7th Grade Cells Review
... 23. Which sequence of terms is in the correct order from simplest to most complex? (1) cells, tissues, organs, organ systems (2) tissues, organisms, cells, organ systems (3) cells, tissues, organ systems, organs (4) organs, organisms, organ systems, cells ...
... 23. Which sequence of terms is in the correct order from simplest to most complex? (1) cells, tissues, organs, organ systems (2) tissues, organisms, cells, organ systems (3) cells, tissues, organ systems, organs (4) organs, organisms, organ systems, cells ...
Gundry Rachel Gundry Bio Lab 1615 April 3, 2012 Summary of
... survive so it basically eats itself from the inside out. It does this so that it can have its components re-used by other organelles or cells. This process is said to be controlled and a normal part of growth of an organism. There are studies out there that say that this type of cell suicide is used ...
... survive so it basically eats itself from the inside out. It does this so that it can have its components re-used by other organelles or cells. This process is said to be controlled and a normal part of growth of an organism. There are studies out there that say that this type of cell suicide is used ...
Types of Cells - Wando High School
... Made of the carbohydrate, cellulose This mesh of cellulose is porous and allows anything to pass through • Plants, fungi, and most bacteria (prokaryotes) have cell walls • Animals DO NOT ...
... Made of the carbohydrate, cellulose This mesh of cellulose is porous and allows anything to pass through • Plants, fungi, and most bacteria (prokaryotes) have cell walls • Animals DO NOT ...
The Way Things Actually Are!!!
... CLASSIFICATION OF LIFE Terms To Know • Prokaryote: – Simple cells that have no nucleus ...
... CLASSIFICATION OF LIFE Terms To Know • Prokaryote: – Simple cells that have no nucleus ...
AS90464 Version 2 Describe cell structure and function Level 2
... chromosomes o cell membrane o mitochondria o cytoplasm o chloroplast o nuclear o Centriole membrane o Vacuole o nucleus No Brain Too Small BIOLOGY ...
... chromosomes o cell membrane o mitochondria o cytoplasm o chloroplast o nuclear o Centriole membrane o Vacuole o nucleus No Brain Too Small BIOLOGY ...
Cell Reproduction - Green Local Schools
... Step 3: Anaphase I Tetrads are split and each homologue is moved toward opposite poles Independent assortment: the random separation of maternal and paternal chromosomes Resulting in genetic variety of offspring ...
... Step 3: Anaphase I Tetrads are split and each homologue is moved toward opposite poles Independent assortment: the random separation of maternal and paternal chromosomes Resulting in genetic variety of offspring ...
Chapter_7PP - biologywithbengele
... 2. Eukaryotes- cells that have organelles and nucleus Example- plants, animals, fungi, protists ...
... 2. Eukaryotes- cells that have organelles and nucleus Example- plants, animals, fungi, protists ...
7th Grade Review - pams
... form tissues, tissues form organs, and organs form systems. • Ex: nervous system; respiratory system; etc…… ...
... form tissues, tissues form organs, and organs form systems. • Ex: nervous system; respiratory system; etc…… ...
SAMPLE – 90 Minute Block Agenda
... between structures and functions in living cells. (a) Explain the role of cell organelles for both ...
... between structures and functions in living cells. (a) Explain the role of cell organelles for both ...
ws flip cell parts - Renton School District
... Draw and label a chloroplast inside your cell. Color it green. Cell movement: 24. Some cells move with tiny oars called: ____________ draw 10 on this cell: 25. Others move by whipping one or two protein filaments called: _____________. Draw one on this cell: 26. And others push out a pseudopod and ...
... Draw and label a chloroplast inside your cell. Color it green. Cell movement: 24. Some cells move with tiny oars called: ____________ draw 10 on this cell: 25. Others move by whipping one or two protein filaments called: _____________. Draw one on this cell: 26. And others push out a pseudopod and ...
essential knowledge Cells and the cell theory
... • All organisms are made up of cells. • New cells are produced from existing cells. • The cell is the smallest organisational unit of a living thing. ...
... • All organisms are made up of cells. • New cells are produced from existing cells. • The cell is the smallest organisational unit of a living thing. ...
Structure
... • He described the cells as tiny boxes or a honeycomb • He thought that cells only existed in plants and fungi ...
... • He described the cells as tiny boxes or a honeycomb • He thought that cells only existed in plants and fungi ...
Lesson 8-9: Building a Cell City
... The teacher will post the question, What services in Madison do we have that resemble the structures/functions in al animal/plant cell? Template Example Teacher facilitation: The teacher will monitor as the students work in pairs using references such as http://www.cellsalive.com, http://www.animalc ...
... The teacher will post the question, What services in Madison do we have that resemble the structures/functions in al animal/plant cell? Template Example Teacher facilitation: The teacher will monitor as the students work in pairs using references such as http://www.cellsalive.com, http://www.animalc ...
The Cell - SNC2PSylvia2011
... Most cells can be seen with the naked eye All living things are made of cells. Plant cells and animal cells are the same. Humans are made up of trillions of cells. New cells come from cells that were already ...
... Most cells can be seen with the naked eye All living things are made of cells. Plant cells and animal cells are the same. Humans are made up of trillions of cells. New cells come from cells that were already ...
