Down
... Are the daughter cells haploid or diploid? Are the daughter cells identical to the parent cell? yes or no Are the daughter cells identical to each other? yes or no What type of cell does this occur in? somatic or sex cells ...
... Are the daughter cells haploid or diploid? Are the daughter cells identical to the parent cell? yes or no Are the daughter cells identical to each other? yes or no What type of cell does this occur in? somatic or sex cells ...
detailed meiosis
... The Role of Meiosis in Sexual Life Cycles • Ploidy refers to the number of chromosome sets in a cell. – Diploid (2n) - condition in which cells contain two sets of chromosomes (one set from each parent) – Haploid (n) - cells contain one set of chromosomes. In animals, these cells are called gametes ...
... The Role of Meiosis in Sexual Life Cycles • Ploidy refers to the number of chromosome sets in a cell. – Diploid (2n) - condition in which cells contain two sets of chromosomes (one set from each parent) – Haploid (n) - cells contain one set of chromosomes. In animals, these cells are called gametes ...
The Cell Cycle - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • When a cell begins to divide uncontrollably the result is cancer. • A cancerous cell becomes stuck in the cell division phase of mitosis. Since the cell does not enter interphase, DNA is not replicated, resulting in new cells being produced without all of the instructions. ...
... • When a cell begins to divide uncontrollably the result is cancer. • A cancerous cell becomes stuck in the cell division phase of mitosis. Since the cell does not enter interphase, DNA is not replicated, resulting in new cells being produced without all of the instructions. ...
chapter 13 meiosis and sexual life cycles
... -The human life cycle begins when a _____________ sperm cell fuses (syngamy) with a ________________ ovum resulting in a diploid fertilized egg (____________________) -______________ generates all the somatic cells of the body, and each autosome is ___________________. -Gametes, which develop in the ...
... -The human life cycle begins when a _____________ sperm cell fuses (syngamy) with a ________________ ovum resulting in a diploid fertilized egg (____________________) -______________ generates all the somatic cells of the body, and each autosome is ___________________. -Gametes, which develop in the ...
Cell Reproduction (continued)
... • The centromeres break, and chromatids move away from each other to opposite ends of the cell. • How they separate is also random, and is called segregation. ...
... • The centromeres break, and chromatids move away from each other to opposite ends of the cell. • How they separate is also random, and is called segregation. ...
File
... This makes for a lot of genetic diversity. This trick is accomplished through independent assortment and crossing-over. ...
... This makes for a lot of genetic diversity. This trick is accomplished through independent assortment and crossing-over. ...
Eukaryo c cell Fundamentals The Cell Cycle Cellular Division
... • If one of these cells mutated so it was resistant, how many resistant cells in 7 more hours? ...
... • If one of these cells mutated so it was resistant, how many resistant cells in 7 more hours? ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
... – Pair of chromosomes that have the same types of genes on them in the same locations ...
... – Pair of chromosomes that have the same types of genes on them in the same locations ...
Section 8-1 Chromosomes - walker2011
... The division of gametes 35. What type of cell undergoes meiosis? Gametes 36. Name the 2 human gametes & tell their chromosome number. Egg (or ovum) = 23 sperm = 23 37. What is the chromosome number for humans? 46 and 23 38. The fusion of a ______sperm_______ and an ______egg_______ produces a _____z ...
... The division of gametes 35. What type of cell undergoes meiosis? Gametes 36. Name the 2 human gametes & tell their chromosome number. Egg (or ovum) = 23 sperm = 23 37. What is the chromosome number for humans? 46 and 23 38. The fusion of a ______sperm_______ and an ______egg_______ produces a _____z ...
Exam V Study Guide
... Organisms use Meiosis for the sole purpose of? Meiosis is often also referred to as? During which stage of Meiosis does synapsis and the formation of tetrads occur? When a cell undergoes Meiosis, the chromosomes duplicate during which of the following phases? The behavior of a pair of homologous chr ...
... Organisms use Meiosis for the sole purpose of? Meiosis is often also referred to as? During which stage of Meiosis does synapsis and the formation of tetrads occur? When a cell undergoes Meiosis, the chromosomes duplicate during which of the following phases? The behavior of a pair of homologous chr ...
Study Guide for Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis, and Sexual and
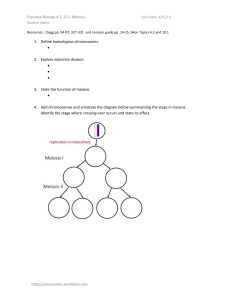
... 6.a. What is the end product of meiosis? 6.b. How many cells are produced from the parent cell? 6.c. Are they genetically identical, or are they genetically different? 6.d. Do they have the same number of chromosomes or a different number? ...
... 6.a. What is the end product of meiosis? 6.b. How many cells are produced from the parent cell? 6.c. Are they genetically identical, or are they genetically different? 6.d. Do they have the same number of chromosomes or a different number? ...
Mitosis process of a cell dividing to produce an exact copy of itself
... of the center of the cell Spindle fibers attach Meiosis is a bit different because there something called crossing-over happens with chromosomes the DNA. This crossing over is an exchange of genes. The genes are mixed up, not resulting in a perfect duplicate like mitosis. ...
