Eukaryotic Cells part II - Westerville City Schools
... mitochondria break down sugar from our food to make a special type of cell energy called ATP (that’s short for Adenosintriphosphate). Mitochondria are the entire reason we inhale oxygen. If the mitochondria in our cells didn’t need oxygen, we wouldn’t need to breath. The organelles in the cell use t ...
... mitochondria break down sugar from our food to make a special type of cell energy called ATP (that’s short for Adenosintriphosphate). Mitochondria are the entire reason we inhale oxygen. If the mitochondria in our cells didn’t need oxygen, we wouldn’t need to breath. The organelles in the cell use t ...
Name Period ___ Lab: Onion Root Mitosis Purpose: To gain a better
... 2. Cells in the root divide many times as the root grows longer and thicker. With each cell division, the chromosomes are divided between two daughter cells, yet the number of chromosomes in each cell does not change. What process ensures that the normal number of chromosomes is restored after each ...
... 2. Cells in the root divide many times as the root grows longer and thicker. With each cell division, the chromosomes are divided between two daughter cells, yet the number of chromosomes in each cell does not change. What process ensures that the normal number of chromosomes is restored after each ...
Cytology: the Study of the Structure and Function of Cells
... We’ll focus on this later in the unit but why do all cells have a membrane? In our bodies cell membranes have 4 functions: 1. Act as a barrier to pathogens, toxins, etc. 2. To mark the cell as self 3. To act as a receptor for messages from other cells in the body 4. To allow things to be transported ...
... We’ll focus on this later in the unit but why do all cells have a membrane? In our bodies cell membranes have 4 functions: 1. Act as a barrier to pathogens, toxins, etc. 2. To mark the cell as self 3. To act as a receptor for messages from other cells in the body 4. To allow things to be transported ...
mitosis. - Cloudfront.net
... S- (Synthesis) this is when DNA is copied. The chromosome goes from one chromatid to 2 chromatids. G2- Is the period between S and mitosis. The cell prepares for Mitosis M- is Mitosis ...
... S- (Synthesis) this is when DNA is copied. The chromosome goes from one chromatid to 2 chromatids. G2- Is the period between S and mitosis. The cell prepares for Mitosis M- is Mitosis ...
Cell Cycle - Studentportalen
... 11. One of the most important cell cycle checkpoints senses DNA damage in the cells. This checkpoint consists of a rapid and a slow response. (a) Describe how the fast, p53-independent response to the single stranded DNA damage operates through the ATR/Chk1 pathway (b) Why is there normally no activ ...
... 11. One of the most important cell cycle checkpoints senses DNA damage in the cells. This checkpoint consists of a rapid and a slow response. (a) Describe how the fast, p53-independent response to the single stranded DNA damage operates through the ATR/Chk1 pathway (b) Why is there normally no activ ...
Botany
... All living things are dependent directly or indirectly on the energy produced by photosynthesis, and the byproduct of this process, oxygen Oxygen is essential to animals Plants also reduce the amount of carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere, reduce soil erosion, and influence water levels a ...
... All living things are dependent directly or indirectly on the energy produced by photosynthesis, and the byproduct of this process, oxygen Oxygen is essential to animals Plants also reduce the amount of carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere, reduce soil erosion, and influence water levels a ...
Mitosis Lab New Version
... 1. Explain how mitosis leads to 2 daughter cells that are diploid and genetically identical to the parent cell. 2. What activities occur during interphase? 3. How does mitosis differ in plant and animal cells? 4. What is the role of the centrosome in mitosis? 5. What additional structure do animal c ...
... 1. Explain how mitosis leads to 2 daughter cells that are diploid and genetically identical to the parent cell. 2. What activities occur during interphase? 3. How does mitosis differ in plant and animal cells? 4. What is the role of the centrosome in mitosis? 5. What additional structure do animal c ...
Cell Cycle - Pearland ISD
... Chromosome – contains genetic information (DNA) passed from one generation to the next Spindle – microtubule that helps separate chromosomes ...
... Chromosome – contains genetic information (DNA) passed from one generation to the next Spindle – microtubule that helps separate chromosomes ...
Cell Physiology BDS lecture
... Won’t the potassium ions want to move down their concentration gradient towards equilibrium? Yes, they will want to, but the cell membranes are semi-permeable and will prevent the potassium (and other particles) from crossing. ...
... Won’t the potassium ions want to move down their concentration gradient towards equilibrium? Yes, they will want to, but the cell membranes are semi-permeable and will prevent the potassium (and other particles) from crossing. ...
The Cell - myndrs.com
... Every cell has a cellular membrane (including both animal and plant cells). It is a thin flexible covering surrounding all cells. Made up of primarily proteins and fats ...
... Every cell has a cellular membrane (including both animal and plant cells). It is a thin flexible covering surrounding all cells. Made up of primarily proteins and fats ...
Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis
... ________________ Pairing up and crossing over between homologous chromosome pairs occurs at prophase ________________Daughter cells are genetically different from each other ________________ DNA replicates before cell division ________________ One cell divides to form 2 daughter cells ______________ ...
