Cell cycle regulation
... 11.9 Mitosis is orchestrated by several protein kinases • The transition from G2 to M is a major control point in many eukaryotic cells. • Activation of several protein kinases is associated with the G2-M transition. ...
... 11.9 Mitosis is orchestrated by several protein kinases • The transition from G2 to M is a major control point in many eukaryotic cells. • Activation of several protein kinases is associated with the G2-M transition. ...
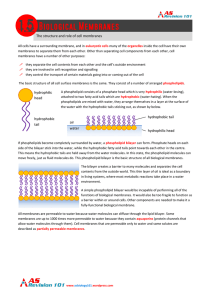
The structure and role of cell membranes hydrophilic head
... move freely, just as fluid molecules do. This phospholipid bilayer is the basic structure of all biological membranes. The bilayer creates a barrier to many molecules and separates the cell contents from the outside world. This thin layer of oil is ideal as a boundary in living systems, where most m ...
... move freely, just as fluid molecules do. This phospholipid bilayer is the basic structure of all biological membranes. The bilayer creates a barrier to many molecules and separates the cell contents from the outside world. This thin layer of oil is ideal as a boundary in living systems, where most m ...
From Cells to Systems
... 2. Chromosomes - threadlike structures that contain information about the characteristics of the organism. (A & P) 3. Cell Membrane - a covering that holds the cell together, and separates it from its surroundings. (A & P) 4. Cytoplasm - a jellylike substance that contains many chemicals to keep the ...
... 2. Chromosomes - threadlike structures that contain information about the characteristics of the organism. (A & P) 3. Cell Membrane - a covering that holds the cell together, and separates it from its surroundings. (A & P) 4. Cytoplasm - a jellylike substance that contains many chemicals to keep the ...
Chapter 8
... Individuals of a species have a characteristic number of chromosomes in each cell Chromosomes differ in length and shape, carry different portions of cell’s hereditary information Mechanisms divide information between daughter cells, along with enough cytoplasm for each cell to operate on its ...
... Individuals of a species have a characteristic number of chromosomes in each cell Chromosomes differ in length and shape, carry different portions of cell’s hereditary information Mechanisms divide information between daughter cells, along with enough cytoplasm for each cell to operate on its ...
The Cell
... • Plant cells have a cell wall – animal cells do not. • Plant cells have chloroplasts – animal cells do not • Plant cells have a large vacuole – animal cells do not ...
... • Plant cells have a cell wall – animal cells do not. • Plant cells have chloroplasts – animal cells do not • Plant cells have a large vacuole – animal cells do not ...
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell
... that were produced in the rough endoplasmic reticulum now move to the Golgi apparatus. The Golgi apparatus appears as a stack of loosely connected membranes. modify, sort and package the The function of the Golgi is to ___________________ proteins that have arrived from the endoplasmic reticulum. Th ...
... that were produced in the rough endoplasmic reticulum now move to the Golgi apparatus. The Golgi apparatus appears as a stack of loosely connected membranes. modify, sort and package the The function of the Golgi is to ___________________ proteins that have arrived from the endoplasmic reticulum. Th ...
Amoeba - TeacherWeb
... Eukaryotic Cell- true nucleus containing DNA surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Contains other double-membrane bound organelles such as the mitochondria. Unspecialized cells with no tissues Unicellular or Multicellular Heterotrophic or Autotrophic Presence of free-living life stage Nonmot ...
... Eukaryotic Cell- true nucleus containing DNA surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Contains other double-membrane bound organelles such as the mitochondria. Unspecialized cells with no tissues Unicellular or Multicellular Heterotrophic or Autotrophic Presence of free-living life stage Nonmot ...
Cell Growth & Division
... the DNA is less tightly coiled allowing its information to be “read” and processed by the cell. • In this loose form the DNA/protein complex is called chromatin. • As the DNA replicates it forms 2 identical halves of the chromosome called chromatids. • These halves are joined by a constricted area k ...
