Human Genetics Review and Jeopardy game worksheet
... $300: ____________ True or False: Autosomal number disorders are the most deadly, or lethal. $400: A sex chromosome disorder that is characterized by males showing poor sexual development and infertility… A. is known as ___________________________________ B. has the following sex chromosomes: _____ ...
... $300: ____________ True or False: Autosomal number disorders are the most deadly, or lethal. $400: A sex chromosome disorder that is characterized by males showing poor sexual development and infertility… A. is known as ___________________________________ B. has the following sex chromosomes: _____ ...
Structure and Function
... Start with one cell with the diploid number End with two cells with diploid number Daughter cells are identical to original cell Mitosis is nuclear division plus cytokinesis, and produces two identical daughter cells during prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Interphase is of ...
... Start with one cell with the diploid number End with two cells with diploid number Daughter cells are identical to original cell Mitosis is nuclear division plus cytokinesis, and produces two identical daughter cells during prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Interphase is of ...
Name
... leptotene is the stage of meiosis where chromatin starts condensing zygotene is the stage of meiosis when chromosomes begin pairing up (3) Define interphase. All stages of the cell cycle not including mitosis (specifically G1, S, and G2) (3) Define carrier. A heterozygous individual for a recessive ...
... leptotene is the stage of meiosis where chromatin starts condensing zygotene is the stage of meiosis when chromosomes begin pairing up (3) Define interphase. All stages of the cell cycle not including mitosis (specifically G1, S, and G2) (3) Define carrier. A heterozygous individual for a recessive ...
Cell Cycle - Sciencebugz
... • Particularly important for mammalian cells are growth factors, proteins released by one group of cells that stimulate other cells to divide. – For example, platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF), produced by platelet blood cells, bind to tyrosine-kinase receptors of fibroblasts, a type of connecti ...
... • Particularly important for mammalian cells are growth factors, proteins released by one group of cells that stimulate other cells to divide. – For example, platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF), produced by platelet blood cells, bind to tyrosine-kinase receptors of fibroblasts, a type of connecti ...
Tài liệu PDF
... other proteins that work together to recruit new membrane and cell-wall materials to the site. FtsZ proteins can form filaments, rings, and other three-dimensional structures resembling the way tubulin forms microtubules, centrioles, and various cytoskeleton components. In addition, both FtsZ and tu ...
... other proteins that work together to recruit new membrane and cell-wall materials to the site. FtsZ proteins can form filaments, rings, and other three-dimensional structures resembling the way tubulin forms microtubules, centrioles, and various cytoskeleton components. In addition, both FtsZ and tu ...
Diploma Sample – Equine Science
... are identical in terms of the positions of the genes on them, they do not necessarily carry identical information, due to the possibility of different alleles. The matching pairs of chromosomes are termed autosomes, and this word is used to refer to all chromosomes that are not the sex chromosomes. ...
... are identical in terms of the positions of the genes on them, they do not necessarily carry identical information, due to the possibility of different alleles. The matching pairs of chromosomes are termed autosomes, and this word is used to refer to all chromosomes that are not the sex chromosomes. ...
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
... chromosomes carry the genetic information and they live inside the nucleus Chromosomes are made up of DNA and proteins (called histones) ...
... chromosomes carry the genetic information and they live inside the nucleus Chromosomes are made up of DNA and proteins (called histones) ...
lecture4(GS351)
... Mitosis vs. Meiosis - The goal of mitosis is to make more “somatic” cells: each daughter cell should have the same chromosome set as the parental cell - The goal of meiosis is to make sperm and eggs: each daughter cell should have half the number of chromosome sets as the parental cell ...
... Mitosis vs. Meiosis - The goal of mitosis is to make more “somatic” cells: each daughter cell should have the same chromosome set as the parental cell - The goal of meiosis is to make sperm and eggs: each daughter cell should have half the number of chromosome sets as the parental cell ...
