What to know Chap 11
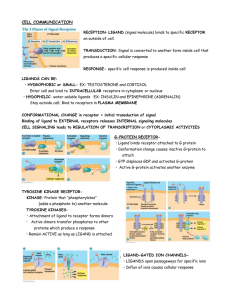
... on outside of cell. TRANSDUCTION- Signal is converted to another form inside cell that produces a specific cellular response RESPONSE- specific cell response is produced inside cell LIGANDS CAN BE: • HYDROPHOBIC or SMALL- EX: TESTOSTERONE and CORTISOL Enter cell and bind to INTRACELLULAR receptors i ...
... on outside of cell. TRANSDUCTION- Signal is converted to another form inside cell that produces a specific cellular response RESPONSE- specific cell response is produced inside cell LIGANDS CAN BE: • HYDROPHOBIC or SMALL- EX: TESTOSTERONE and CORTISOL Enter cell and bind to INTRACELLULAR receptors i ...
Cell Membrane: Cytoplasm: Microtubules: Microfilaments: Golgi
... Zebra Cake (with frosting on the outside, white filling on the inside) ...
... Zebra Cake (with frosting on the outside, white filling on the inside) ...
Document
... ___ 19.Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ___ 20.Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ___ 21.Chloroplasts ...
... ___ 19.Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ___ 20.Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ___ 21.Chloroplasts ...
Cell Cycle
... chromosomes, and moves the sister chromatids apart. • Mitosis consists of several steps that are essential for the creation of new daughter cells. ...
... chromosomes, and moves the sister chromatids apart. • Mitosis consists of several steps that are essential for the creation of new daughter cells. ...
CRCT Jeopardy - Thomas County Schools
... • To learn how things work • To teach school • To help living things survive • To clean up the environment ...
... • To learn how things work • To teach school • To help living things survive • To clean up the environment ...
notes
... Molecules are always on the move They bump into each other As the bump they begin to spread out What do you think the goal of diffusion is? ...
... Molecules are always on the move They bump into each other As the bump they begin to spread out What do you think the goal of diffusion is? ...
Mitosis/Cell Cycle PP
... 2 Major Phases of Cell Division 1.) Interphase G1 Stage – primary growth phase S Stage- synthesis; DNA replication G2 Stage – secondary growth phase 2.) Cell division (M-Phase) M – Mitosis C - Cytokinesis ...
... 2 Major Phases of Cell Division 1.) Interphase G1 Stage – primary growth phase S Stage- synthesis; DNA replication G2 Stage – secondary growth phase 2.) Cell division (M-Phase) M – Mitosis C - Cytokinesis ...
Chapter 12 – The Cell Cycle – Pages 215
... microtubules are attached and they have an in interaction with nonkinetochore microtubules from the opposite poles. These overlap during metaphase and the centromeres line up in metaphase called the metaphase plate. Asters –microtubules extend from the centrosomes in the shape of a star, hence the n ...
... microtubules are attached and they have an in interaction with nonkinetochore microtubules from the opposite poles. These overlap during metaphase and the centromeres line up in metaphase called the metaphase plate. Asters –microtubules extend from the centrosomes in the shape of a star, hence the n ...
Cell Unit Test Review Sheet 1. What are the three parts of the cell
... 13. A digestive system is used to breakdown food into smaller pieces producing energy, which cellular organelle has a similar function to the digestive system? ...
... 13. A digestive system is used to breakdown food into smaller pieces producing energy, which cellular organelle has a similar function to the digestive system? ...
Cell Division Jeopardy Cheat Sheet
... What is the cell cycle? It is the life of a cell from the time it is first formed from a dividing parent cell until its own division into two cells. What events occur in the G1 phase? The cell increases in size. The cell doubles the number of enzymes and cytoplasmic organelles. What occurs during th ...
... What is the cell cycle? It is the life of a cell from the time it is first formed from a dividing parent cell until its own division into two cells. What events occur in the G1 phase? The cell increases in size. The cell doubles the number of enzymes and cytoplasmic organelles. What occurs during th ...
Cells
... cytoplasm that store water, ions and waste materials. Cell Wall A rigid cell wall (made of cellulose) is present around a plant cell that helps it maintain its shape. Cell wall is absent. This allows animal cells to adopt different shapes. Chloroplasts Present. Chlorophyll is the pigment that traps ...
... cytoplasm that store water, ions and waste materials. Cell Wall A rigid cell wall (made of cellulose) is present around a plant cell that helps it maintain its shape. Cell wall is absent. This allows animal cells to adopt different shapes. Chloroplasts Present. Chlorophyll is the pigment that traps ...
