There are different kinds of voice or speech "engines" that take the
... machine language object code that a computer can execute. An interpreted program runs each line of code individually and translates it into machine language while it is executing the program. A compiled program is run through a compilation process that converts the entire program from the source cod ...
... machine language object code that a computer can execute. An interpreted program runs each line of code individually and translates it into machine language while it is executing the program. A compiled program is run through a compilation process that converts the entire program from the source cod ...
pptx
... Higher-order functions The “magic”: How do we use the “right environment” for lexical scope when functions may return other functions, store them in data structures, etc.? Lack of magic: The interpreter uses a closure data structure (with two parts) to keep the environment it will need to use later ...
... Higher-order functions The “magic”: How do we use the “right environment” for lexical scope when functions may return other functions, store them in data structures, etc.? Lack of magic: The interpreter uses a closure data structure (with two parts) to keep the environment it will need to use later ...
Workshop on Functional Programming in the Real World
... Recent developments in research on efficiency of code generation and on graphical input/output interfacing have made it possible to use a pure, lazy functional language to write efficient programs that can compete with industrial applications written in a traditional language. Ongoing work is descri ...
... Recent developments in research on efficiency of code generation and on graphical input/output interfacing have made it possible to use a pure, lazy functional language to write efficient programs that can compete with industrial applications written in a traditional language. Ongoing work is descri ...
A first look at Vanilla
... Changing contexts for computer science • systems distributed at Internet scales - security, robustness, ... • component-based software engineering ...
... Changing contexts for computer science • systems distributed at Internet scales - security, robustness, ... • component-based software engineering ...
More Lambda Calculus
... • How can we program with functions? • How can we program with only functions? ...
... • How can we program with functions? • How can we program with only functions? ...
Type Checking
... ie the system can derive the types of all objects. This is different to the philosophy of languages like Pascal where all typing is explicit. The aim in this part of the course is to examine in more detail how the type of any object (function, or expression) can be derived. ...
... ie the system can derive the types of all objects. This is different to the philosophy of languages like Pascal where all typing is explicit. The aim in this part of the course is to examine in more detail how the type of any object (function, or expression) can be derived. ...
Functional Programming Languages and Dataflow Principles
... Instruction Store: holds coding of the dataflow graph (equivalent to object code/machine code) Processor Bank: a number of processors – all holding zero state from one execution to next! Token Queue: buffering (and the place to insert any input data) ...
... Instruction Store: holds coding of the dataflow graph (equivalent to object code/machine code) Processor Bank: a number of processors – all holding zero state from one execution to next! Token Queue: buffering (and the place to insert any input data) ...
Computers: Software Computer Layers
... Programming languages A programming language is an artificial language that can be used to control the behavior of a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages are used to facilitate communication about the task of organizing and manipulating information, and to express algorithms preci ...
... Programming languages A programming language is an artificial language that can be used to control the behavior of a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages are used to facilitate communication about the task of organizing and manipulating information, and to express algorithms preci ...
Computer Science - Holyport College
... USB devices, digital devices and eavesdropping, Protect software from cyberattacks: ...
... USB devices, digital devices and eavesdropping, Protect software from cyberattacks: ...
Homework 2
... readability, because it makes it difficult to keep track of where the program has been and will go during debugging. Extensive use of go to statements make it difficult to impossible to keep the program code in a top down format. 2. How does the distinguishing between upper- and lowercase in identif ...
... readability, because it makes it difficult to keep track of where the program has been and will go during debugging. Extensive use of go to statements make it difficult to impossible to keep the program code in a top down format. 2. How does the distinguishing between upper- and lowercase in identif ...
1Introduction
... examples of behavior of two objects “boss” and “car” respectively • Behavior is like function, you call a function to do something (e.g. stop the car, find factorial etc) ...
... examples of behavior of two objects “boss” and “car” respectively • Behavior is like function, you call a function to do something (e.g. stop the car, find factorial etc) ...
Programming Languages
... computer, and were used to direct the behavior of machines . • Thousands of different programming languages have been created, mainly in the computer field, and still many are being created every year. • Many programming languages require computation to be specified in an imperative form (i.e., as a ...
... computer, and were used to direct the behavior of machines . • Thousands of different programming languages have been created, mainly in the computer field, and still many are being created every year. • Many programming languages require computation to be specified in an imperative form (i.e., as a ...
