Honors Biology - LangdonBiology.org
... the ribosome relate to the nucleolus? Ribosomes are large molecules that build proteins from the instructions encoded in mRNA. They are made of proteins and rRNA. The rRNA is a ribozyme, which catalyzes the building of the protein. Ribosomes are either found in the cytosol or attached to the ER (the ...
... the ribosome relate to the nucleolus? Ribosomes are large molecules that build proteins from the instructions encoded in mRNA. They are made of proteins and rRNA. The rRNA is a ribozyme, which catalyzes the building of the protein. Ribosomes are either found in the cytosol or attached to the ER (the ...
N Level Science Biology Examination Notes
... 3. The important structures and organelles covered in the current syllabus are described below in alphabetical order: Cell Wall - Found only in plants, the cell wall is made of cellulose (a polysaccharide). - It is found just outside the cell membrane and is permeable to most substances. - It forms ...
... 3. The important structures and organelles covered in the current syllabus are described below in alphabetical order: Cell Wall - Found only in plants, the cell wall is made of cellulose (a polysaccharide). - It is found just outside the cell membrane and is permeable to most substances. - It forms ...
PDF Steady State of Living Cells and Donnan Equilibrium
... The previous PDF handout points out that since the Nernst potential, Vi Nernst ≠ ΔV is ...
... The previous PDF handout points out that since the Nernst potential, Vi Nernst ≠ ΔV is ...
Unit 3 - Genetics - Notes - Part 1.pps
... egg and deliver its DNA, so it is streamlined and small. 3. If, during metaphase I, all 23 maternal chromosomes lined up on one side of the cell, would genetic diversity increase? Explain. Genetic diversity would not increase because the maternal and paternal chromosomes would not become arranged ...
... egg and deliver its DNA, so it is streamlined and small. 3. If, during metaphase I, all 23 maternal chromosomes lined up on one side of the cell, would genetic diversity increase? Explain. Genetic diversity would not increase because the maternal and paternal chromosomes would not become arranged ...
File
... pathways and inhibit T cell proliferation. MDSC numbers correlate with viral titers and are inversely proportional to CD4 T cell numbers, suggesting that G-MDSCs may play a role in the pathogenesis of the disease. We recently reported that tumor-associated MDSCs activate fatty acid oxidation (FAO) a ...
... pathways and inhibit T cell proliferation. MDSC numbers correlate with viral titers and are inversely proportional to CD4 T cell numbers, suggesting that G-MDSCs may play a role in the pathogenesis of the disease. We recently reported that tumor-associated MDSCs activate fatty acid oxidation (FAO) a ...
Chapter 7 III. Cell Boundaries
... 2 examples of endocytosis are – ___________________-extensions of cytoplasm surround a particle and package it in a food vacuole,then the cell engulfs it ---This is how amoebas eat-----is a form of active transport • _______________-Cells use this to take up liquids in the environment—tiny pockets ...
... 2 examples of endocytosis are – ___________________-extensions of cytoplasm surround a particle and package it in a food vacuole,then the cell engulfs it ---This is how amoebas eat-----is a form of active transport • _______________-Cells use this to take up liquids in the environment—tiny pockets ...
5 Eukaryotic Microbial Structure and Function
... consists of the plasma membrane and all coverings external to it plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer – major membrane lipids include phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, and cholesterol, all of which contribute to strength of membrane unlike the peptidoglycan in the cell wall of Bacteria and Archaea, ma ...
... consists of the plasma membrane and all coverings external to it plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer – major membrane lipids include phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, and cholesterol, all of which contribute to strength of membrane unlike the peptidoglycan in the cell wall of Bacteria and Archaea, ma ...
Fermoplus Omega 3 lett inglese.FH11
... It is the nutriment preventing the cell ageing and its functional components are sterols, amino acids, vitamins deriving from yeast cell hulls and Omega-3 carried by ichthyo-proteins. The last researches highlighted that the polyunsaturated fatty acids are important for the maintenance of the entire ...
... It is the nutriment preventing the cell ageing and its functional components are sterols, amino acids, vitamins deriving from yeast cell hulls and Omega-3 carried by ichthyo-proteins. The last researches highlighted that the polyunsaturated fatty acids are important for the maintenance of the entire ...
Cell boundaries
... This is a fast and specific form of diffusion, but it is still diffusion – therefore it must follow the rules of diffusion ([high]>[low]) and doesn’t require energy ...
... This is a fast and specific form of diffusion, but it is still diffusion – therefore it must follow the rules of diffusion ([high]>[low]) and doesn’t require energy ...
AP Bio Review - Cells, CR, and Photo Jeopardy
... themselves, require energy input (have a positive free-energy change) can occur because the reactions may be coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP take place very slowly take place when the cells are at unusually high temperatures ...
