Chapter 4: Writing Classes
... Objects can have various types of relationships to each other A general association is sometimes referred to as a use relationship A general association indicates that one object (or class) uses or refers to another object (or class) in some way ...
... Objects can have various types of relationships to each other A general association is sometimes referred to as a use relationship A general association indicates that one object (or class) uses or refers to another object (or class) in some way ...
Folie 1
... (http://koala.ilog.fr/djava/) as a frontend and thus accepts almost all Java features that you would want to use for introductory programming, however, the implementation of the animation might not animate all features. ...
... (http://koala.ilog.fr/djava/) as a frontend and thus accepts almost all Java features that you would want to use for introductory programming, however, the implementation of the animation might not animate all features. ...
Media:OOP
... • Small, simple programs and problems are more complex • E.g. Java’s requirement of classes and methods vs. Python ...
... • Small, simple programs and problems are more complex • E.g. Java’s requirement of classes and methods vs. Python ...
Basic Concepts of Programming
... New languages, Smalltalk, C++, Python, and Java use an object-oriented approach. ...
... New languages, Smalltalk, C++, Python, and Java use an object-oriented approach. ...
Linked Lists
... • They ensure that objects created are properly initialised • They ensure that they are properly destroyed – So they can sort out any garbage collection, for example memory de-allocation. ...
... • They ensure that objects created are properly initialised • They ensure that they are properly destroyed – So they can sort out any garbage collection, for example memory de-allocation. ...
PowerPoint form - University of Wisconsin
... Many of these objects are controlled by computers. Computers rely on ___________ to determine their execution. ...
... Many of these objects are controlled by computers. Computers rely on ___________ to determine their execution. ...
Lecture 6
... and concise. As you see, the new class is shorter and leaner. Many Java development tools use inner classes to generate adapters for handling events. Event-driven programming is introduced in Chapter 8, "Getting Started with Graphics Programming.” ...
... and concise. As you see, the new class is shorter and leaner. Many Java development tools use inner classes to generate adapters for handling events. Event-driven programming is introduced in Chapter 8, "Getting Started with Graphics Programming.” ...
Java Classes and Objects
... Create objects with function, then instruct the objects to do something. Programming becomes an interaction between objects. ...
... Create objects with function, then instruct the objects to do something. Programming becomes an interaction between objects. ...
Visitor pattern
... Every class has a stylized “accept” method, there is a separate hierarchy of visitors class STNode { void accept(Visitor v) { ...
... Every class has a stylized “accept” method, there is a separate hierarchy of visitors class STNode { void accept(Visitor v) { ...
Malegos, Al-Mutairi, Hester - cse.sc.edu
... • C# contains more primitive data types than Java , and also allows more extension to the value types. For example, C# supports 'enumerators', types which are limited to a defined set of constant variables and structs, which are userdefined value types. ...
... • C# contains more primitive data types than Java , and also allows more extension to the value types. For example, C# supports 'enumerators', types which are limited to a defined set of constant variables and structs, which are userdefined value types. ...
Fill in the Blank Questions:
... 1 . Java is a ____ programming language. (1pt) a) low-level b) high-level c) business-oriented d) CPU-oriented 2. The primary task of a compiler is to (1 pt) a) translate from source code into class files b) translate from class files to source code c) generate meaningful error messages d) all of th ...
... 1 . Java is a ____ programming language. (1pt) a) low-level b) high-level c) business-oriented d) CPU-oriented 2. The primary task of a compiler is to (1 pt) a) translate from source code into class files b) translate from class files to source code c) generate meaningful error messages d) all of th ...
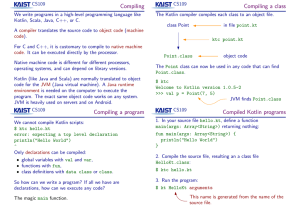
Compiling Compiling a class Compiling a program Compiled Kotlin
... operating systems, and can depend on library versions. Kotlin (like Java and Scala) are normally translated to object code for the JVM (Java virtual machine). A Java runtime environment is needed on the computer to execute the program. The exact same object code works on any system. JVM is heavily u ...
