the only process that can be almost 100% efficient, but dust must cover a large solid angle. The low momentum of photons with respect to their energy also limits the mass that can be ejected through this mechanism, as photons are massless particles. If the momentum in the photons radiated by an AGN ...
... the only process that can be almost 100% efficient, but dust must cover a large solid angle. The low momentum of photons with respect to their energy also limits the mass that can be ejected through this mechanism, as photons are massless particles. If the momentum in the photons radiated by an AGN ...
Some interesting geometric facts about eclipsing binaries (see if you
... Some interesting geometric facts about eclipsing binaries (see if you can prove these): The probability of a binary being properly oriented in space for us to observe it as an eclipsing system becomes progressively smaller as the distance between the two stars increases. It turns out that no visual ...
... Some interesting geometric facts about eclipsing binaries (see if you can prove these): The probability of a binary being properly oriented in space for us to observe it as an eclipsing system becomes progressively smaller as the distance between the two stars increases. It turns out that no visual ...
Nucleosynthesis and the death of stars
... • A supernova is a massive explosion of a star that occurs under two possible scenarios. The first is that a white dwarf star undergoes a nuclear based explosion after it reaches its Chandrasekhar limit from absorbing mass from a neighboring star (usually a red giant). • The second, and more common, ...
... • A supernova is a massive explosion of a star that occurs under two possible scenarios. The first is that a white dwarf star undergoes a nuclear based explosion after it reaches its Chandrasekhar limit from absorbing mass from a neighboring star (usually a red giant). • The second, and more common, ...
astro-ph/0504597 PDF
... Thus, as no more nuclear fusion is possible, a core of iron builds up in the centers of massive supergiants. Eventually, the iron core reaches something called the Chandrasekhar Mass, which is about 1.4 times the mass of the Sun. When something is this massive, not even electron degeneracy pressure ...
... Thus, as no more nuclear fusion is possible, a core of iron builds up in the centers of massive supergiants. Eventually, the iron core reaches something called the Chandrasekhar Mass, which is about 1.4 times the mass of the Sun. When something is this massive, not even electron degeneracy pressure ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.