Programming Languages
... Lexical analysis Also known as scanning Divides the string of input characters into single elements, tokens, based on strict computer punctuation ...
... Lexical analysis Also known as scanning Divides the string of input characters into single elements, tokens, based on strict computer punctuation ...
A computational science agenda for programming language research
... the previous time step for the current (line 15) is a stateful computation; if instead h = h old is written, then the calculation stays in the initial state. Such problems worsen with the use of parallelism and as implementations grow in size. Our example program also exploits implicit truncation of ...
... the previous time step for the current (line 15) is a stateful computation; if instead h = h old is written, then the calculation stays in the initial state. Such problems worsen with the use of parallelism and as implementations grow in size. Our example program also exploits implicit truncation of ...
COS_470-Practice-Week_05YanaAleksieva
... define here the base case to stop the recursion: if nums is empty or if num is <= than the first element in nums then the function returns a list constructed by num and the list nums. Which constructor will you use? ...
... define here the base case to stop the recursion: if nums is empty or if num is <= than the first element in nums then the function returns a list constructed by num and the list nums. Which constructor will you use? ...
Table of contents
... Object-oriented programming .................................................................................................. 13 Referential transparency ........................................................................................................... 18 Function object (functor) ........ ...
... Object-oriented programming .................................................................................................. 13 Referential transparency ........................................................................................................... 18 Function object (functor) ........ ...
Slides
... • How do we perform an action? • We need a function with type: –Io a -> a • If we have such a function then we break the abstraction which hides how Io is implemented. • In Haskell, the real IO can only be preformed at top level, when because the main function must have type IO() ...
... • How do we perform an action? • We need a function with type: –Io a -> a • If we have such a function then we break the abstraction which hides how Io is implemented. • In Haskell, the real IO can only be preformed at top level, when because the main function must have type IO() ...
Computer Technology Computer Technology
... Information Systems Specialist Career Path Credit Requirements: 69 Semester Credit Hours This program prepares students for careers in a variety of information technology areas. It gives students a foundation in computer hardware, computer applications, computer programming, the Internet and compute ...
... Information Systems Specialist Career Path Credit Requirements: 69 Semester Credit Hours This program prepares students for careers in a variety of information technology areas. It gives students a foundation in computer hardware, computer applications, computer programming, the Internet and compute ...
The Bridge between Mathematical Models of Physics and Generic
... established, and the concept of toposes paved the way to the formalization of set theory and foundations of mathematics via categories. This line continued to evolve, and we only note [3] as recent research direction into founding physics on this concept. More recently category theory found applica ...
... established, and the concept of toposes paved the way to the formalization of set theory and foundations of mathematics via categories. This line continued to evolve, and we only note [3] as recent research direction into founding physics on this concept. More recently category theory found applica ...
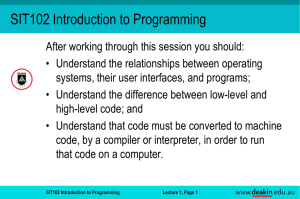
SIT102 Introduction to Programming
... Machine and assembly languages are low-level languages because they both use instructions that are directly tied to one type of computer ...
... Machine and assembly languages are low-level languages because they both use instructions that are directly tied to one type of computer ...
COS 333: Advanced Programming Techniques Robert M. Dondero, Ph.D.
... See "General Information" Web page ...
... See "General Information" Web page ...
Functional Programming, Parametricity, Types
... FP is a commitment to preserving referential transparency Quite a while ago, FP won by not-a-little-bit. Moving on. we use tools to achieve this commitment parametricity is one such tool with high reward ...
... FP is a commitment to preserving referential transparency Quite a while ago, FP won by not-a-little-bit. Moving on. we use tools to achieve this commitment parametricity is one such tool with high reward ...
- Darren`s Data Analytics Blog
... • python –m py_compile script-name.py • python –m compileall . • Py and Pyc files available ...
... • python –m py_compile script-name.py • python –m compileall . • Py and Pyc files available ...
An Overview of Visual Basic .NET
... The object-oriented/event-driven high-level languages simplified the task of programming applications for Windows. In object-oriented/event-driven high-level languages, the emphasis of a program is on objects included in the user interface (such as scroll bars and buttons) and the events (such as sc ...