... ________________ Pairing up and crossing over between homologous chromosome pairs occurs at prophase ________________Daughter cells are genetically different from each other ________________ DNA replicates before cell division ________________ One cell divides to form 2 daughter cells ______________ ...
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells (and viruses)
... Many chemical reactions can take place at the same time ...
... Many chemical reactions can take place at the same time ...
Skills Worksheet
... 1. What is the cytoskeleton, and what is its function? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. What are three types of cytoskeleton fibers, and what does each do? ______________________________________________ ...
... 1. What is the cytoskeleton, and what is its function? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. What are three types of cytoskeleton fibers, and what does each do? ______________________________________________ ...
Answer Key: What do I need to know for the test
... 4. Diffusion is the movement of materials (ions, molecules, gases) from an area of high conc. to low conc. Some examples of diffusion are: burning toast, perfume sprayed, food coloring added to water, baggie experiment (starch and iodine) ...
... 4. Diffusion is the movement of materials (ions, molecules, gases) from an area of high conc. to low conc. Some examples of diffusion are: burning toast, perfume sprayed, food coloring added to water, baggie experiment (starch and iodine) ...
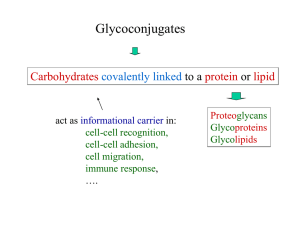
Bacterial Cell Walls Contain Peptidoglycans
... • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features of glycans act as destination l ...
... • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features of glycans act as destination l ...
Ch 10 CP Cell Cycle
... • The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough nutrients and wastes across the cell membrane. – The rate at which food, oxygen, water, and wastes are moved in and out of the cell is dependent on the surface area of the c ...
... • The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough nutrients and wastes across the cell membrane. – The rate at which food, oxygen, water, and wastes are moved in and out of the cell is dependent on the surface area of the c ...
cells - District 196
... Can also see bacteria cells. Light passes through the specimen and lenses, bends the light to magnify the image. Magnification: ratio of an object’s image to its real size (max. about 1,000x) Resolution: measure of the clarity of the image (max. about 200nm – size of bacteria) ...
... Can also see bacteria cells. Light passes through the specimen and lenses, bends the light to magnify the image. Magnification: ratio of an object’s image to its real size (max. about 1,000x) Resolution: measure of the clarity of the image (max. about 200nm – size of bacteria) ...
Biology EOC Class
... Tissue – group of cells that perform a task Organ- many groups of tissue working together Organ System – a group of organs working ...
... Tissue – group of cells that perform a task Organ- many groups of tissue working together Organ System – a group of organs working ...
Quiz 2 Review Sheet
... 26. THIS IS A QUESTION: You are inside a liver cell taking a cytoplasmic swim. On the outside, you observe insulin molecules bind insulin membrane receptors. This causes the genes for the glucose transporter, an integral membrane protein that allows glucose to enter cell, to be turned on so that the ...
... 26. THIS IS A QUESTION: You are inside a liver cell taking a cytoplasmic swim. On the outside, you observe insulin molecules bind insulin membrane receptors. This causes the genes for the glucose transporter, an integral membrane protein that allows glucose to enter cell, to be turned on so that the ...
Topic 2: Cells - Cerebralenhancementzone
... It has taken several hundred years of research to formulate modern cell theory. Many scientists have contributed to developing the three main principles of this theory. These are: All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest units of life. All cells come from pre-exi ...
... It has taken several hundred years of research to formulate modern cell theory. Many scientists have contributed to developing the three main principles of this theory. These are: All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest units of life. All cells come from pre-exi ...
Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, and Volvox
... All are protists: eukaryotes that cannot be classified as animals, plants, or fungi. ...
... All are protists: eukaryotes that cannot be classified as animals, plants, or fungi. ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... Actin Filaments • Actin interacts with motor molecules such as myosin. • In the presence of ATP, myosin pulls actin along • Example: muscle cells ...
... Actin Filaments • Actin interacts with motor molecules such as myosin. • In the presence of ATP, myosin pulls actin along • Example: muscle cells ...
File
... Be able to state the purpose of each checkpoint during the cell cycle. Be able to list the events that occur during the cell cycle in order and be able to differentiate what happens during mitosis, meiosis, interphase and cytokinesis. Be able to state the molecule that controls the cell cycle. Be ab ...
... Be able to state the purpose of each checkpoint during the cell cycle. Be able to list the events that occur during the cell cycle in order and be able to differentiate what happens during mitosis, meiosis, interphase and cytokinesis. Be able to state the molecule that controls the cell cycle. Be ab ...
Learning Guide: Origins of Life
... o Create the two column table with the headings (material and method). Consider the following materials that must cross the membrane. For each tell how it is accomplished: carbon dioxide, glucose, H+, oxygen, water o Describe the structure and function of transport proteins. Passive transport is d ...
... o Create the two column table with the headings (material and method). Consider the following materials that must cross the membrane. For each tell how it is accomplished: carbon dioxide, glucose, H+, oxygen, water o Describe the structure and function of transport proteins. Passive transport is d ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.