... operating systems, and can depend on library versions. Kotlin (like Java and Scala) are normally translated to object code for the JVM (Java virtual machine). A Java runtime environment is needed on the computer to execute the program. The exact same object code works on any system. JVM is heavily u ...
Abstraction, Inheritance, and Polymorphism in Java
... GUI programming ________ Easier program maintenance ________ ...
... GUI programming ________ Easier program maintenance ________ ...
EXERCISE 2 FLOW CONTROL
... String firstName and protected String secondName. Again with this class Name build the simplest constructor possible. The class Student has an instance variable protected Name studentsName, which is a reference to Name object and an instance variable protected Address studentsAddress which is a refe ...
... String firstName and protected String secondName. Again with this class Name build the simplest constructor possible. The class Student has an instance variable protected Name studentsName, which is a reference to Name object and an instance variable protected Address studentsAddress which is a refe ...
Java Methods
... Encapsulation means that all data members (fields) of a class are declared private. Some methods may be private, too. The class interacts with other classes (called the clients of this class) only through the class’s constructors and public methods. Constructors and public methods of a class serve a ...
... Encapsulation means that all data members (fields) of a class are declared private. Some methods may be private, too. The class interacts with other classes (called the clients of this class) only through the class’s constructors and public methods. Constructors and public methods of a class serve a ...
C++ Programming
... into a single unit that can be referred to by name • Polymorphism - using the same name to invoke different operations on objects of different data types. • Inheritence - defining objects data types as extensions and/or restrictions of other object data types. ...
... into a single unit that can be referred to by name • Polymorphism - using the same name to invoke different operations on objects of different data types. • Inheritence - defining objects data types as extensions and/or restrictions of other object data types. ...
Object Oriented Programming
... Moodle website: https://courses.imsa.edu Java API: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/ ...
... Moodle website: https://courses.imsa.edu Java API: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/ ...
Method Overloading
... Overloaded methods are two or more methods of the same class with the same name but different signatures. I.e., they must have different numbers of parameters or different types of parameters, or both. ...
... Overloaded methods are two or more methods of the same class with the same name but different signatures. I.e., they must have different numbers of parameters or different types of parameters, or both. ...
se1011-9-1-Design
... Old Muddiest Points having multiple classes and the exact use of each one. Plus that, how can I figure which classes to create? More on what can or can't be passed to a method How do you know when to do this before you've completed writing the duplicate code? why make another class, when you can ke ...
... Old Muddiest Points having multiple classes and the exact use of each one. Plus that, how can I figure which classes to create? More on what can or can't be passed to a method How do you know when to do this before you've completed writing the duplicate code? why make another class, when you can ke ...
Introduction to Object Oriented Programming
... behaviour of an object, the idea of encapsulation is to hide the details of how something is achieved. ● e.g. If you are using a class that someone else has written, you want to be able to call a method (Save File for example) without knowing what is going on in the background. ...
... behaviour of an object, the idea of encapsulation is to hide the details of how something is achieved. ● e.g. If you are using a class that someone else has written, you want to be able to call a method (Save File for example) without knowing what is going on in the background. ...
Week 3 (June 24 and 29) Introduction to Java Integrated
... represented in the programming environment through their properties(its characteristics) as data of the program and behaviours(how it behaves) as the methods of Java. It is an instance/example of a class. ...
... represented in the programming environment through their properties(its characteristics) as data of the program and behaviours(how it behaves) as the methods of Java. It is an instance/example of a class. ...
GUIs - DCU School of Computing
... graphical user interfaces. Java’s GUI classes are located in two packages called the AWT and Swing packages (it is usual to see import java.awt.*; and import java.swing.*; in programs that use GUIs). AWT and Swing make huge use of inheritance, interfaces, and abstract classes. Abstract classes are u ...
... graphical user interfaces. Java’s GUI classes are located in two packages called the AWT and Swing packages (it is usual to see import java.awt.*; and import java.swing.*; in programs that use GUIs). AWT and Swing make huge use of inheritance, interfaces, and abstract classes. Abstract classes are u ...