Prokaryote cells
... _______________ cells do not contain these organelles and hence most of the processes are carried out in the ______________ of the cell. The genetic material of prokaryotes consists of a single _______ of DNA which floats free in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, genetic material is enclosed within the ...
... _______________ cells do not contain these organelles and hence most of the processes are carried out in the ______________ of the cell. The genetic material of prokaryotes consists of a single _______ of DNA which floats free in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, genetic material is enclosed within the ...
Dendrite, nucleus, cell body, Axon, nodes, Myelin Sheath, Axon
... At Resting Potential _____________________________ working to maintain cell membrane being polarized with a more _______________ charge inside the cell than outside the cell. There is a _______________ signal within neurotransmitters that move across the _______________ from one terminal axon to ano ...
... At Resting Potential _____________________________ working to maintain cell membrane being polarized with a more _______________ charge inside the cell than outside the cell. There is a _______________ signal within neurotransmitters that move across the _______________ from one terminal axon to ano ...
Cell Organelle Matching and Diagrams
... _________ 3. A large organelle that produces and stores DNA and direct cell activities ...
... _________ 3. A large organelle that produces and stores DNA and direct cell activities ...
How are Plant and Animal Cells Different Similar.indd
... Directions: Compare and contrast plant and animals cells by completing the Venn Diagram using the terms from the word bank. Then answer the questions. 1. What does the plant cell have that the animal cell doesn’t? ____________________________ _________________________________________________________ ...
... Directions: Compare and contrast plant and animals cells by completing the Venn Diagram using the terms from the word bank. Then answer the questions. 1. What does the plant cell have that the animal cell doesn’t? ____________________________ _________________________________________________________ ...
Cell Organelles
... Cell Organelles Organelle= “little organ” Found only inside eukaryotic cells All the stuff in between the organelles is cytosol Everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm ...
... Cell Organelles Organelle= “little organ” Found only inside eukaryotic cells All the stuff in between the organelles is cytosol Everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm ...
Cell Variety - eduBuzz.org
... 2. Name each of the tissues and the types of cells present. 3. Below each diagram describe the function of each cell type. 4. Describe how palisade mesophyll cells and root hair cells are suited to their ...
... 2. Name each of the tissues and the types of cells present. 3. Below each diagram describe the function of each cell type. 4. Describe how palisade mesophyll cells and root hair cells are suited to their ...
File - LFHS AP Biology
... b. genes are not replicated on chromosomes in prokaryotic cells. c. the duplicated chromosomes are attached to the nuclear membrane in prokaryotic cells and are separated from each other as the membrane grows. d. the chromosomes do not separate along a mitotic spindle in prokaryotic cells. e. the ch ...
... b. genes are not replicated on chromosomes in prokaryotic cells. c. the duplicated chromosomes are attached to the nuclear membrane in prokaryotic cells and are separated from each other as the membrane grows. d. the chromosomes do not separate along a mitotic spindle in prokaryotic cells. e. the ch ...
Project Title: Functional characterisation of centrosome proteins in
... Many stem cells divide asymmetrically thereby generating mother and daughter cells with distinct cell fates. The differential distribution of cell fate determinants and/or cellular components depends on the correct orientation of the mitotic spindle accordingly to the cell polarity axis. The centros ...
... Many stem cells divide asymmetrically thereby generating mother and daughter cells with distinct cell fates. The differential distribution of cell fate determinants and/or cellular components depends on the correct orientation of the mitotic spindle accordingly to the cell polarity axis. The centros ...
Mor-ganelles - JhaveriChemBioWiki
... Cell Wall The cell wall is only found in plant cells. It is on the outside of the cell, outside the cell membrane. It gives support and structure to plant cells. *Notice- plant cells are usually rectangular because of the cell wall ...
... Cell Wall The cell wall is only found in plant cells. It is on the outside of the cell, outside the cell membrane. It gives support and structure to plant cells. *Notice- plant cells are usually rectangular because of the cell wall ...
Primary Cell Walls
... • outside of the plasma membrane • deposited while cell grows • contain thin areas • primary pit fields • plasmodesmata connect cell-tocell • (cytoplasmic connections) ...
... • outside of the plasma membrane • deposited while cell grows • contain thin areas • primary pit fields • plasmodesmata connect cell-tocell • (cytoplasmic connections) ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.























