Unit #3 - The Cell
... nucleus but inside plasma membrane • Cytosol: Fluid portion • Cytoskeleton: Supports the cell – Microtubules – Microfilaments – Intermediate filaments • Cytoplasmic inclusions ...
... nucleus but inside plasma membrane • Cytosol: Fluid portion • Cytoskeleton: Supports the cell – Microtubules – Microfilaments – Intermediate filaments • Cytoplasmic inclusions ...
1827: ROBERT BROWN DISCOVERED THAT POLLEN
... 3. Recognition Proteins: Recognizes other cells. Usually have a short polysacharide chain attached to it, extending out of the cell. 4. Receptor Proteins: Chemicals called hormones land here to trigger the cell to do something. 5. Electron Transfer proteins: Pass electrons to other proteins ( kind o ...
... 3. Recognition Proteins: Recognizes other cells. Usually have a short polysacharide chain attached to it, extending out of the cell. 4. Receptor Proteins: Chemicals called hormones land here to trigger the cell to do something. 5. Electron Transfer proteins: Pass electrons to other proteins ( kind o ...
Sexual reproduction in spirogyra is describes as
... can withstand adverse conditions. D. Stems have thicker epidermis which prevents water loss. ...
... can withstand adverse conditions. D. Stems have thicker epidermis which prevents water loss. ...
Cells Every organism is made up of a cell or many cells Humans have
... • Tags cells for destruction if their DNA is damaged beyond repair • Without this protein, damaged cells could proliferate leading to cancer ...
... • Tags cells for destruction if their DNA is damaged beyond repair • Without this protein, damaged cells could proliferate leading to cancer ...
Cells Test Review Packet Key
... functions necessary to keep the cell alive. Cells grow by increasing slightly in size (size is limited by S-V ratio). Multicellular organisms are made of many cells. These cells have specialized functions (nerve, muscle, etc.) so they each do one type of job to benefit the organism. These organisms ...
... functions necessary to keep the cell alive. Cells grow by increasing slightly in size (size is limited by S-V ratio). Multicellular organisms are made of many cells. These cells have specialized functions (nerve, muscle, etc.) so they each do one type of job to benefit the organism. These organisms ...
The Cell
... – Unorganized cells – Found only as unicellular organisms – Ex: bacteria – Have caused some of the worst human diseases in the history of the world ...
... – Unorganized cells – Found only as unicellular organisms – Ex: bacteria – Have caused some of the worst human diseases in the history of the world ...
cell transport review sheet
... Name______________________________ Date______________ Biology 512 ...
... Name______________________________ Date______________ Biology 512 ...
File
... A cell in prophase of mitosis is successfully fused to a cell in G2 of interphase, and then after fusion both nuclei are seen to have fully condensed chromosomes and to proceed on through mitosis. a) Fusion of these cells is stressful, and stress induces cells to enter mitosis. b) A cytosolic mitoti ...
... A cell in prophase of mitosis is successfully fused to a cell in G2 of interphase, and then after fusion both nuclei are seen to have fully condensed chromosomes and to proceed on through mitosis. a) Fusion of these cells is stressful, and stress induces cells to enter mitosis. b) A cytosolic mitoti ...
PPT
... e.g. tadpole tail of frog. Needed in one sex but not another e.g. Mullerian duct important for female is eliminated in males by apoptosis. Produced in excess, e.g. extra neurons are removed by apoptosis during neurogenesis. Serve in immune system as a defense mechanism to get rid of harmful or damag ...
... e.g. tadpole tail of frog. Needed in one sex but not another e.g. Mullerian duct important for female is eliminated in males by apoptosis. Produced in excess, e.g. extra neurons are removed by apoptosis during neurogenesis. Serve in immune system as a defense mechanism to get rid of harmful or damag ...
Cells
... The cells of plants and animals were the same. B. All plant parts were made of cells. C. The cells of plants were different from those of animals. D. All animal tissues were made of cells A. ...
... The cells of plants and animals were the same. B. All plant parts were made of cells. C. The cells of plants were different from those of animals. D. All animal tissues were made of cells A. ...
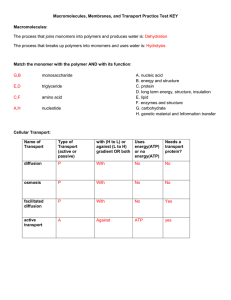
Macromolecules, Membranes, and Transport Practice Test KEY
... The process that joins monomers into polymers and produces water is: Dehydration The process that breaks up polymers into monomers and uses water is: Hydrolysis ...
... The process that joins monomers into polymers and produces water is: Dehydration The process that breaks up polymers into monomers and uses water is: Hydrolysis ...
Cell Growth and Division unit - mr-roes
... organisms grow and develop. A hallmark of higherorder life is having a multi-cellular body, but since reproduction gives only a single fertilized cell, the cell must divide over and over again in order to make an organism. Mitosis is the process across all of the eukaryotic kingdoms by which this gr ...