... the DNA is less tightly coiled allowing its information to be “read” and processed by the cell. • In this loose form the DNA/protein complex is called chromatin. • As the DNA replicates it forms 2 identical halves of the chromosome called chromatids. • These halves are joined by a constricted area k ...
Cell Membrane - Fall River Public Schools
... The cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall This is called plasmolysis and is the reason plants wilt when they ...
... The cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall This is called plasmolysis and is the reason plants wilt when they ...
1-4 Enrich: Facilitated Diffusion
... the cell membrane even though they are moving from an area of higher to an area of lower concentration. To pass through the cell membrane, these molecules must be facilitated, or helped, by a carrier molecule that is embedded in the cell membrane. The carrier molecule attaches to a passenger molecul ...
... the cell membrane even though they are moving from an area of higher to an area of lower concentration. To pass through the cell membrane, these molecules must be facilitated, or helped, by a carrier molecule that is embedded in the cell membrane. The carrier molecule attaches to a passenger molecul ...
The Importance of Vacuoles - LS-Biology
... higher the turgor pressure. This affects the rigidity of the cell wall, furthermore supporting the shape and structure of plants, helping them maintain an upright position. If a vacuole contains too much liquid, then it is able to export this material to avoid cytolysis or the bursting of the cell. ...
... higher the turgor pressure. This affects the rigidity of the cell wall, furthermore supporting the shape and structure of plants, helping them maintain an upright position. If a vacuole contains too much liquid, then it is able to export this material to avoid cytolysis or the bursting of the cell. ...
Sample presentation slides (Green and gold texture design)
... where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated. The process by which particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration is known as diffusion. Diffusion is the driving force behind the movement of many substances across the cell membrane ...
... where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated. The process by which particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration is known as diffusion. Diffusion is the driving force behind the movement of many substances across the cell membrane ...
Bacterial Shape: Concave Coiled Coils Curve
... was intact, but the curved shape was lost. The authors then identified the protein encoded by the interrupted gene, which they dubbed CreS, for crescentin. Remarkably, studies with immunofluorescence or with a green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion to CreS showed that crescentin localizes specifical ...
... was intact, but the curved shape was lost. The authors then identified the protein encoded by the interrupted gene, which they dubbed CreS, for crescentin. Remarkably, studies with immunofluorescence or with a green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion to CreS showed that crescentin localizes specifical ...
Cell Analogy Webquest
... Below is a list of the websites available for you to use on your Cell Webquest. To access these sites in the computer lab, click on the Science links on Westland’s homepage. You can also access these from your home computer if you have internet access. ...
... Below is a list of the websites available for you to use on your Cell Webquest. To access these sites in the computer lab, click on the Science links on Westland’s homepage. You can also access these from your home computer if you have internet access. ...
comparison of cheek and onion cells
... explain how the cell is the basic unit for all living things. relate characteristics of living things to cell structure. diagram prepared slides of prokaryotic cells (bacteria) and label the cell wall, cell membrane, and cytoplasm. Identify the shape of the species of bacteria. measure the length an ...
... explain how the cell is the basic unit for all living things. relate characteristics of living things to cell structure. diagram prepared slides of prokaryotic cells (bacteria) and label the cell wall, cell membrane, and cytoplasm. Identify the shape of the species of bacteria. measure the length an ...
Aim - What is the fluid mosaic model?
... • Build a cell membrane with play-dohdemonstrate the fluid mosaic model • Make sure you include the phospholipid bilayer and the substances that can be found floating in the membrane. ...
... • Build a cell membrane with play-dohdemonstrate the fluid mosaic model • Make sure you include the phospholipid bilayer and the substances that can be found floating in the membrane. ...
Cell Structure Answers Worksheet
... membranes, noticeably around the nucleus) and eukaryotes (larger and more organised cells which have internal membranes surrounding its cell components which are then called organelles). 9. Plant cells contain chlorophyll in chloroplasts, a cell wall as well as a cell membrane, and larger vacuoles, ...
... membranes, noticeably around the nucleus) and eukaryotes (larger and more organised cells which have internal membranes surrounding its cell components which are then called organelles). 9. Plant cells contain chlorophyll in chloroplasts, a cell wall as well as a cell membrane, and larger vacuoles, ...