... themselves, require energy input (have a positive free-energy change) can occur because the reactions may be coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP take place very slowly take place when the cells are at unusually high temperatures ...
name date ______ period - Ms. Shunkwiler`s Wiki!
... 1. Which of the following are TRUE of a cell membranes (choose more than one)? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly mo ...
... 1. Which of the following are TRUE of a cell membranes (choose more than one)? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly mo ...
Cytotoxicity tests MEDETOX EN
... The dye exclusion test is used to determine the number of viable cells present in a cell suspension. It is based on the principle that live cells possess intact cell membranes that exclude certain dyes, such as trypan blue, Eosin, or propidium, whereas dead cells do not. In this test, a cell suspens ...
... The dye exclusion test is used to determine the number of viable cells present in a cell suspension. It is based on the principle that live cells possess intact cell membranes that exclude certain dyes, such as trypan blue, Eosin, or propidium, whereas dead cells do not. In this test, a cell suspens ...
1 Chapter 8: Cell Growth and Division
... 1. G1 Phase G=GAP Normal cellular activity and cell growth 2. S Phase S=Synthesis In order for an identical clone to be made, DNA (Chromosomes) must be Cloned/Copied/Synthesized 3. G2 Phase Gap 2 Phase Cell conserves energy for the impending division 4. M Phase Mitosis (Cell Splitting) ...
... 1. G1 Phase G=GAP Normal cellular activity and cell growth 2. S Phase S=Synthesis In order for an identical clone to be made, DNA (Chromosomes) must be Cloned/Copied/Synthesized 3. G2 Phase Gap 2 Phase Cell conserves energy for the impending division 4. M Phase Mitosis (Cell Splitting) ...
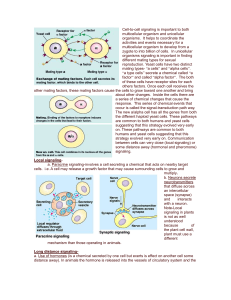
Long distance signaling
... also found in the plasma membrane. They are activated when the G-proteinlinked receptors causes GTP to replace GDP on the G-protein. Once this happens the activated Gprotein now moves laterally to interact with a given enzyme also located in the plasma membrane which causes a certain biochemical pat ...
... also found in the plasma membrane. They are activated when the G-proteinlinked receptors causes GTP to replace GDP on the G-protein. Once this happens the activated Gprotein now moves laterally to interact with a given enzyme also located in the plasma membrane which causes a certain biochemical pat ...
Unit 2A Neurophysiology
... Glial Cells: support neurons a. _________________ are cells that produce the myelin sheath of the (CNS, PNS) and is known as “white matter” b. _________________ produce the myelin sheath of the (CNS, PNS) c. _________________ = insulation to conduct action potentials! ...
... Glial Cells: support neurons a. _________________ are cells that produce the myelin sheath of the (CNS, PNS) and is known as “white matter” b. _________________ produce the myelin sheath of the (CNS, PNS) c. _________________ = insulation to conduct action potentials! ...
Characterizing Individual Tissue-Infiltrating T Cell
... lymphocytes are inefficient given that the pathogenic population will comprise only a small fraction of the analyzed cells. In addition, we have observed that in patients with autoimmunity and healthy controls there are often many peripherally expanded T cell clones, the significance of which is unk ...
... lymphocytes are inefficient given that the pathogenic population will comprise only a small fraction of the analyzed cells. In addition, we have observed that in patients with autoimmunity and healthy controls there are often many peripherally expanded T cell clones, the significance of which is unk ...
Cell Structure - cloudfront.net
... The pressure of the central vacuole in these cells makes it possible for plants to support heavy structures such as leaves and flowers. Vacuoles are also found in some unicellular organisms and in some animals. Every factory needs a place to store things, and cells contain places for storage as well ...
... The pressure of the central vacuole in these cells makes it possible for plants to support heavy structures such as leaves and flowers. Vacuoles are also found in some unicellular organisms and in some animals. Every factory needs a place to store things, and cells contain places for storage as well ...
... Completion: Write the word or words that best complete each statement below. The three major purposes for cell division are: 1 , 2 , and 3 . If you take one 4 from each parent then put them together, you’ll create a 5 which determines one trait. If you stack hundreds of these pairs together, you’ll ...
Is there a universal tree of life?
... bacteria, of course—were entombed in rocks more than 3 billion years ago. On any possible, reasonable or fair criterion, bacteria are—and always have been— the dominant forms of life on Earth. Our failure to grasp this most evident of biological facts arises in part from the blindness of our arrogan ...
... bacteria, of course—were entombed in rocks more than 3 billion years ago. On any possible, reasonable or fair criterion, bacteria are—and always have been— the dominant forms of life on Earth. Our failure to grasp this most evident of biological facts arises in part from the blindness of our arrogan ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.