Chapter 9 Post-main sequence evolution through helium burning
... degenerate, a very strong density contrast has developed between the core and the envelope. The envelope is so extended that it exerts very little weight on the compact core, while there is a very large pressure gradient between core and envelope. The pressure at the bottom of the envelope (see eq. ...
... degenerate, a very strong density contrast has developed between the core and the envelope. The envelope is so extended that it exerts very little weight on the compact core, while there is a very large pressure gradient between core and envelope. The pressure at the bottom of the envelope (see eq. ...
17_Testbank
... 4) There is no limit to the mass with which a star can be born. Answer: FALSE 5) Stars with high masses live longer than stars with lower masses. Answer: FALSE 6) Stars of lower mass have deeper convection zones outside their cores than stars of higher mass. Answer: TRUE 7) Convection never occurs i ...
... 4) There is no limit to the mass with which a star can be born. Answer: FALSE 5) Stars with high masses live longer than stars with lower masses. Answer: FALSE 6) Stars of lower mass have deeper convection zones outside their cores than stars of higher mass. Answer: TRUE 7) Convection never occurs i ...
Chapter 21 - apel slice
... On a clear night, your eyes can see at most a few thousand stars. But with a telescope, you can see many millions. Why? The light from stars spreads out as it moves through space, and your eyes are too small to gather much light. Telescopes are instruments that collect and focus light and other form ...
... On a clear night, your eyes can see at most a few thousand stars. But with a telescope, you can see many millions. Why? The light from stars spreads out as it moves through space, and your eyes are too small to gather much light. Telescopes are instruments that collect and focus light and other form ...
6 The mysterious universe
... well-known for identifying the comet named after him, used his telescope to check three particularly bright stars: Sirius, Procyon and Arcturus. He found that the position of each one relative to surrounding stars was noticeably different from the positions recorded by ancient Greek astronomers cent ...
... well-known for identifying the comet named after him, used his telescope to check three particularly bright stars: Sirius, Procyon and Arcturus. He found that the position of each one relative to surrounding stars was noticeably different from the positions recorded by ancient Greek astronomers cent ...
Astronomical Toolkit
... faint stars that just happen to lie very close to us. When observing, we are forced to stay on Earth or nearby and can only measure the intensity of the light that reaches us. Unfortunately this does not immediately tell us anything about a star’s internal properties. If we want to know more about a ...
... faint stars that just happen to lie very close to us. When observing, we are forced to stay on Earth or nearby and can only measure the intensity of the light that reaches us. Unfortunately this does not immediately tell us anything about a star’s internal properties. If we want to know more about a ...
Standards
... 4. The Sun is about 150 million kilometers away from Earth. How does that compare to the distance of other stars? Information you may want to discuss about the sun might include the following (some facts may be more than you want to discuss with stars): The sun is a star Closest star to Earth ...
... 4. The Sun is about 150 million kilometers away from Earth. How does that compare to the distance of other stars? Information you may want to discuss about the sun might include the following (some facts may be more than you want to discuss with stars): The sun is a star Closest star to Earth ...
flyer
... these objects exist ever since they were first observed as pulsars. They are the collapsed cores of massive stars that have run out of fuel and undergone a supernova explosion. With a mass of slightly more than the Sun's (∼2.8×1030 kg) packed into a sphere of radius ∼10 km, neutron stars are about 4 ...
... these objects exist ever since they were first observed as pulsars. They are the collapsed cores of massive stars that have run out of fuel and undergone a supernova explosion. With a mass of slightly more than the Sun's (∼2.8×1030 kg) packed into a sphere of radius ∼10 km, neutron stars are about 4 ...
Stellar Continua
... due to hydrogen bound-free absorption • Measured using U-B photometry • Sensitive to temperature BUT ALSO • Sensitive to pressure or luminosity (at lower gravity, the Balmer jump is bigger – recall that kbf depends on ionization, and hence on Pe) • Works for 5000 < Teff < 10,000 (where Hbf opacity i ...
... due to hydrogen bound-free absorption • Measured using U-B photometry • Sensitive to temperature BUT ALSO • Sensitive to pressure or luminosity (at lower gravity, the Balmer jump is bigger – recall that kbf depends on ionization, and hence on Pe) • Works for 5000 < Teff < 10,000 (where Hbf opacity i ...
