Lab 2. Plant Cells, Propagation and Mitosis In
... ability to regenerate new organs from cuttings (roots and shoots). Plants are commonly propagated by inducing root or shoot cuttings to grow into new whole plants. You will take advantage of this property in plants and propagate several species of plants from cuttings and monitor their growth in the ...
... ability to regenerate new organs from cuttings (roots and shoots). Plants are commonly propagated by inducing root or shoot cuttings to grow into new whole plants. You will take advantage of this property in plants and propagate several species of plants from cuttings and monitor their growth in the ...
Volume 169 No. 3 March 1, 1989 T - The Journal of Experimental
... PREPARATION OF MANUSCRIPT Articles should conform to the style of a current issue of this journal or to the recommendations of the Council of Biology Editors Style Manual (5th edition, 1983, Council of Biology Editors, Inc., 9650 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20814) . Note that each reference should ...
... PREPARATION OF MANUSCRIPT Articles should conform to the style of a current issue of this journal or to the recommendations of the Council of Biology Editors Style Manual (5th edition, 1983, Council of Biology Editors, Inc., 9650 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20814) . Note that each reference should ...
Cytokinesis in Scytosiphon zygotes - Journal of Cell Science
... there is no specialized structure such as the phragmoplast. Brown algal cells have a combination of features similar to centrosomal spindle formation in animal cells and cell plate formation in mitosis and cytokinesis in land plants. In brown algae, the conclusive factor that determines the cytokine ...
... there is no specialized structure such as the phragmoplast. Brown algal cells have a combination of features similar to centrosomal spindle formation in animal cells and cell plate formation in mitosis and cytokinesis in land plants. In brown algae, the conclusive factor that determines the cytokine ...
Cells
... Cells use special processes to move nondissolved particles, or large amounts of material, into and out of the cytoplasm ...
... Cells use special processes to move nondissolved particles, or large amounts of material, into and out of the cytoplasm ...
Cell-Rubric
... Build a 3-dimensional model of a cell that illustrates all of the basic parts of the cell. Your cell model should have the following characteristics: Major organelles named and labeled Show the 3-dimensional nature of cells Be a typical plant or animal cell-your choice Come with definitions ...
... Build a 3-dimensional model of a cell that illustrates all of the basic parts of the cell. Your cell model should have the following characteristics: Major organelles named and labeled Show the 3-dimensional nature of cells Be a typical plant or animal cell-your choice Come with definitions ...
3.1 AS Unit: Cells, Exchange and Transport Module 1: Cells 1.1.1
... The cytoskeleton is a cellular "scaffolding" or "skeleton" contained within the cytoplasm. The cytoskeleton is present in all cells; it was once thought this structure was unique to eukaryotes, but recent research has identified the prokaryotic cytoskeleton. It is a dynamic structure that maintains ...
... The cytoskeleton is a cellular "scaffolding" or "skeleton" contained within the cytoplasm. The cytoskeleton is present in all cells; it was once thought this structure was unique to eukaryotes, but recent research has identified the prokaryotic cytoskeleton. It is a dynamic structure that maintains ...
THE HISTORY OF CELL BIOLOGY
... THE HISTORY OF CELL BIOLOGY Both Living and Nonliving Things are composed of molecules made from chemical elements such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. The organization of these molecules into Cells is one feature that distinguishes Living Things from all other matter. The CELL is the sma ...
... THE HISTORY OF CELL BIOLOGY Both Living and Nonliving Things are composed of molecules made from chemical elements such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. The organization of these molecules into Cells is one feature that distinguishes Living Things from all other matter. The CELL is the sma ...
cells final - educ399portfolioedwinawilson
... Most hormones circulate in blood, coming into contact with essentially all cells. ...
... Most hormones circulate in blood, coming into contact with essentially all cells. ...
Name: Date: Period: BIOLOGY H EU#1: THE CELL Venn Diagram
... Are membrane-enclosed organelles present? ...
... Are membrane-enclosed organelles present? ...
200 300 400 100 200 300 400 100 200 300 400 100 200 300 400
... because it is too big to fit through the holes in the cell membrane. The water molecules move from high concentration on the left to low concentration on the right. This is also known as osmosis. ...
... because it is too big to fit through the holes in the cell membrane. The water molecules move from high concentration on the left to low concentration on the right. This is also known as osmosis. ...
Plant and Animal Cell Info
... of a school is a student, and the smallest functional unit of an organism is a cell. Cells work together to perform specific tasks and complete functions that contribute to the overall functionality of the organism. ...
... of a school is a student, and the smallest functional unit of an organism is a cell. Cells work together to perform specific tasks and complete functions that contribute to the overall functionality of the organism. ...
cell-parts-and-functions-review-1
... 3. Cell organelles are located within the ____ of the cell. nucleus cytoplasm cell membrane lysosomes 4. The endoplasmic reticulum functions to: transport materials destroy old cell parts make ribosomes package proteins 5. Genetic material is contained within the ___ of the cell. ribosomes cytoplasm ...
... 3. Cell organelles are located within the ____ of the cell. nucleus cytoplasm cell membrane lysosomes 4. The endoplasmic reticulum functions to: transport materials destroy old cell parts make ribosomes package proteins 5. Genetic material is contained within the ___ of the cell. ribosomes cytoplasm ...