Cells in Their Environment
... 3. What type of membrane do cells have? Explain why. 4. Hypothesize why the pores in the cell membrane are different sizes. 5. Do you think cells could survive without diffusion? Explain why or why not. 6. Speculate on what would happen if cell membranes were permeable instead of selectively permeab ...
... 3. What type of membrane do cells have? Explain why. 4. Hypothesize why the pores in the cell membrane are different sizes. 5. Do you think cells could survive without diffusion? Explain why or why not. 6. Speculate on what would happen if cell membranes were permeable instead of selectively permeab ...
Chapter 4 – Part B: Prokaryotic (bacterial) cells
... Chapter 4 – Part B: Prokaryotic (bacterial) cells ...
... Chapter 4 – Part B: Prokaryotic (bacterial) cells ...
1.7 Cells in Their Environment
... 3. What type of membrane do cells have? Explain why. 4. Hypothesize why the pores in the cell membrane are different sizes. 5. Do you think cells could survive without diffusion? Explain why or why not. 6. Speculate on what would happen if cell membranes were permeable instead of selectively permeab ...
... 3. What type of membrane do cells have? Explain why. 4. Hypothesize why the pores in the cell membrane are different sizes. 5. Do you think cells could survive without diffusion? Explain why or why not. 6. Speculate on what would happen if cell membranes were permeable instead of selectively permeab ...
Worksheet
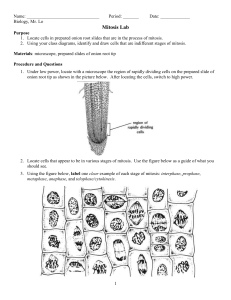
... 1. Locate cells in prepared onion root slides that are in the process of mitosis. 2. Using your class diagrams, identify and draw cells that are indifferent stages of mitosis. Materials: microscope, prepared slides of onion root tip Procedure and Questions 1. Under low power, locate with a microscop ...
... 1. Locate cells in prepared onion root slides that are in the process of mitosis. 2. Using your class diagrams, identify and draw cells that are indifferent stages of mitosis. Materials: microscope, prepared slides of onion root tip Procedure and Questions 1. Under low power, locate with a microscop ...
Mechanisms of Animal Growth and Development
... Prerequisites: Courses of: Cell biology, and Histology and Embryology Course Objective: Course in Мechanisms of growth and development has goal to offer to students detailed insights in biology of development and in the last advance in knowalage and investigations in this area. Taken in account priv ...
... Prerequisites: Courses of: Cell biology, and Histology and Embryology Course Objective: Course in Мechanisms of growth and development has goal to offer to students detailed insights in biology of development and in the last advance in knowalage and investigations in this area. Taken in account priv ...
Organizing Organelles
... 4. _____________ are manufactured in the ______________ , a dark, dense region within the nucleus. 5. What important molecule does the nucleus contain? 6. When a cell is about to divide, DNA coils up into _______________________________. 7. Is the following sentence true or false? The number of chro ...
... 4. _____________ are manufactured in the ______________ , a dark, dense region within the nucleus. 5. What important molecule does the nucleus contain? 6. When a cell is about to divide, DNA coils up into _______________________________. 7. Is the following sentence true or false? The number of chro ...
2/16/15 Opener 1. PROTIST- CAUSING DISEASES B) African
... Amoebic Dysentery is a disease that is caused by which type of Protist? Protozoan, Algae, or Fungus-like? Learning Objective Students will review the different features of microbes and their role in causing disease. ...
... Amoebic Dysentery is a disease that is caused by which type of Protist? Protozoan, Algae, or Fungus-like? Learning Objective Students will review the different features of microbes and their role in causing disease. ...
Name des Moduls: Current aspects and methods of plant cell
... Modulart (Pflicht- oder Wahlpflichtmodul): Wahlpflichtmodul The lecture will focus on current research and methods in the cell biological analysis of plant growth and development. The topics discussed will be cellular and sub-cellular functions of plant hormone biosynthesis, transport and response p ...
... Modulart (Pflicht- oder Wahlpflichtmodul): Wahlpflichtmodul The lecture will focus on current research and methods in the cell biological analysis of plant growth and development. The topics discussed will be cellular and sub-cellular functions of plant hormone biosynthesis, transport and response p ...
Cell Structure
... • Think of a drawing for your title page. Will you use an animal cell drawing with labels…what kind of drawing do you want to have for your catalog. (1 point) • Label the drawing (1 point) • Think of a name for your catalog of organelles (What analogy will you use for this catalog) (1 point) • Put y ...
... • Think of a drawing for your title page. Will you use an animal cell drawing with labels…what kind of drawing do you want to have for your catalog. (1 point) • Label the drawing (1 point) • Think of a name for your catalog of organelles (What analogy will you use for this catalog) (1 point) • Put y ...
How do cells communicate?
... • Phosphorylation - converts from inactive form to active form. • hundreds of protein kinases, each specific – 1% of genes code for protein kinases ...
... • Phosphorylation - converts from inactive form to active form. • hundreds of protein kinases, each specific – 1% of genes code for protein kinases ...
target cell. - mleonessciencepage
... recognizes and responds only to the few signals that are important for its function. This response to some signals, but not to others, is made possible by receptor proteins, such as the ones in the cell’s membrane. ...
... recognizes and responds only to the few signals that are important for its function. This response to some signals, but not to others, is made possible by receptor proteins, such as the ones in the cell’s membrane. ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.