PDF format
... a) They are useful in measuring the distances of other galaxies. b) Their variability enables us to determine their masses. c) Their variability enables us to determine their rotation rates. d) They are useful in studying sunspots on other stars. e) They are useful in understanding stellar flar ...
... a) They are useful in measuring the distances of other galaxies. b) Their variability enables us to determine their masses. c) Their variability enables us to determine their rotation rates. d) They are useful in studying sunspots on other stars. e) They are useful in understanding stellar flar ...
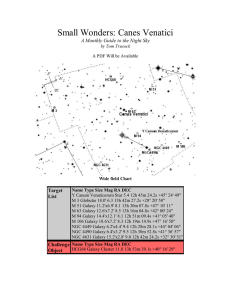
Small Wonders: Canes Venatici
... the differences seen when moving between different size scopes. Can you spot the large HII region visually? ...
... the differences seen when moving between different size scopes. Can you spot the large HII region visually? ...
A rocky planet transiting a nearby low-mass star
... ±"0.018, W4"="7.916"±"0.184). The colour (V–Ks"="5.168"±"0.040) and absolute magnitude (M V"="13.088"±"0.054) of GJ 1132 are consistent with those of single M4V dwarfs 34. Metallicity of the star Before discovering the planet, we gathered a near-infrared spectrum of GJ 1132 with the FIRE spectrograp ...
... ±"0.018, W4"="7.916"±"0.184). The colour (V–Ks"="5.168"±"0.040) and absolute magnitude (M V"="13.088"±"0.054) of GJ 1132 are consistent with those of single M4V dwarfs 34. Metallicity of the star Before discovering the planet, we gathered a near-infrared spectrum of GJ 1132 with the FIRE spectrograp ...
to get the file
... •One possible conclusion is that the blue is scattered in the atmosphere by the molecular oxygen and ozone while the red may be scattered by various airborne debris such as dust or other particulate ...
... •One possible conclusion is that the blue is scattered in the atmosphere by the molecular oxygen and ozone while the red may be scattered by various airborne debris such as dust or other particulate ...
Bright Quasar 3C 273 Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics eaa.iop.org Thierry J-L Courvoisier
... several emission mechanisms. Electrons moving along bent paths radiate part of their energy as electromagnetic radiation. In quasars there are many ways through which the paths of electrons are bent; there are correspondingly many emission mechanisms. Magnetic fields are one way of bending electron ...
... several emission mechanisms. Electrons moving along bent paths radiate part of their energy as electromagnetic radiation. In quasars there are many ways through which the paths of electrons are bent; there are correspondingly many emission mechanisms. Magnetic fields are one way of bending electron ...
Sky Maps Teacher`s Guide - Northern Stars Planetarium
... Meteors are often called "falling stars" or "shooting stars." These streaks of light that fly rapidly across the sky are really tiny rocks falling through the Earth's upper atmosphere. Friction and compression between rock and the air create enough heat to make the object burn. Most meteors never re ...
... Meteors are often called "falling stars" or "shooting stars." These streaks of light that fly rapidly across the sky are really tiny rocks falling through the Earth's upper atmosphere. Friction and compression between rock and the air create enough heat to make the object burn. Most meteors never re ...
IAU-Perraut-2013 - Putting A Stars into Context
... fundamental parameters of A stars through accurate angular diameter determinations. With long-baseline arrays an angular resolution of about 0.3 mas is now reachable. There is a huge potential of combining interferometric (radius and derived effective temperature) and asteroseismic (large frequency ...
... fundamental parameters of A stars through accurate angular diameter determinations. With long-baseline arrays an angular resolution of about 0.3 mas is now reachable. There is a huge potential of combining interferometric (radius and derived effective temperature) and asteroseismic (large frequency ...
Extragalactic Globular Cluster Systems
... above the atomic cooling mass at z = 12 exceeds f c = 1 per cent. A normal stellar population with a Salpeter-type initial mass function emits about 4000 hydrogen-ionizing photons per stellar baryon. A star formation efficiency of 10 per cent therefore implies the emission of 4 000 × f ∗ × f c ∼ a f ...
... above the atomic cooling mass at z = 12 exceeds f c = 1 per cent. A normal stellar population with a Salpeter-type initial mass function emits about 4000 hydrogen-ionizing photons per stellar baryon. A star formation efficiency of 10 per cent therefore implies the emission of 4 000 × f ∗ × f c ∼ a f ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.