Chapter205.ppt
... earthquake is a vibration. This vibrational energy moves as seismic waves through the solid earth, the oceans, and on the surface. Earthquakes can produce a new fracture in the earth’s crust or can cause sliding or movement on an existing fracture or can occur on a “blind fault” (an old fracture tha ...
... earthquake is a vibration. This vibrational energy moves as seismic waves through the solid earth, the oceans, and on the surface. Earthquakes can produce a new fracture in the earth’s crust or can cause sliding or movement on an existing fracture or can occur on a “blind fault” (an old fracture tha ...
Handout
... earthquake is a vibration. This vibrational energy moves as seismic waves through the solid earth, the oceans, and on the surface. Earthquakes can produce a new fracture in the earth’s crust or can cause sliding or movement on an existing fracture or can occur on a “blind fault” (an old fracture tha ...
... earthquake is a vibration. This vibrational energy moves as seismic waves through the solid earth, the oceans, and on the surface. Earthquakes can produce a new fracture in the earth’s crust or can cause sliding or movement on an existing fracture or can occur on a “blind fault” (an old fracture tha ...
UNIT 5 Text: Where to Look for Petroleum Grammar Revision
... A joint is a fracture that has opened without displacement of its adjacent walls. The two sides of a fracture may move in relation to each other. If they do, the fracture is called a fault. Geologists classify faults mainly by the direction of the movement. Movement is mostly vertical in normal and ...
... A joint is a fracture that has opened without displacement of its adjacent walls. The two sides of a fracture may move in relation to each other. If they do, the fracture is called a fault. Geologists classify faults mainly by the direction of the movement. Movement is mostly vertical in normal and ...
Plate Tectonics - Teacher Background File
... Scientific data recorded to support the theory that continents were moving apart: 1. Discovery of mid-ocean ridges The possibility of undersea mountain ranges in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean was already suggested by readings from naval marine depth soundings. It was noticed that the ocean did no ...
... Scientific data recorded to support the theory that continents were moving apart: 1. Discovery of mid-ocean ridges The possibility of undersea mountain ranges in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean was already suggested by readings from naval marine depth soundings. It was noticed that the ocean did no ...
8.2 Continental Drift Theory and Sea-Floor Spreading
... continents were always in the same place Scientists OBSERVED: coasts of continents looked like they fit together. . . So Alfred Wegener made an important ...
... continents were always in the same place Scientists OBSERVED: coasts of continents looked like they fit together. . . So Alfred Wegener made an important ...
Study Guide: Academic Standard 8-3 Earth`s Structure and Processes
... Igneous: Forms when molten rock cools and hardens. If cooling takes place slowly beneath Earth’s surface, the igneous rock is called intrusive and the mineral crystals that form are large. If cooling takes place rapidly on Earth’s surface, the igneous rock is extrusive and the mineral crystals are s ...
... Igneous: Forms when molten rock cools and hardens. If cooling takes place slowly beneath Earth’s surface, the igneous rock is called intrusive and the mineral crystals that form are large. If cooling takes place rapidly on Earth’s surface, the igneous rock is extrusive and the mineral crystals are s ...
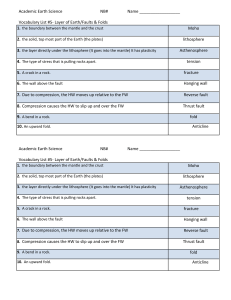
Layers of Earth/Faults Vocab List
... Vocabulary List #5- Layer of Earth/Faults & Folds 1. the boundary between the mantle and the crust ...
... Vocabulary List #5- Layer of Earth/Faults & Folds 1. the boundary between the mantle and the crust ...
TYPES OF CRUSTAL MATERIAL
... ocean crust sinks lower into the asthenosphere than the less dense granitic continental crust. This is the reason why continents are higher than ocean basins; the basins would exist whether or not there was any water on the Earth. Their existence derives from the greater density of basalt. When we s ...
... ocean crust sinks lower into the asthenosphere than the less dense granitic continental crust. This is the reason why continents are higher than ocean basins; the basins would exist whether or not there was any water on the Earth. Their existence derives from the greater density of basalt. When we s ...
Classroom Space Volcano!
... The lava flows are relatively young and continued to flow long after the periods of heavy bombardment (after 3.5 billion years ago), therefore each new lava flow created new igneous rock and erased any surface features that previously existed. Again there will be some small craters on the lava flows ...
... The lava flows are relatively young and continued to flow long after the periods of heavy bombardment (after 3.5 billion years ago), therefore each new lava flow created new igneous rock and erased any surface features that previously existed. Again there will be some small craters on the lava flows ...
Plate Tectonics – The Lecture Notes
... Mid-Atlantic ridge. What they found changed geology and oceanography. a) Continental Rocks date the Earth at about 5 billion years old. Since the ocean floor is lower in the lithosphere, scientists expected to find older rocks at those depths. Continental geology’s law of Superposition states that o ...
... Mid-Atlantic ridge. What they found changed geology and oceanography. a) Continental Rocks date the Earth at about 5 billion years old. Since the ocean floor is lower in the lithosphere, scientists expected to find older rocks at those depths. Continental geology’s law of Superposition states that o ...
CH. 12 Notes
... Magma (molten rock) flows up through resulting cracks Creates Ocean Ridges, high peeks and deep canyons ...
... Magma (molten rock) flows up through resulting cracks Creates Ocean Ridges, high peeks and deep canyons ...
Types of rocks
... - is formed from sediment (loose material – rock, minerals, plant and animal remains - that is layered and compacted together by the pressure of the material above it) - stratification is the visible evidence of the layers - cementation - some of the minerals that dissolve with the addition of water ...
