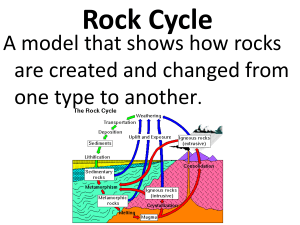
Rock Cycle
... 1. Go to www.phschool.com 2. Enter cfp-1056 into the Web Code area on the top left hand side of the web page. 3. Press the yellow circle to the right of the area where you entered the web code. 4. Press the orange start button. 5. Read the description at the top of the page titled “The Rock cycle” a ...
... 1. Go to www.phschool.com 2. Enter cfp-1056 into the Web Code area on the top left hand side of the web page. 3. Press the yellow circle to the right of the area where you entered the web code. 4. Press the orange start button. 5. Read the description at the top of the page titled “The Rock cycle” a ...
The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or
... The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic material Rock cycle – the continual process by which new rock forms from old rock material Erosion – the process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity moves soil and sediment from one location to another Dep ...
... The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic material Rock cycle – the continual process by which new rock forms from old rock material Erosion – the process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity moves soil and sediment from one location to another Dep ...
chapter1
... at sufficiently high pressures some of the hydrogen reacts to form helium - light is emitted the chemical elements are formed within the interiors of stars ...
... at sufficiently high pressures some of the hydrogen reacts to form helium - light is emitted the chemical elements are formed within the interiors of stars ...
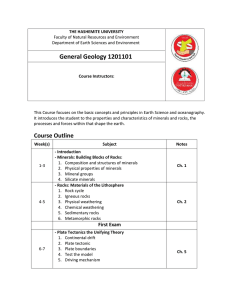
Outline General Geology 2011
... THE HASHEMITE UNIVERSITY Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment Department of Earth Sciences and Environment ...
... THE HASHEMITE UNIVERSITY Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment Department of Earth Sciences and Environment ...
No Slide Title
... The small Canadian vegetation region that has the greatest chance of disappearing due to pressures of urbanization ...
... The small Canadian vegetation region that has the greatest chance of disappearing due to pressures of urbanization ...
Name: Chapter 7 Review Guide Directions: Please answer all
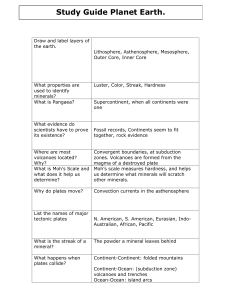
... 1. List the correct order of the layer of the Earth (start with the crust and work your way towards the center). ...
... 1. List the correct order of the layer of the Earth (start with the crust and work your way towards the center). ...
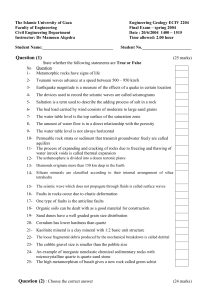
Question (1) (25 marks) State whether the following statements are
... 16- Faults in rocks occur due to elastic deformation 17- One type of faults is the anticline faults 18- Organic soils can be dealt with as a good material for construction 19- Sand dunes have a well graded grain size distribution 20- Corndum has lower hardness than quartz 21- Kaolinite mineral is a ...
... 16- Faults in rocks occur due to elastic deformation 17- One type of faults is the anticline faults 18- Organic soils can be dealt with as a good material for construction 19- Sand dunes have a well graded grain size distribution 20- Corndum has lower hardness than quartz 21- Kaolinite mineral is a ...
Catastrophic Event
... Tsunami • caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, usually an ocean, but can occur in large lakes ...
... Tsunami • caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, usually an ocean, but can occur in large lakes ...
practice exam. - UTEP Geology Homepage
... d. a major volcanic eruption of gas and dust, which contaminated the atmosphere and ...
... d. a major volcanic eruption of gas and dust, which contaminated the atmosphere and ...
Rocks: Mineral Mixtures
... –A solid mixture of crystals of one or more minerals, that range in all sizes from pebbles to formations that are thousands of kilometers long. ...
... –A solid mixture of crystals of one or more minerals, that range in all sizes from pebbles to formations that are thousands of kilometers long. ...
Section 7.3 Student note
... -crystal size depends on how slow it cooled -Intrusive igneous rocks formed well below the surface, ‘intruded into the rock’ -Extrusive rocks formed on the Earth’s surface (exited the Earth) -reach the surface through cracks in the crust/plates, or through erosion and uplift of layers of rock -figur ...
... -crystal size depends on how slow it cooled -Intrusive igneous rocks formed well below the surface, ‘intruded into the rock’ -Extrusive rocks formed on the Earth’s surface (exited the Earth) -reach the surface through cracks in the crust/plates, or through erosion and uplift of layers of rock -figur ...
Rock Cycle
... weight and takes up space. (noun) Examples of products of the rock cycle: Magma Sedimentary rock ...
... weight and takes up space. (noun) Examples of products of the rock cycle: Magma Sedimentary rock ...
Types of Weathering
... When rocks sit in water for extended periods of time they begin to break down and have a clay-like texture. ...
... When rocks sit in water for extended periods of time they begin to break down and have a clay-like texture. ...
Science Chapter 4 Study Guide Vocabulary
... pollution—harmful materials in the air, water, or land and burning fossil fuels causes pollution nonrenewable resource—resources that can not be replace (example-fuel, coal, natural gas) ...
... pollution—harmful materials in the air, water, or land and burning fossil fuels causes pollution nonrenewable resource—resources that can not be replace (example-fuel, coal, natural gas) ...
Heat From the outer core causes convection currents in the semi
... Heat From the outer core causes convection currents in the semi-liquid mantle. These currents cause the crust, floating on top of the mantle, to move. ...
... Heat From the outer core causes convection currents in the semi-liquid mantle. These currents cause the crust, floating on top of the mantle, to move. ...
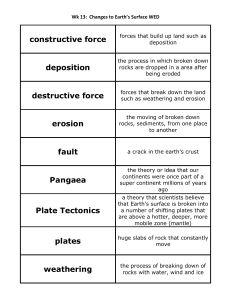
Rock Cycle Unit Vocabulary
... 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth made of the crust and upper mantle - broken into plates that move around on the lower mantle 2. mantle – largest layer of Earth’s interior that lies below the crust - although solid, it flows slowly like putty 3. igneous rock – rock that forms when melted r ...
... 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth made of the crust and upper mantle - broken into plates that move around on the lower mantle 2. mantle – largest layer of Earth’s interior that lies below the crust - although solid, it flows slowly like putty 3. igneous rock – rock that forms when melted r ...
Rock Cycle Unit Vocabulary 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth
... 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth made of the crust and upper mantle - broken into plates that move around on the lower mantle 2. mantle – largest layer of Earth’s interior that lies below the crust - although solid, it flows slowly like putty 3. igneous rock – rock that forms when melted r ...
... 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth made of the crust and upper mantle - broken into plates that move around on the lower mantle 2. mantle – largest layer of Earth’s interior that lies below the crust - although solid, it flows slowly like putty 3. igneous rock – rock that forms when melted r ...
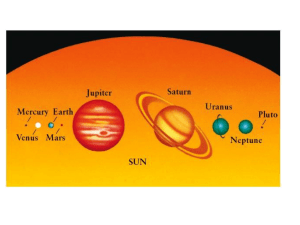
Composition of Mars

The composition of Mars covers the branch of the geology of Mars that describes the make-up of the planet Mars.