The slow-neutron capture process at low metallicity
... The puzzle of the CEMP-s/r stars • About 50% of CEMP stars with an s-process signature also show an enrichment in r-process elements • It is puzzling how CEMP-s/r could have formed in such large ...
... The puzzle of the CEMP-s/r stars • About 50% of CEMP stars with an s-process signature also show an enrichment in r-process elements • It is puzzling how CEMP-s/r could have formed in such large ...
Solutions for homework #5, AST 203, Spring 2009
... after which they decay into an electron, a muon neutrino, and an anti-electron neutrino. Very fast-moving muons are produced in the upper atmosphere of the Earth (i.e., 100 km above the Earth’s surface) in collisions with high-energy cosmic rays (produced ultimately from distant supernova explosions ...
... after which they decay into an electron, a muon neutrino, and an anti-electron neutrino. Very fast-moving muons are produced in the upper atmosphere of the Earth (i.e., 100 km above the Earth’s surface) in collisions with high-energy cosmic rays (produced ultimately from distant supernova explosions ...
aaswinter07ppt
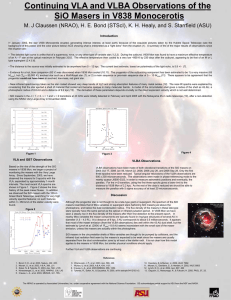
... Although the progenitor star is not thought to be a late-type giant or supergiant, the spectrum of the SiO masers resembles that of Mira variables or supergiant stars harboring SiO masers just above the photosphere, and below the dust condensation radius. The flux density of the masers in these late ...
... Although the progenitor star is not thought to be a late-type giant or supergiant, the spectrum of the SiO masers resembles that of Mira variables or supergiant stars harboring SiO masers just above the photosphere, and below the dust condensation radius. The flux density of the masers in these late ...
Lecture21 - Michigan State University
... atomic hydrogen is confined to an extremely flat layer that is about 400 LY thick • In the plane of the Galaxy, this cold hydrogen extends out 80,000 LY from the center • Dust is also confined to the plane of the Galaxy being about the same thickness as the hydrogen gas but more concentrated in the ...
... atomic hydrogen is confined to an extremely flat layer that is about 400 LY thick • In the plane of the Galaxy, this cold hydrogen extends out 80,000 LY from the center • Dust is also confined to the plane of the Galaxy being about the same thickness as the hydrogen gas but more concentrated in the ...
Orion - Starry Starry Night!
... Visible : Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, Dec Winter - Spring Canis Major contains Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, known as the "dog star". It is bright because of its proximity to our Solar System. In contrast, the other bright stars of the constellation are stars of great distance and high lumino ...
... Visible : Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, Dec Winter - Spring Canis Major contains Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, known as the "dog star". It is bright because of its proximity to our Solar System. In contrast, the other bright stars of the constellation are stars of great distance and high lumino ...
Star position tutorial
... Nightly Motion of the Stars • For stars (the Moon and planets) that appear in the southern sky: Stars first rise near the eastern horizon, move upward and toward the south, and then move down and set near the western horizon. ...
... Nightly Motion of the Stars • For stars (the Moon and planets) that appear in the southern sky: Stars first rise near the eastern horizon, move upward and toward the south, and then move down and set near the western horizon. ...
gravitational wave Universe - UO Physics
... From 2007 to 2011, Virgo, LIGO and GEO600 have formed the first worldwide network of interferometers in history and have observed the sky for gravitational waves. This collaboration will continue in the era of the Advanced Virgo and Advanced LIGO, which will continue to share the data that will be c ...
... From 2007 to 2011, Virgo, LIGO and GEO600 have formed the first worldwide network of interferometers in history and have observed the sky for gravitational waves. This collaboration will continue in the era of the Advanced Virgo and Advanced LIGO, which will continue to share the data that will be c ...
