Chapter 30: Stars
... a temperature range of 1 million to 2 million K. The density of the gas in the corona is very low, which explains why the corona is so dim that it can be seen only when the photosphere is blocked by either special instruments, as in a coronagraph, or by the Moon during an eclipse, as in Figure 30-2. ...
... a temperature range of 1 million to 2 million K. The density of the gas in the corona is very low, which explains why the corona is so dim that it can be seen only when the photosphere is blocked by either special instruments, as in a coronagraph, or by the Moon during an eclipse, as in Figure 30-2. ...
81 - Armenian Astronomical Society
... The IAU fully supports the involvement of the general public in the naming of astronomical objects, whether directly or through an independent organised vote, in the naming of planetary satellites, newly discovered exoplanets, and their host stars. This follows a well-established tradition for namin ...
... The IAU fully supports the involvement of the general public in the naming of astronomical objects, whether directly or through an independent organised vote, in the naming of planetary satellites, newly discovered exoplanets, and their host stars. This follows a well-established tradition for namin ...
Modeling non-thermal emission from stellar bow shocks
... is now seen as an O4If. BD+43 3654 has been reported to have formed a bow shock detected in the IR (Comerón & Pasquali 2007) and in radio (Benaglia et al. 2010). Both observations are coincident and extensive. Assuming the velocity of this star is 67 km s−1 (Kobulnicky et al. 2010), the mass-loss r ...
... is now seen as an O4If. BD+43 3654 has been reported to have formed a bow shock detected in the IR (Comerón & Pasquali 2007) and in radio (Benaglia et al. 2010). Both observations are coincident and extensive. Assuming the velocity of this star is 67 km s−1 (Kobulnicky et al. 2010), the mass-loss r ...
Moitinho et al. - Wiley Online Library
... overdensity would be the remaining core of the disrupted galaxy and the ring would be the tidal debris left behind. However, unlike the Sagittarius dwarf, which is well below the Galactic plane and whose orbit, and thus tidal tail, is nearly perpendicular to the plane of the Milky Way, the putative ...
... overdensity would be the remaining core of the disrupted galaxy and the ring would be the tidal debris left behind. However, unlike the Sagittarius dwarf, which is well below the Galactic plane and whose orbit, and thus tidal tail, is nearly perpendicular to the plane of the Milky Way, the putative ...
Big Bear Valley Astronomical Society
... them into doves and after death placed them in the heavens a little away from the gaze of Orion. The Pleiades are among the first stars positively identified in astronomical literature, with references as early as the 3rd millennium BC when Alcyone would have marked the vernal equinox - thus, the ti ...
... them into doves and after death placed them in the heavens a little away from the gaze of Orion. The Pleiades are among the first stars positively identified in astronomical literature, with references as early as the 3rd millennium BC when Alcyone would have marked the vernal equinox - thus, the ti ...
Animated Planets PowerPoint Presentation
... emitting a halo of dust and gas as it approaches the sun. Rosetta will make history later this year when it orbits and lands on the comet's surface. Comets get their coma, when the sun heats frozen gases erupting from the surface. Dust particles remain in orbit around the nucleus, and make it appear ...
... emitting a halo of dust and gas as it approaches the sun. Rosetta will make history later this year when it orbits and lands on the comet's surface. Comets get their coma, when the sun heats frozen gases erupting from the surface. Dust particles remain in orbit around the nucleus, and make it appear ...
A n A n c i e n... How Astronomers Know the Vast Scale of Cosmic Time
... And what we learn from our instruments is that we live in a wonderful universe. No wonder astronomy has inspired artists and poets through the ages, from ancient Greece to today’s television series. Astronomy, the study of the universe, reveals a cosmos that is vast, varied, and beautiful. The sky i ...
... And what we learn from our instruments is that we live in a wonderful universe. No wonder astronomy has inspired artists and poets through the ages, from ancient Greece to today’s television series. Astronomy, the study of the universe, reveals a cosmos that is vast, varied, and beautiful. The sky i ...
3. Neutron Star X-ray Binaries
... and ZX-ray - Sources: ---rapidly called spinning “slow” accretion-powered period 1s or more. LMXBs divided in these two typespulsars, depending on ~their timing ...
... and ZX-ray - Sources: ---rapidly called spinning “slow” accretion-powered period 1s or more. LMXBs divided in these two typespulsars, depending on ~their timing ...
Ch 11a (Measuring Stars 10-28-10)
... Apparent brightness: how bright a star looks in the sky The inverse-square Law: light from stars gets fainter as the inverse square of the distance (brightness proportional to 1/d2). If we know the apparent brightness and the distance to a star we can calculate its absolute (intrinsic) brightness ...
... Apparent brightness: how bright a star looks in the sky The inverse-square Law: light from stars gets fainter as the inverse square of the distance (brightness proportional to 1/d2). If we know the apparent brightness and the distance to a star we can calculate its absolute (intrinsic) brightness ...
Spectral classification of blue supergiants in M31
... few tens of solar masses. At the same time, they are enormously large with radii comparable to the Earth’s orbit. Because of those features they have been identified as very promising targets for stellar astronomy, enabling quantitative spectral analysis outside the Milky Way [4, 1]. This work adds ...
... few tens of solar masses. At the same time, they are enormously large with radii comparable to the Earth’s orbit. Because of those features they have been identified as very promising targets for stellar astronomy, enabling quantitative spectral analysis outside the Milky Way [4, 1]. This work adds ...