... The object-oriented/event-driven high-level languages simplified the task of programming applications for Windows. In object-oriented/event-driven high-level languages, the emphasis of a program is on objects included in the user interface (such as scroll bars and buttons) and the events (such as sc ...
Functional programming - University of Cape Town
... only be read, once they have been created – remember no assignment (no destructive update) ...
... only be read, once they have been created – remember no assignment (no destructive update) ...
CS 2110 Object-Oriented Programming and Data Structures Spring
... working together. It is a violation of the code to split the work into parts, do the parts independently, and then merge. Programming Proficiency A CS 2110 student should be able to write simple programs in some programming language. They should have fluency with strings, arrays, two-dimensional arr ...
... working together. It is a violation of the code to split the work into parts, do the parts independently, and then merge. Programming Proficiency A CS 2110 student should be able to write simple programs in some programming language. They should have fluency with strings, arrays, two-dimensional arr ...
Course: CS 2110 —also ENGRD 2210
... working together. It is a violation of the code to split the work into parts, do the parts independently, and then merge. Programming Proficiency A CS 2110 student should be able to write simple programs in some programming language. They should have fluency with strings, arrays, two-dimensional arr ...
... working together. It is a violation of the code to split the work into parts, do the parts independently, and then merge. Programming Proficiency A CS 2110 student should be able to write simple programs in some programming language. They should have fluency with strings, arrays, two-dimensional arr ...
C Programming Lecture Series - Students` Gymkhana, IIT Kanpur
... C Course, Programming club, Fall 2008 ...
... C Course, Programming club, Fall 2008 ...
AI2
... – “The exciting new effort to make computer think ….. machine with minds, in the full an literal sense” – “Activities that we associate with human thinking, activities such as decision-making, problem-solving, learning…” ...
... – “The exciting new effort to make computer think ….. machine with minds, in the full an literal sense” – “Activities that we associate with human thinking, activities such as decision-making, problem-solving, learning…” ...
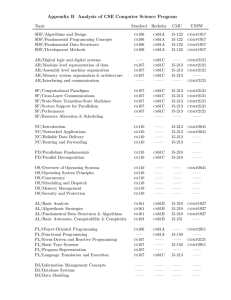
Appendix B Analysis of CSE Computer Science Program
... For students with a basic understanding of programming (variables, expressions, loops, arrays, functions). Teaches imperative programming and methods for ensuring the correctness of programs. Students will learn the process and concepts needed to go from high-level descriptions of algorithms to corr ...
... For students with a basic understanding of programming (variables, expressions, loops, arrays, functions). Teaches imperative programming and methods for ensuring the correctness of programs. Students will learn the process and concepts needed to go from high-level descriptions of algorithms to corr ...
The Introduction to Object
... users of the objects do not need to know the details of the data and operations of the objects. Data Abstraction -- the procedure to define a class from objects. Abstract Data Type-- Class. ...
... users of the objects do not need to know the details of the data and operations of the objects. Data Abstraction -- the procedure to define a class from objects. Abstract Data Type-- Class. ...
Chapter 7 - CSUDH Computer Science
... syntactically and type-wise correct program. • Three approaches – Operational semantics • The meaning attached by compiling using compiler C and executing using machine M. Ex: Fortran on IBM 709. • Direct and straightforward program meaning ...
... syntactically and type-wise correct program. • Three approaches – Operational semantics • The meaning attached by compiling using compiler C and executing using machine M. Ex: Fortran on IBM 709. • Direct and straightforward program meaning ...
View
... languages, sometimes referred to as “machine languages” or “assembly languages.” Loosely speaking, computers can only execute programs written in low-level languages. Thus, programs written in a high-level language have to be processed before they can run. This extra processing takes some time, wh ...
... languages, sometimes referred to as “machine languages” or “assembly languages.” Loosely speaking, computers can only execute programs written in low-level languages. Thus, programs written in a high-level language have to be processed before they can run. This extra processing takes some time, wh ...
Overview of Leda Programming Language
... In addition to static binding, Leda supports the concept of dynamic dispatch which is sometimes referred to as dynamic binding. Dynamic binding allows the programmer to use a technique called polymorphism which is one of the more powerful features of object oriented programming. With static binding, ...
... In addition to static binding, Leda supports the concept of dynamic dispatch which is sometimes referred to as dynamic binding. Dynamic binding allows the programmer to use a technique called polymorphism which is one of the more powerful features of object oriented programming. With static binding, ...