Introduction to Programming Systems Goals CS 217
... – originally used to write Unix and Unix tools – data types and control structures close to most machines – now also a popular application programming language ...
... – originally used to write Unix and Unix tools – data types and control structures close to most machines – now also a popular application programming language ...
www.aryansexport.com
... • Report generators take a description of the data format and the report to generate and from that they either generate the required report directly or they generate a program to generate the report. • Data management 4GLs such as SAS, SPSS and Stata provide sophisticated coding commands for data ma ...
... • Report generators take a description of the data format and the report to generate and from that they either generate the required report directly or they generate a program to generate the report. • Data management 4GLs such as SAS, SPSS and Stata provide sophisticated coding commands for data ma ...
Slide 1
... Characteristics of algorithms in C++ standard library: Functional style, generally don’t use explicit recursion or loops Implicit loop structure (for loop) Do something to each element of the vector Implicit data structure is a vector (array) In C++ standard library, there is a set of ve ...
... Characteristics of algorithms in C++ standard library: Functional style, generally don’t use explicit recursion or loops Implicit loop structure (for loop) Do something to each element of the vector Implicit data structure is a vector (array) In C++ standard library, there is a set of ve ...
Powerpoint ()
... • Scala has this, known as Option • In general, if null is possible, use Option ...
... • Scala has this, known as Option • In general, if null is possible, use Option ...
DipProg Programming Principles and Paradigms
... languages with sets and maps. Topics covered include type systems, abstraction mechanisms, declarativeness, and efficient implementations, concurrency and parallelism. The course objectives are: to provide an introduction to formalisms for specifying syntax and semantics of programming languages, in ...
... languages with sets and maps. Topics covered include type systems, abstraction mechanisms, declarativeness, and efficient implementations, concurrency and parallelism. The course objectives are: to provide an introduction to formalisms for specifying syntax and semantics of programming languages, in ...
View
... • A program is a model of some process in the real or mathematical world. • A program is a sequence of instructions for a machine to perform a specific task. • A notational system for describing computation in machine-readable and humanreadable form Slide 5 ...
... • A program is a model of some process in the real or mathematical world. • A program is a sequence of instructions for a machine to perform a specific task. • A notational system for describing computation in machine-readable and humanreadable form Slide 5 ...
Matt Hartzell`s Richter Scholar Proposal
... 1]. I myself used a scripting language exclusively for programming exercises in the upper-division course The Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Scripting languages also excel at “gluing” other self-contained pieces of software together, and this is what they have traditionally been used for. Howeve ...
... 1]. I myself used a scripting language exclusively for programming exercises in the upper-division course The Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Scripting languages also excel at “gluing” other self-contained pieces of software together, and this is what they have traditionally been used for. Howeve ...
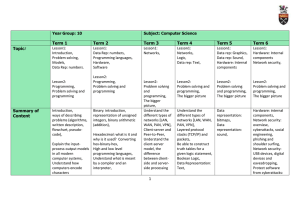
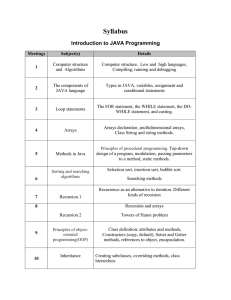
Syllabus
... Recurrence as an alternative to iteration. Different kinds of recursion Recursion and arrays ...
... Recurrence as an alternative to iteration. Different kinds of recursion Recursion and arrays ...
Mathematically Structured but not Necessarily Functional
... be extracted from a proof, we might prefer an impure handwritten one because it is more efficient, or because it is easier to write the code than the proof. In fact, an important advantage of realizability is the fact that it allows programmers to implement specifications in any way they see fit. 2 ...
... be extracted from a proof, we might prefer an impure handwritten one because it is more efficient, or because it is easier to write the code than the proof. In fact, an important advantage of realizability is the fact that it allows programmers to implement specifications in any way they see fit. 2 ...
CSC 272 - Software II: Principles of Programming Languages What
... • Artificial Intelligence deals with emulating human-style reasoning on a computer. • These applications usually involve symbolic computation, where most of the symbols are names and not numbers. • The most common data structure is the list, not the matrix or array as in scientific computing and not ...
... • Artificial Intelligence deals with emulating human-style reasoning on a computer. • These applications usually involve symbolic computation, where most of the symbols are names and not numbers. • The most common data structure is the list, not the matrix or array as in scientific computing and not ...