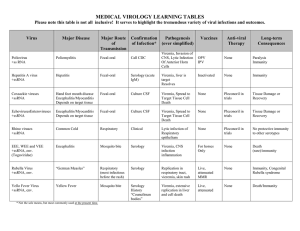
No Slide Title
... and harder for you to get well. • "V" is for Virus, which refers to the specific type of germ that causes the disease. Unfortunately, viruses can't be killed because they aren't alive. You can't take medicine like an antibiotic to get rid of HIV. Viruses stay with you forever. ...
... and harder for you to get well. • "V" is for Virus, which refers to the specific type of germ that causes the disease. Unfortunately, viruses can't be killed because they aren't alive. You can't take medicine like an antibiotic to get rid of HIV. Viruses stay with you forever. ...
Causes Of Feline Leukemia
... In this respect, feline leukemia is similar to FIV (feline immunodeficiency virus). Leukemia will have no typical symptoms in the first stages of the disease. The cat may have fever, be lethargic or lack appetite. The cat will start to contract different diseases, and these conditions will tend to r ...
... In this respect, feline leukemia is similar to FIV (feline immunodeficiency virus). Leukemia will have no typical symptoms in the first stages of the disease. The cat may have fever, be lethargic or lack appetite. The cat will start to contract different diseases, and these conditions will tend to r ...
HIV: Preventing New Infections: New Options
... May: R0 = β c D, where • β = transmission probability • c = number of contacts • D = average time spent infectious (= 1/b if the infection rate is b) • Can also be thought of as new infections caused by each current infected source person ...
... May: R0 = β c D, where • β = transmission probability • c = number of contacts • D = average time spent infectious (= 1/b if the infection rate is b) • Can also be thought of as new infections caused by each current infected source person ...
epidemiological overview of tuberculosis - epidat
... Number of droplets nuclei in air Duration of exposure of a susceptible individual to that droplet ...
... Number of droplets nuclei in air Duration of exposure of a susceptible individual to that droplet ...
Chapter 5 ( Contd.)
... virus, fungi, protozoan etc.) used to intentionally inflict harm on humans. The definition is extended to include biologically derived toxins and poisons. Generally, the types of agents used as biological weapons cause systemic diseases, hemorrhagic fevers, pneumonias, or involve toxins and biol ...
... virus, fungi, protozoan etc.) used to intentionally inflict harm on humans. The definition is extended to include biologically derived toxins and poisons. Generally, the types of agents used as biological weapons cause systemic diseases, hemorrhagic fevers, pneumonias, or involve toxins and biol ...
IPFA Position Paper on ZIKA virus and the safety of plasma
... ZIKA virus and the safety of plasma-derived medicinal products Zika virus is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that was first identified in Uganda in 19471. Two epidemics were reported in the Yap Isles in 2007 and in French Polynesia in 2013-2014. In April 2015, locallyacquired cases of Zika virus infecti ...
... ZIKA virus and the safety of plasma-derived medicinal products Zika virus is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that was first identified in Uganda in 19471. Two epidemics were reported in the Yap Isles in 2007 and in French Polynesia in 2013-2014. In April 2015, locallyacquired cases of Zika virus infecti ...
Document
... mucous, circulating blood, antibodies, WBCs, and complement that would easily be able to recognize and attack the organism cannot reach it. ii. Other organisms have developed ways to evade complement-mediated lysis. (ex: E. coli) iii. Antigenic shift occurs when the organism mutates and/or rearrange ...
... mucous, circulating blood, antibodies, WBCs, and complement that would easily be able to recognize and attack the organism cannot reach it. ii. Other organisms have developed ways to evade complement-mediated lysis. (ex: E. coli) iii. Antigenic shift occurs when the organism mutates and/or rearrange ...
... illness usually is mild with symptoms lasting for several days to a week. Severe disease requiring hospitalization is uncommon and fatalities are rare. During the current outbreak in Brazil, Zika virus RNA has been identified in tissues from several infants with microcephaly and from fetal losses in ...