Critical Thinking
... are many types of methane-making archaebacteria, and because many types of archaebacteria live in very hot places. mitochondrion B C ...
... are many types of methane-making archaebacteria, and because many types of archaebacteria live in very hot places. mitochondrion B C ...
Cell Cycle & Cell Division
... Cell Division in Prokaryotes Prokaryotes such as bacteria divide into 2 Parent cell identical cells by the process of binary fission Chromosome Single chromosome relicates makes a copy of itself Cell wall forms Cell splits between the chromosomes dividing the cell 2 identical daughter cells ...
... Cell Division in Prokaryotes Prokaryotes such as bacteria divide into 2 Parent cell identical cells by the process of binary fission Chromosome Single chromosome relicates makes a copy of itself Cell wall forms Cell splits between the chromosomes dividing the cell 2 identical daughter cells ...
Cells Answers - Science Skool!
... 2. Name the part of a cell that is filled with cell sap. Vacuole 3. Give the name of two parts that can be found in a leaf cell but not in a human liver cell. Chloroplasts, vacuole, cell wall 4. What is the function of a ribosome? Protein synthesis/ enzyme synthesis 5. How are plant cells different ...
... 2. Name the part of a cell that is filled with cell sap. Vacuole 3. Give the name of two parts that can be found in a leaf cell but not in a human liver cell. Chloroplasts, vacuole, cell wall 4. What is the function of a ribosome? Protein synthesis/ enzyme synthesis 5. How are plant cells different ...
Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport
... that open to allows OR close • Gates may open due to three kinds of stimuli – Stretching of cell membrane – Electrical signals – Chemicals in cytosol or external environment ...
... that open to allows OR close • Gates may open due to three kinds of stimuli – Stretching of cell membrane – Electrical signals – Chemicals in cytosol or external environment ...
3.5.3 - OpenStudy
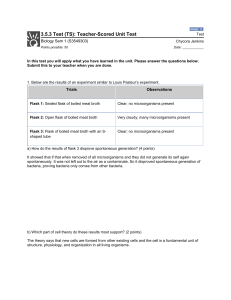
... It showed that if that when removed of all microorganisms and they did not generate its self again spontaneously. It was not left out to the air as a contaminate. So it disproved spontaneous generation of bacteria, proving bacteria only comes from other bacteria. ...
... It showed that if that when removed of all microorganisms and they did not generate its self again spontaneously. It was not left out to the air as a contaminate. So it disproved spontaneous generation of bacteria, proving bacteria only comes from other bacteria. ...
Cell Membranes and Transport
... they will not dehydrate in their salt water ocean, which is hypertonic to their cells. 4. Our cells are constantly bathed in blood (isotonic). Our lungs and kidneys get rid of excess water in our body so our blood can always be isotonic to the rest of our cells. ...
... they will not dehydrate in their salt water ocean, which is hypertonic to their cells. 4. Our cells are constantly bathed in blood (isotonic). Our lungs and kidneys get rid of excess water in our body so our blood can always be isotonic to the rest of our cells. ...
The biosynthetic basis of budding yeast cell size control
... Department of Biology, Stanford University Cell size is an important physiological trait that sets the scale of all biosynthetic processes. Although physiological studies have revealed that cells actively regulate their size, the molecular mechanisms underlying this regulation have remained unclear. ...
... Department of Biology, Stanford University Cell size is an important physiological trait that sets the scale of all biosynthetic processes. Although physiological studies have revealed that cells actively regulate their size, the molecular mechanisms underlying this regulation have remained unclear. ...
20.1 viruses wkbk key - OG
... Virus that attacks bacteria *2. What are viruses? Particles of nucleic acid, protein, and lipids that reproduce only by infecting living cells *3. What is a capsid? Protein coat on a virus (for protection) 4. How does a typical virus get inside a cell? Capsid proteins “trick” the cell by binding to ...
... Virus that attacks bacteria *2. What are viruses? Particles of nucleic acid, protein, and lipids that reproduce only by infecting living cells *3. What is a capsid? Protein coat on a virus (for protection) 4. How does a typical virus get inside a cell? Capsid proteins “trick” the cell by binding to ...
The amazing plant cell.
... Each cell is functionally independent (it can live on its own under the right conditions). What does it involve? ...
... Each cell is functionally independent (it can live on its own under the right conditions). What does it involve? ...
Cell Cycle Notes File
... imaginary plane across the middle of the parent cell At anaphase: o Centromeres divide, separating the sister chromatids. o Each individual chromatid is pulled toward the pole to which it is attached by spindle fibers. o By the end, the two opposite poles of the parent cell have equivalent collectio ...
... imaginary plane across the middle of the parent cell At anaphase: o Centromeres divide, separating the sister chromatids. o Each individual chromatid is pulled toward the pole to which it is attached by spindle fibers. o By the end, the two opposite poles of the parent cell have equivalent collectio ...
Class Notes
... 2. The structures that make up a cell also have unique functions. 3. Every cell is surrounded by a protective covering called a membrane. The cell membrane is a flexible covering that protects the inside of a cell from the environment outside a cell. Cell membranes are mostly made of two different m ...
... 2. The structures that make up a cell also have unique functions. 3. Every cell is surrounded by a protective covering called a membrane. The cell membrane is a flexible covering that protects the inside of a cell from the environment outside a cell. Cell membranes are mostly made of two different m ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.