Stellar Spectroscopy (GA 3.0) - National Optical Astronomy
... a function of wavelength. In the diagram above the three types of spectra are shown. In the bottom frame they are shown together, as they might appear in an object’s spectrum. ...
... a function of wavelength. In the diagram above the three types of spectra are shown. In the bottom frame they are shown together, as they might appear in an object’s spectrum. ...
PDF format
... a) radiation along the magnetic axis of a rapidly rotating neutron star b) radiation from hydrogen fusion on the surface of a neutron star in a binary system c) radiation from helium fusion on the surface of a neutron star in a binary system d) the collapse of a white dwarf into a neutron star e ...
... a) radiation along the magnetic axis of a rapidly rotating neutron star b) radiation from hydrogen fusion on the surface of a neutron star in a binary system c) radiation from helium fusion on the surface of a neutron star in a binary system d) the collapse of a white dwarf into a neutron star e ...
Blackholes - Indiana University Astronomy
... • The process by which elements (nuclei) are created (synthesized) is called nucleosynthesis • Nucleosynthesis has occurred since the creation of the universe and will essentially go on forever • The elements created come together to form everything material we know, including us ...
... • The process by which elements (nuclei) are created (synthesized) is called nucleosynthesis • Nucleosynthesis has occurred since the creation of the universe and will essentially go on forever • The elements created come together to form everything material we know, including us ...
New Scientist - Quark Nova Project
... Pagliara of the University of Ferrara in Italy. As the density in the core continues to increase, the star’s innards “melt”, freeing quarks from their bound state. In fact, a single droplet of strange matter is enough to trigger a runaway process that converts all the neutrons. What was a neutron st ...
... Pagliara of the University of Ferrara in Italy. As the density in the core continues to increase, the star’s innards “melt”, freeing quarks from their bound state. In fact, a single droplet of strange matter is enough to trigger a runaway process that converts all the neutrons. What was a neutron st ...
The radial scale length of the Milky Way
... This value seems quite low when compared with the obtained values in the optical (see for instance van der Kruit, 1986; and Barteldress and Dettmar, 1994) but it is well known than the exponential scale lengths decrease with increasing wavelength (de Grijs and van der Kruit, 1996; Peletier et al., 1 ...
... This value seems quite low when compared with the obtained values in the optical (see for instance van der Kruit, 1986; and Barteldress and Dettmar, 1994) but it is well known than the exponential scale lengths decrease with increasing wavelength (de Grijs and van der Kruit, 1996; Peletier et al., 1 ...
Chapter 9 Post-main sequence evolution through helium burning
... degenerate, a very strong density contrast has developed between the core and the envelope. The envelope is so extended that it exerts very little weight on the compact core, while there is a very large pressure gradient between core and envelope. The pressure at the bottom of the envelope (see eq. ...
... degenerate, a very strong density contrast has developed between the core and the envelope. The envelope is so extended that it exerts very little weight on the compact core, while there is a very large pressure gradient between core and envelope. The pressure at the bottom of the envelope (see eq. ...
Galaxies
... Astronomers now suspect that most elliptical galaxies are formed by the merger of at least two or more galaxies. Evidence supports that they are often found near the center of galaxy clusters. ...
... Astronomers now suspect that most elliptical galaxies are formed by the merger of at least two or more galaxies. Evidence supports that they are often found near the center of galaxy clusters. ...
KINEMATIC DISCOVERY OF A STELLAR STREAM LOCATED IN
... DR8 spectra within the on- and off-stream fields, respectively. We also show subsets of the spectra with properties expected for the PSS. The subscripts on the magnitudes g0 and (g − r)0 mean that these magnitudes have been extinction-corrected based on the Schlegel et al. (1998) maps (using the ext ...
... DR8 spectra within the on- and off-stream fields, respectively. We also show subsets of the spectra with properties expected for the PSS. The subscripts on the magnitudes g0 and (g − r)0 mean that these magnitudes have been extinction-corrected based on the Schlegel et al. (1998) maps (using the ext ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.