The Influence of Infectious Diseases on Dentistry
... be epidemiologically associated. Although a vaccine is not available, various treatments against this infection including chemotherapy, have shown to help in controlling the disease and reduce viral load. This virus is highly infective, therefore health care providers must take adequate precautions ...
... be epidemiologically associated. Although a vaccine is not available, various treatments against this infection including chemotherapy, have shown to help in controlling the disease and reduce viral load. This virus is highly infective, therefore health care providers must take adequate precautions ...
Proinflammatory Cytokine and Human
... previous report, we identified patients from a prospective, randomized study which lasted for over a year [5]. Of interest, in this prospective study, serum TNF-a levels rose in all patients irrespective of MAC disease, suggesting that TNF-a expression increases over time in HIV disease as has been ...
... previous report, we identified patients from a prospective, randomized study which lasted for over a year [5]. Of interest, in this prospective study, serum TNF-a levels rose in all patients irrespective of MAC disease, suggesting that TNF-a expression increases over time in HIV disease as has been ...
Original article Binding modes of two novel non
... isoleucine for valine (V106V/I) and L214F substitutions were found at P-11 (Figure 1B). At P‑16, V106V/I changed to solely V106I and additional partial substitutions, V108V/I and E138E/K, were identified. At P‑20, at a concentration of >20 µM, the substitution of V106I changed to V106L and the parti ...
... isoleucine for valine (V106V/I) and L214F substitutions were found at P-11 (Figure 1B). At P‑16, V106V/I changed to solely V106I and additional partial substitutions, V108V/I and E138E/K, were identified. At P‑20, at a concentration of >20 µM, the substitution of V106I changed to V106L and the parti ...
Section A: The Genetics of Viruses
... • The newly made DNA is inserted as a provirus into a chromosome in the animal cell. • The host’s RNA polymerase transcribes the viral DNA into more RNA molecules. • These can function both as mRNA for the synthesis of viral proteins and as genomes for new virus particles released from the cell. ...
... • The newly made DNA is inserted as a provirus into a chromosome in the animal cell. • The host’s RNA polymerase transcribes the viral DNA into more RNA molecules. • These can function both as mRNA for the synthesis of viral proteins and as genomes for new virus particles released from the cell. ...
18A-GeneticsOfViruses
... genome as a provirus. • The provirus remains latent within the nucleus until triggered by physical or emotional stress to leave the genome and initiate active viral production. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... genome as a provirus. • The provirus remains latent within the nucleus until triggered by physical or emotional stress to leave the genome and initiate active viral production. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Getah virus infection. Mair, T.S. and Timoney, P.J.
... 1985; Brown and Timoney 1998). If possible, paired samples taken during the acute and convalescent stages of the disease should be assayed. The neutralisation test is considered the most specific test at differentiating Getah virus infection from other antigenically related alphaviruses (Chanas et a ...
... 1985; Brown and Timoney 1998). If possible, paired samples taken during the acute and convalescent stages of the disease should be assayed. The neutralisation test is considered the most specific test at differentiating Getah virus infection from other antigenically related alphaviruses (Chanas et a ...
Nerve activates contraction
... genome as a provirus. • The provirus remains latent within the nucleus until triggered by physical or emotional stress to leave the genome and initiate active viral production. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... genome as a provirus. • The provirus remains latent within the nucleus until triggered by physical or emotional stress to leave the genome and initiate active viral production. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Full text PDF
... screen such risk groups as sex workers, and yield the most accurate result in defining all the stages of syphilis (13–15). Results from our study indicate that 12.9% of HIV/AIDS patients have been exposed to T. pallidum. Syphilis seroprevalence in newly diagnosed HIV infected individuals was reporte ...
... screen such risk groups as sex workers, and yield the most accurate result in defining all the stages of syphilis (13–15). Results from our study indicate that 12.9% of HIV/AIDS patients have been exposed to T. pallidum. Syphilis seroprevalence in newly diagnosed HIV infected individuals was reporte ...