... organisms grow and develop. A hallmark of higherorder life is having a multi-cellular body, but since reproduction gives only a single fertilized cell, the cell must divide over and over again in order to make an organism. Mitosis is the process across all of the eukaryotic kingdoms by which this gr ...
Chapter 5 - Southern Matters
... segregation of traits and independent assortment 16 , Mendel’s two principles. Although the meiotic mechanism itself is generally similar among sexual organisms, the timing of meiosis and karyogamy varies dramatically 17 . BOT 3015L does not address the mechanism of meiosis (see BSC 2010/2011) in de ...
... segregation of traits and independent assortment 16 , Mendel’s two principles. Although the meiotic mechanism itself is generally similar among sexual organisms, the timing of meiosis and karyogamy varies dramatically 17 . BOT 3015L does not address the mechanism of meiosis (see BSC 2010/2011) in de ...
Weather Assessment Review
... The cells of plants and animals were the same. B. All plant parts were made of cells. C. The cells of plants were different from those of animals. D. All animal tissues were made of cells A. ...
... The cells of plants and animals were the same. B. All plant parts were made of cells. C. The cells of plants were different from those of animals. D. All animal tissues were made of cells A. ...
Cell Transport - Teacher Pages
... Osmosis – diffusion of water Facilitated diffusion – assisted by transport proteins; from high to low concentration; no energy required ...
... Osmosis – diffusion of water Facilitated diffusion – assisted by transport proteins; from high to low concentration; no energy required ...
Cell Penetrating Peptides
... Introduction Cell Penetrating Principles Mechanisms Specific Pathways Specific Applications Conclusion Questions References ...
... Introduction Cell Penetrating Principles Mechanisms Specific Pathways Specific Applications Conclusion Questions References ...
Textbook for Nursing Assistants – “A Humanistic
... most other organelles. Bacteria and another group of organisms called the archaea are prokaryotic cells. Prokaryotic organisms appear earliest in Earth’s fossil record. In contrast, a eukaryotic cell has a nucleus and other internal organelles bounded by membranes. Protists, fungi, plants, and anima ...
... most other organelles. Bacteria and another group of organisms called the archaea are prokaryotic cells. Prokaryotic organisms appear earliest in Earth’s fossil record. In contrast, a eukaryotic cell has a nucleus and other internal organelles bounded by membranes. Protists, fungi, plants, and anima ...
coloring packet cells and organelles
... semi-permeable (selectively permeable), allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. It is composed of a double layer of phospholipids and embedded proteins. Color and label the cell membrane tan (light brown) on both the plant & animal cells. Plant cells have an additional la ...
... semi-permeable (selectively permeable), allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. It is composed of a double layer of phospholipids and embedded proteins. Color and label the cell membrane tan (light brown) on both the plant & animal cells. Plant cells have an additional la ...
CELL ADAPTATIONS CELL INJURY CELL DEATH DR.SAMINA
... • Altered/changed steady state in structure and function of cell. • WHY: In response to physical/ pathological stimuli. Increased or decreased stimulation or any irritation. ...
... • Altered/changed steady state in structure and function of cell. • WHY: In response to physical/ pathological stimuli. Increased or decreased stimulation or any irritation. ...
Cell Membranes - WordPress.com
... specific molecule. In biology, a general term for any molecule that binds is called a _____________________. Receptor-mediated endocytosis allows a cell to take in ___________ substances than it normally would, even if the substance is in ________ concentrations outside of the cell. For example, ___ ...
... specific molecule. In biology, a general term for any molecule that binds is called a _____________________. Receptor-mediated endocytosis allows a cell to take in ___________ substances than it normally would, even if the substance is in ________ concentrations outside of the cell. For example, ___ ...
5E Template
... organisms are single cells; other organisms, including humans, are multicellular. Cells carry on the many functions needed to sustain life. They grow and divide, thereby producing more cells. This requires that they take in nutrients, which they use to provide energy for the work that cells do and t ...
... organisms are single cells; other organisms, including humans, are multicellular. Cells carry on the many functions needed to sustain life. They grow and divide, thereby producing more cells. This requires that they take in nutrients, which they use to provide energy for the work that cells do and t ...
KONTRAK KULIAH & STRUKTUR DAN FUNGSI SEL
... • The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by the nuclear envelope • The nucleus is the cellular control center – It contains the DNA that directs the cell’s activities ...
... • The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by the nuclear envelope • The nucleus is the cellular control center – It contains the DNA that directs the cell’s activities ...
Stem Cells - California Science Teacher
... The Dilemma • “The status of the human embryo and human embryonic stem cell research is a controversial issue as, with the present state of technology, the creation of a human embryonic stem cell line requires the destruction of a human embryo.” ...
... The Dilemma • “The status of the human embryo and human embryonic stem cell research is a controversial issue as, with the present state of technology, the creation of a human embryonic stem cell line requires the destruction of a human embryo.” ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.