PCB5065 Exam 2 - UF Plant Pathology
... a) mitotic recombination results in crossing over half the time. F b) mitotic recombination is usually the result of gene conversion T c) in Drosophila and most organisms, mitotic recombination differs from meiotic in that the homology search during mitotic recombination must cover the whole genome. ...
... a) mitotic recombination results in crossing over half the time. F b) mitotic recombination is usually the result of gene conversion T c) in Drosophila and most organisms, mitotic recombination differs from meiotic in that the homology search during mitotic recombination must cover the whole genome. ...
Plant Reproduction
... megaspores, three of which disintegrate • One megaspore undergoes mitosis to form the female gametophyte, which contains one haploid egg, five other haploid cells, and one endosperm mother cell with two nuclei (n + n) ...
... megaspores, three of which disintegrate • One megaspore undergoes mitosis to form the female gametophyte, which contains one haploid egg, five other haploid cells, and one endosperm mother cell with two nuclei (n + n) ...
Repaso del capítulo
... Sample answer: Before mitosis begins, the chromosomes are copied. In phase 1, the nuclear membrane dissolves, and the chromosomes condense. In phase 2, the chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell, and homologous chromosomes pair up. In phase 3, the chromatids move to opposite sides of the ...
... Sample answer: Before mitosis begins, the chromosomes are copied. In phase 1, the nuclear membrane dissolves, and the chromosomes condense. In phase 2, the chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell, and homologous chromosomes pair up. In phase 3, the chromatids move to opposite sides of the ...
BIOLOGY EOCT REVIEW SHEET GILES
... 5) What is the difference between natural selection and artificial selection? 6) List several things in the environment that could lead to natural selection. 7) Discuss how the fossil record provides evidence for evolution. 8) What are homologous structures? Discuss how homologous structures provide ...
... 5) What is the difference between natural selection and artificial selection? 6) List several things in the environment that could lead to natural selection. 7) Discuss how the fossil record provides evidence for evolution. 8) What are homologous structures? Discuss how homologous structures provide ...
Chapter 29
... • United on the basis that they are not fungi, plants, or animals • Vary considerably in every other aspect – Unicellular, colonial, and multicellular groups – Most are microscopic but some are huge – All symmetries – All types of nutrition ...
... • United on the basis that they are not fungi, plants, or animals • Vary considerably in every other aspect – Unicellular, colonial, and multicellular groups – Most are microscopic but some are huge – All symmetries – All types of nutrition ...
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
... chromosomes carry the genetic information and they live inside the nucleus Chromosomes are made up of DNA and proteins (called histones) ...
... chromosomes carry the genetic information and they live inside the nucleus Chromosomes are made up of DNA and proteins (called histones) ...
1. True or false? Genes that are located sufficiently close together in
... B. the frequency of double crossovers is 1/4 of the number expected if there were no interference. 9 C. there were four times as many single crossovers as double crossovers. D. there were four times as many single crossovers in one region as there were in an adjacent region. E. there were f ...
... B. the frequency of double crossovers is 1/4 of the number expected if there were no interference. 9 C. there were four times as many single crossovers as double crossovers. D. there were four times as many single crossovers in one region as there were in an adjacent region. E. there were f ...
Document
... ii) Paired chromosomes segregate during meiosis. Each sex cell or gamete has half the number of chromosomes found in a somatic cell iii) Chromosomes sort independently during meiosis. Each gamete receives one of the pairs and that one chromosome has no influence on the movement of a member of anothe ...
... ii) Paired chromosomes segregate during meiosis. Each sex cell or gamete has half the number of chromosomes found in a somatic cell iii) Chromosomes sort independently during meiosis. Each gamete receives one of the pairs and that one chromosome has no influence on the movement of a member of anothe ...
animal_vs_plant_cell_cycle_comparison
... -G1 phase: The cell increases in size (period of Interphase growth) and synthesizes new proteins and organelles. -S phase - As the cell prepares for mitosis, the chromosomes replicates during this phase of interphase during the cell cycle. -G2 phase - Organelles and molecules required for cell divis ...