Reflections on 30 Years of AIDS - International Society of Drug
... zoonotic infections that are essentially restricted to central Africa. HIV-2, a second type of HIV rarely found outside western Africa, originated in sooty mangabeys. Phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1 and SIVcpz (the simian immunodeficiency virus of chimpanzees closely related to HIV-1), combined with ...
... zoonotic infections that are essentially restricted to central Africa. HIV-2, a second type of HIV rarely found outside western Africa, originated in sooty mangabeys. Phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1 and SIVcpz (the simian immunodeficiency virus of chimpanzees closely related to HIV-1), combined with ...
3 Virus Replication Cycles
... and heightened awareness to recognize this new viral disease in patients. ...
... and heightened awareness to recognize this new viral disease in patients. ...
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
... Etiology HIV is a retrovirus of which two types have been identified: type 1 (HIV-1) and type 2 (HIV-2). These viruses are serologically, geographically, and epidemiologically distinct.(1) In Alberta, HIV-1 is the predominant virus, with HIV-2 being extremely uncommon (Provincial Laboratory of Publi ...
... Etiology HIV is a retrovirus of which two types have been identified: type 1 (HIV-1) and type 2 (HIV-2). These viruses are serologically, geographically, and epidemiologically distinct.(1) In Alberta, HIV-1 is the predominant virus, with HIV-2 being extremely uncommon (Provincial Laboratory of Publi ...
Ebola-Virus-Advice - Hardwick Primary School
... may wish to use the following key points from the Public Health England advice to reassure them: ...
... may wish to use the following key points from the Public Health England advice to reassure them: ...
Production and evaluation of FMDV stabilised capsids as potent, rapidly deployable vaccines, B. Charleston
... Proof of principle that an engineered mutation (his to cys) is consistent with capsid assembly. Similar approaches can be used for infectious copies. ...
... Proof of principle that an engineered mutation (his to cys) is consistent with capsid assembly. Similar approaches can be used for infectious copies. ...
latvia - unaids
... implementing in the mainstream of health policy development by the leadership of MoH since 1993, and is based on the national Public Health Strategy and national programmes to limit spread of HIV/AIDS in Latvia. First national program has been implemented in 1999; however current interventions in La ...
... implementing in the mainstream of health policy development by the leadership of MoH since 1993, and is based on the national Public Health Strategy and national programmes to limit spread of HIV/AIDS in Latvia. First national program has been implemented in 1999; however current interventions in La ...
MUMPS
... Parotid returns to normal size within a week. Patients with parotitis have difficulty with pronunciation and mastication. Citrus fruits and juices exacerbates the pain. Other salivary glands involved include submandibular adenitis and sublingual adenitis. ...
... Parotid returns to normal size within a week. Patients with parotitis have difficulty with pronunciation and mastication. Citrus fruits and juices exacerbates the pain. Other salivary glands involved include submandibular adenitis and sublingual adenitis. ...
2nd generation HIV surveillance
... • Information: informs program designs and serves as an early warning system • Evaluation: provides documentation of behavior change over time (in response to interventions) • Triangulation: contributes to biological and behavioral surveillance systems to provide additional data for HIV/AIDS estimat ...
... • Information: informs program designs and serves as an early warning system • Evaluation: provides documentation of behavior change over time (in response to interventions) • Triangulation: contributes to biological and behavioral surveillance systems to provide additional data for HIV/AIDS estimat ...
HIV

The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a lentivirus (a subgroup of retrovirus) that causes HIV infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). AIDS is a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype. Infection with HIV occurs by the transfer of blood, semen, vaginal fluid, pre-ejaculate, or breast milk. Within these bodily fluids, HIV is present as both free virus particles and virus within infected immune cells.HIV infects vital cells in the human immune system such as helper T cells (specifically CD4+ T cells), macrophages, and dendritic cells. HIV infection leads to low levels of CD4+ T cells through a number of mechanisms, including apoptosis of uninfected bystander cells, direct viral killing of infected cells, and killing of infected CD4+ T cells by CD8 cytotoxic lymphocytes that recognize infected cells. When CD4+ T cell numbers decline below a critical level, cell-mediated immunity is lost, and the body becomes progressively more susceptible to opportunistic infections.