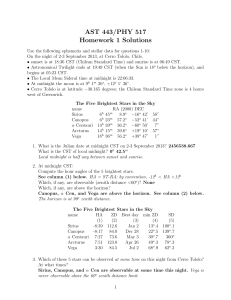
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1 Solutions
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
ph507lecnote06
... parallax accuracy to 0.001” within a few years. Before 1990, fewer than 10,000 stellar parallaxes had been measured (and only 500 known well), but there are about 1012 stars in our Galaxy. Space observations made by the European Space Agency with the Hipparcos mission (1989-1993) accurately determin ...
... parallax accuracy to 0.001” within a few years. Before 1990, fewer than 10,000 stellar parallaxes had been measured (and only 500 known well), but there are about 1012 stars in our Galaxy. Space observations made by the European Space Agency with the Hipparcos mission (1989-1993) accurately determin ...
WORD - Astrophysics
... J-band magnitude of 25.2 and thus be hard to detect against the glare of the Sun. However, when relatively young, gas giant planets radiate away excess energy from their formation and are thus self-luminous, making them potentially much easier to detect. For example, at 1 Gyr, a 5 Jupiter-mass (MJ) ...
... J-band magnitude of 25.2 and thus be hard to detect against the glare of the Sun. However, when relatively young, gas giant planets radiate away excess energy from their formation and are thus self-luminous, making them potentially much easier to detect. For example, at 1 Gyr, a 5 Jupiter-mass (MJ) ...
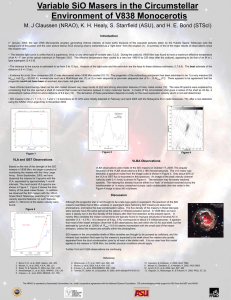
aaswinter06
... Although the progenitor star is not thought to be a late-type giant or supergiant, the spectrum of the SiO masers resembles that of Mira variables or supergiant stars harboring SiO masers just above the photosphere, and below the dust condensation radius. The flux density of the masers in these late ...
... Although the progenitor star is not thought to be a late-type giant or supergiant, the spectrum of the SiO masers resembles that of Mira variables or supergiant stars harboring SiO masers just above the photosphere, and below the dust condensation radius. The flux density of the masers in these late ...
Gravity-Bending Find Leads to Kepler Meeting Einstein
... NASA Headquarters, Washington. "But with this detection, we are witnessing Einstein's general theory of relativity at play in a far-flung star system." One of the consequences of Einstein's general theory of relativity is that gravity bends light. Astronomers regularly observe this phenomenon, often ...
... NASA Headquarters, Washington. "But with this detection, we are witnessing Einstein's general theory of relativity at play in a far-flung star system." One of the consequences of Einstein's general theory of relativity is that gravity bends light. Astronomers regularly observe this phenomenon, often ...
Big Bang Theory notes
... Pg. 13: History of the Atom Review packet Pg. 14: Atomic Structure packet Pg. 15: Atoms Brain Pop Quiz Pg. 16: Metal? Non-metal? Metalloid? Pg. 17: Solid, Liquid, Gas notes Pg. 18: Organizing Matter Concept Map Pg. 19: Heterogenous or Homogenous Meal? Pg. 20: Classifying Matter notes Pg. 21: Stuff W ...
... Pg. 13: History of the Atom Review packet Pg. 14: Atomic Structure packet Pg. 15: Atoms Brain Pop Quiz Pg. 16: Metal? Non-metal? Metalloid? Pg. 17: Solid, Liquid, Gas notes Pg. 18: Organizing Matter Concept Map Pg. 19: Heterogenous or Homogenous Meal? Pg. 20: Classifying Matter notes Pg. 21: Stuff W ...
PDF Full-text
... leading to the production of H, OH, and O and the destruction of H2 . These effects are sensitive to atmospheric temperature as collision rates increase rapidly with temperture such that equilibrium chemistry dominates at temperatures above 2500 K at all pressure levels. To estimate the importance o ...
... leading to the production of H, OH, and O and the destruction of H2 . These effects are sensitive to atmospheric temperature as collision rates increase rapidly with temperture such that equilibrium chemistry dominates at temperatures above 2500 K at all pressure levels. To estimate the importance o ...
The Naked Eye Stars as Data Supporting Galileo`s
... If stars are not suns scattered through space then there is no reason for the real sky to look like the top row. For example, if the stars are simply bodies distributed along a spherical shell centered on Earth as in geocentric theories then there is no reason why their numbers by brightness might n ...
... If stars are not suns scattered through space then there is no reason for the real sky to look like the top row. For example, if the stars are simply bodies distributed along a spherical shell centered on Earth as in geocentric theories then there is no reason why their numbers by brightness might n ...
Chapter 15, Galaxies
... Because the mass of white dwarfs when they explode as supernovae is always around 1.0 M⊙, its luminosity is very consistent, and can be used as a standard candle for the measurement of distance to distant galaxies (Chapter 15). The amount of energy produced by white dwarf supernovae and massive star ...
... Because the mass of white dwarfs when they explode as supernovae is always around 1.0 M⊙, its luminosity is very consistent, and can be used as a standard candle for the measurement of distance to distant galaxies (Chapter 15). The amount of energy produced by white dwarf supernovae and massive star ...
Article PDF - IOPscience
... that observable high-mass X-ray binaries may be found with a millisecond pulsar accretor. Lyutikov (2014) suggests that the extremely super-Eddington accretion rates require a new MT regime, where an optically thick accretion curtain shields the interior gas from the outgoing X-ray flux. Furthermore, ...
... that observable high-mass X-ray binaries may be found with a millisecond pulsar accretor. Lyutikov (2014) suggests that the extremely super-Eddington accretion rates require a new MT regime, where an optically thick accretion curtain shields the interior gas from the outgoing X-ray flux. Furthermore, ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.