... -G1 phase: The cell increases in size (period of Interphase growth) and synthesizes new proteins and organelles. -S phase - As the cell prepares for mitosis, the chromosomes replicates during this phase of interphase during the cell cycle. -G2 phase - Organelles and molecules required for cell divis ...
Prenatal Microarray Testing - Scotland`s Health on the Web
... What is microarray testing? Microarray testing allows the detection of chromosome imbalances which are too small to be seen by the routine chromosome tests offered during a pregnancy. Why have you been offered microarray testing? Your serum screening results or your ultrasound has shown that there i ...
... What is microarray testing? Microarray testing allows the detection of chromosome imbalances which are too small to be seen by the routine chromosome tests offered during a pregnancy. Why have you been offered microarray testing? Your serum screening results or your ultrasound has shown that there i ...
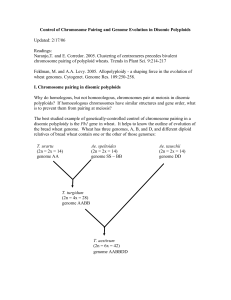
Control of Chromosome Pairing and Genome Evolution in Disomic
... recombinant chromosome from the F1, and this recombinant chromosome can be maintained intact (with no further recombination) over selfing generations, so it is a “permanent” recombinant progeny. 96 monosomic progenies were recovered from this cross and the genetic map of this population serves as a ...
... recombinant chromosome from the F1, and this recombinant chromosome can be maintained intact (with no further recombination) over selfing generations, so it is a “permanent” recombinant progeny. 96 monosomic progenies were recovered from this cross and the genetic map of this population serves as a ...
Presentation
... Human somatic cells contain…. 46 individual chromosomes or 23 chromosome pairs Of these 23 pairs… SEX CHROMOSOMES (1 pair) • determine the sex of an individual AUTOSOMES (22 pairs) • do not determine the sex of an individual ...
... Human somatic cells contain…. 46 individual chromosomes or 23 chromosome pairs Of these 23 pairs… SEX CHROMOSOMES (1 pair) • determine the sex of an individual AUTOSOMES (22 pairs) • do not determine the sex of an individual ...
Mendel`s Laws Haldane`s Mapping Formula
... • If there is an even number of crossovers between two sites, they wind up on the same gamete. The net effect is no recombination. • If there is an odd number of crossovers between sites, they recombine. • AB = event “recombination between A & B” = “odd # of crossovers between A & B” ...
... • If there is an even number of crossovers between two sites, they wind up on the same gamete. The net effect is no recombination. • If there is an odd number of crossovers between sites, they recombine. • AB = event “recombination between A & B” = “odd # of crossovers between A & B” ...
Mech63-RvwGeneticDisordersPt1
... This, too, is aneuploidy where there’s 1 less chromosome due to a deletion of 1 X. The nondisjunction occurs in meiosis. There are a number of karyotypes for this, but (45,X) is the most common. Most common sex chromosome abnormality in females ...
... This, too, is aneuploidy where there’s 1 less chromosome due to a deletion of 1 X. The nondisjunction occurs in meiosis. There are a number of karyotypes for this, but (45,X) is the most common. Most common sex chromosome abnormality in females ...
Hair: Curly or Straight?
... of physical characteristics (traits), from the parents to the offspring. Genes are basically small parts of every single organism’s DNA, which is the genetic material found in the nucleus of a cell. DNA is made up of the information about an organism, which is then passed down from the parental gene ...
... of physical characteristics (traits), from the parents to the offspring. Genes are basically small parts of every single organism’s DNA, which is the genetic material found in the nucleus of a cell. DNA is made up of the information about an organism, which is then passed down from the parental gene ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.