... of the center of the cell Spindle fibers attach Meiosis is a bit different because there something called crossing-over happens with chromosomes the DNA. This crossing over is an exchange of genes. The genes are mixed up, not resulting in a perfect duplicate like mitosis. ...
Mitosis Lecture
... more cells. • The new cells made during mitosis are called daughter cells. • DNA in a cell is bundled into chromosomes. • Humans have 46 chromosomes, 23 from each parent. Every cell has the same 46 chromosomes. ...
... more cells. • The new cells made during mitosis are called daughter cells. • DNA in a cell is bundled into chromosomes. • Humans have 46 chromosomes, 23 from each parent. Every cell has the same 46 chromosomes. ...
Meiosis - Ms. Fahey
... • The spindle from one end of the cell attaches to one pair of sister chromatids while a spindle fiber from the other end attaches to the other pair of sister chromatids. • Independent Assortment—maternal and paternal chromosomes are line up on the opposite sides of the metaphase plate in a random f ...
... • The spindle from one end of the cell attaches to one pair of sister chromatids while a spindle fiber from the other end attaches to the other pair of sister chromatids. • Independent Assortment—maternal and paternal chromosomes are line up on the opposite sides of the metaphase plate in a random f ...
Genetics – word list
... Each cell has divided again. The result is the production of four haploid gametes. Each of these cells are genetically different to each other. ...
... Each cell has divided again. The result is the production of four haploid gametes. Each of these cells are genetically different to each other. ...
Meiosis
... passed on to offspring. Depending on how the chromosomes line up at the equator, four gametes with four different combinations of chromosomes can result. Genetic variation also is produced during crossing over and during fertilization, when gametes randomly ...
... passed on to offspring. Depending on how the chromosomes line up at the equator, four gametes with four different combinations of chromosomes can result. Genetic variation also is produced during crossing over and during fertilization, when gametes randomly ...
meiosis - Dayton Independent Schools
... 2. Gametes are the “sex” cells and contain only ½ the normal number of chromosomes…. called the “Haploid” number (the symbol is n)….. Sperm cells and ova are gametes. n = number of chromosomes in the set… so….2n means 2 chromosomes in the set…. Polyploid cells have more than two ...
... 2. Gametes are the “sex” cells and contain only ½ the normal number of chromosomes…. called the “Haploid” number (the symbol is n)….. Sperm cells and ova are gametes. n = number of chromosomes in the set… so….2n means 2 chromosomes in the set…. Polyploid cells have more than two ...
Table 3.2 Mitosis vs Meiosis
... the events of mitosis in animal and plant cells the events of meiosis (gametogenesis in animals and sporogenesis in plants) the key mechanical and genetic differences between meiosis and mitosis After doing this lab you should be able to: recognize the stages of mitosis in plant and animal c ...
... the events of mitosis in animal and plant cells the events of meiosis (gametogenesis in animals and sporogenesis in plants) the key mechanical and genetic differences between meiosis and mitosis After doing this lab you should be able to: recognize the stages of mitosis in plant and animal c ...
Genetics Unit Test_Study_Guide_KEY
... b. Mitosis-Prophase Chromosomes form; nuclear membrane disappears c. Mitosis – Metaphase Chromosomes line up d. Mitosis – Anaphase Chromosomes separate e. Mitosis – Telophase New nuclear membrane forms around each group of chromosomes f. Cytokinesis Division of parent cell’s cytoplasm 5. After Mitos ...
... b. Mitosis-Prophase Chromosomes form; nuclear membrane disappears c. Mitosis – Metaphase Chromosomes line up d. Mitosis – Anaphase Chromosomes separate e. Mitosis – Telophase New nuclear membrane forms around each group of chromosomes f. Cytokinesis Division of parent cell’s cytoplasm 5. After Mitos ...
Name
... Chromosome Number Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that correspond in body cells. One chromosome from each pair comes from each parent. A cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes has a diploid number of chromosomes (meaning “two sets”). Haploid cells contain only one ...
... Chromosome Number Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that correspond in body cells. One chromosome from each pair comes from each parent. A cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes has a diploid number of chromosomes (meaning “two sets”). Haploid cells contain only one ...
Mitosis Jeopardy Review
... Most of the cells growth and activity take place in this phase. Be specific. ...
... Most of the cells growth and activity take place in this phase. Be specific. ...
CONNECT!
... produce gametes (sex cells or sperm and egg). • Meiosis cuts the number of chromosomes in half, so it is referred to as reduction division. • The gametes are haploid (half the normal chromosome number of body cells). ...
... produce gametes (sex cells or sperm and egg). • Meiosis cuts the number of chromosomes in half, so it is referred to as reduction division. • The gametes are haploid (half the normal chromosome number of body cells). ...
Blog resource: http://tinyurl
... 14. A diploid cell carries genes A and B. There are dominant and recessive alleles for these genes. The cell is heterozygous for both genes. a. What combination of gametes could be produced if there was no crossing over? AB or ____ ...
... 14. A diploid cell carries genes A and B. There are dominant and recessive alleles for these genes. The cell is heterozygous for both genes. a. What combination of gametes could be produced if there was no crossing over? AB or ____ ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.