... - is formed from sediment (loose material – rock, minerals, plant and animal remains - that is layered and compacted together by the pressure of the material above it) - stratification is the visible evidence of the layers - cementation - some of the minerals that dissolve with the addition of water ...
Final Examination Key
... A. An aggregate of one or more minerals B. A body of undifferentiated mineral or glassy matter C. Bodies of solid organic matter D. Any of the above ...
... A. An aggregate of one or more minerals B. A body of undifferentiated mineral or glassy matter C. Bodies of solid organic matter D. Any of the above ...
Geologic Dating
... Earth’s History • Principle of Uniformitarianism –Major assumption in geology –Events in the past occurred the same way that they are occurring today. Examples Include: • Weathering/erosion • Deposition • Volcanism • Plate tectonics ...
... Earth’s History • Principle of Uniformitarianism –Major assumption in geology –Events in the past occurred the same way that they are occurring today. Examples Include: • Weathering/erosion • Deposition • Volcanism • Plate tectonics ...
bYTEBoss Platinum & Gold Prospects Choco
... Chocó is an area of oceanic crust placed in western Colombia. It is part of an islands arc which continues along Panamá to Northwest and to the South along the Pacific shelf to Ecuador territory. The parts of the islands arc in Chocó are well defined, the subduction zone is along the Baudó coast, w ...
... Chocó is an area of oceanic crust placed in western Colombia. It is part of an islands arc which continues along Panamá to Northwest and to the South along the Pacific shelf to Ecuador territory. The parts of the islands arc in Chocó are well defined, the subduction zone is along the Baudó coast, w ...
Mineral Resources and Geology
... Earthquake: sudden movement of Earth’s crust caused by the release of potential energy along a fault, causing vibration or movement at the surface. Epicenter: exact point on the surface of Earth directly above the location where the rock ruptures. ...
... Earthquake: sudden movement of Earth’s crust caused by the release of potential energy along a fault, causing vibration or movement at the surface. Epicenter: exact point on the surface of Earth directly above the location where the rock ruptures. ...
New Title - Geneva Area City Schools
... scale. This scale measures the amount of energy released by an earthquake. Every day, earthquakes occur all around the world. Most earthquakes occur along plate boundaries because this is where many faults are found. Scientists have used data on earthquakes to learn more about the inside of Earth. F ...
... scale. This scale measures the amount of energy released by an earthquake. Every day, earthquakes occur all around the world. Most earthquakes occur along plate boundaries because this is where many faults are found. Scientists have used data on earthquakes to learn more about the inside of Earth. F ...
The state of Georgia wants you to…
... related to the tectonic nature of the Earth. Such earthquakes are called tectonic earthquakes. The Earth's lithosphere is a patchwork of plates in slow but constant motion caused by the release to space of the heat in the Earth's mantle and core. ...
... related to the tectonic nature of the Earth. Such earthquakes are called tectonic earthquakes. The Earth's lithosphere is a patchwork of plates in slow but constant motion caused by the release to space of the heat in the Earth's mantle and core. ...
Study Guide: Academic Standard 8-3 Earth`s Structure and Processes
... Igneous: Forms when molten rock cools and hardens. If cooling takes place slowly beneath Earth’s surface, the igneous rock is called intrusive and the mineral crystals that form are large. If cooling takes place rapidly on Earth’s surface, the igneous rock is extrusive and the mineral crystals are s ...
... Igneous: Forms when molten rock cools and hardens. If cooling takes place slowly beneath Earth’s surface, the igneous rock is called intrusive and the mineral crystals that form are large. If cooling takes place rapidly on Earth’s surface, the igneous rock is extrusive and the mineral crystals are s ...
Chapter 7 Section 2 Pages 198-201
... of the same plant and animal species are found on continents that are on different side of the Atlantic. • In Wegener's mind, the drifting of continents after the break-up of Pangaea explained not only the matching fossil occurrences but also the evidence of dramatic climate changes on some continen ...
... of the same plant and animal species are found on continents that are on different side of the Atlantic. • In Wegener's mind, the drifting of continents after the break-up of Pangaea explained not only the matching fossil occurrences but also the evidence of dramatic climate changes on some continen ...
9 Geography Investigating Australia`s Physical Environments Term 1
... more brittle and will snap under pressure. Faults are formed when these rocks break. Evidence for Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Many fossils have been found which link continents together and support the idea that the continents were once joined together. They show that a plant or animal liv ...
... more brittle and will snap under pressure. Faults are formed when these rocks break. Evidence for Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Many fossils have been found which link continents together and support the idea that the continents were once joined together. They show that a plant or animal liv ...
Presentation
... of the same plant and animal species are found on continents that are on different side of the Atlantic. • In Wegener's mind, the drifting of continents after the break-up of Pangaea explained not only the matching fossil occurrences but also the evidence of dramatic climate changes on some continen ...
... of the same plant and animal species are found on continents that are on different side of the Atlantic. • In Wegener's mind, the drifting of continents after the break-up of Pangaea explained not only the matching fossil occurrences but also the evidence of dramatic climate changes on some continen ...
Subsoil - Eniscuola
... mixed with gaseous substances. The mixture is called magma: it consists of different minerals that belong to the group of silicates. The gradual cooling of the magmatic mass leads to the crystallization of minerals and rock formation. Crystal structures form more easily when the magma contains gaseo ...
... mixed with gaseous substances. The mixture is called magma: it consists of different minerals that belong to the group of silicates. The gradual cooling of the magmatic mass leads to the crystallization of minerals and rock formation. Crystal structures form more easily when the magma contains gaseo ...
Composition of Mars

The composition of Mars covers the branch of the geology of Mars that describes the make-up of the planet Mars.