Chapter 6 – A Tour of the Cell CELL THEORY: • All living things are
... change length by adding/removing dimers make tracks for motor proteins to move organelles/vesicles separate chromosomes during cell division found in eukaryotic cilia + flagella/centrioles/basal bodies CENTROSOME = microtubule organizing region in many cells - In animal cells, centrosome contains CE ...
... change length by adding/removing dimers make tracks for motor proteins to move organelles/vesicles separate chromosomes during cell division found in eukaryotic cilia + flagella/centrioles/basal bodies CENTROSOME = microtubule organizing region in many cells - In animal cells, centrosome contains CE ...
Ch 6 Cells Kelly
... change length by adding/removing dimers make tracks for motor proteins to move organelles/vesicles separate chromosomes during cell division found in eukaryotic cilia + flagella/centrioles/basal bodies CENTROSOME = microtubule organizing region in many cells - In animal cells, centrosome contains CE ...
... change length by adding/removing dimers make tracks for motor proteins to move organelles/vesicles separate chromosomes during cell division found in eukaryotic cilia + flagella/centrioles/basal bodies CENTROSOME = microtubule organizing region in many cells - In animal cells, centrosome contains CE ...
The Cell - Mr regh`s science site
... Phospholipids, proteins, and associated carbohydrates Regulates what gets in and out of cells Important for communication ...
... Phospholipids, proteins, and associated carbohydrates Regulates what gets in and out of cells Important for communication ...
Mitosis
... Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in each daughter cell having an exact copy of the DNA found in the mother cell. Cell division can actually be divided into two stages, Interphase and Mitosis. Interphase is usually the stage that most cells are in. During interphase, cells do the ...
... Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in each daughter cell having an exact copy of the DNA found in the mother cell. Cell division can actually be divided into two stages, Interphase and Mitosis. Interphase is usually the stage that most cells are in. During interphase, cells do the ...
Biology 12
... in treating cancer patients. Suggest a hypothesis to explain how vinblastine slows tumour growth by inhibiting cell division. Microtubules form spindle bundle etc. which is necessary for cell division. vinblastine interferes with m.t. assembly, so it would slow the growth of rapidly dividing cells ...
... in treating cancer patients. Suggest a hypothesis to explain how vinblastine slows tumour growth by inhibiting cell division. Microtubules form spindle bundle etc. which is necessary for cell division. vinblastine interferes with m.t. assembly, so it would slow the growth of rapidly dividing cells ...
answer_key_review_classification_protists_prokaryotes__fungi
... Answer Key Classification, Protists, Prokaryotes and Fungi Review Questions 1. Why do biologists assign each organism a universally accepted name? Scientific names are created so that the entire scientific community, no matter the culture and language, can understand what organism is being discussed ...
... Answer Key Classification, Protists, Prokaryotes and Fungi Review Questions 1. Why do biologists assign each organism a universally accepted name? Scientific names are created so that the entire scientific community, no matter the culture and language, can understand what organism is being discussed ...
Mitosis - LiveText
... the blood supply to other parts of the body, where they start to multiply. – It occurs because tumor cells lose the proteins on their surface that hold them to other cells. ...
... the blood supply to other parts of the body, where they start to multiply. – It occurs because tumor cells lose the proteins on their surface that hold them to other cells. ...
Life Science Chapter 7 Part 2 Taxonomy Puma concolor
... • All other organisms are Eukaryotes • Eukaryotes are organisms whose cell contain an organized nucleus surround by a membrane. The cells also contain other organ bound structures like mitochonria, ER’s, vacuoles, chloroplasts, etc. • Include organisms in the Kingdoms Protista, Fungi, Plantae & Anim ...
... • All other organisms are Eukaryotes • Eukaryotes are organisms whose cell contain an organized nucleus surround by a membrane. The cells also contain other organ bound structures like mitochonria, ER’s, vacuoles, chloroplasts, etc. • Include organisms in the Kingdoms Protista, Fungi, Plantae & Anim ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.