Biology and Society, Exam II
... 32. What is the relationship between the IA and IB alleles in blood type inheritance? a. One is dominant over the other. b. They are codominant. c. They are both recessive to the i allele. d. None of the above. 33. Two parents have a child that has sickle-cell anemia, a disease caused by a recessive ...
... 32. What is the relationship between the IA and IB alleles in blood type inheritance? a. One is dominant over the other. b. They are codominant. c. They are both recessive to the i allele. d. None of the above. 33. Two parents have a child that has sickle-cell anemia, a disease caused by a recessive ...
Cell Children’s Book Project - Iroquois Central School
... would you do it? • Your job is to create a children’s book that shows the different parts of the cell. • You must use pictures to show the parts as well as explain what each part does in a manner that a 5 -10year old can understand. ...
... would you do it? • Your job is to create a children’s book that shows the different parts of the cell. • You must use pictures to show the parts as well as explain what each part does in a manner that a 5 -10year old can understand. ...
Bacteria - WordPress.com
... Cell Membrane – controls what materials come in and out of the cell. Cytoplasm – fluid in the cell containing organelles and genetic material and allows structures to move within the cell ...
... Cell Membrane – controls what materials come in and out of the cell. Cytoplasm – fluid in the cell containing organelles and genetic material and allows structures to move within the cell ...
Chapter 5: Cell Structure and Function
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1670’s): Early observations of protists Theodor Schwann (1830’s): Early observations of animal cells • Lack of cell wall delayed discovery (made observation difficult) Rudolf Virchow (1850’s): Principles of Modern Cell Theory 1) Every living organism is made up of 1 or more ce ...
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1670’s): Early observations of protists Theodor Schwann (1830’s): Early observations of animal cells • Lack of cell wall delayed discovery (made observation difficult) Rudolf Virchow (1850’s): Principles of Modern Cell Theory 1) Every living organism is made up of 1 or more ce ...
Cellular Reproduction - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... made up of DNA and proteins. • Two chromatids make up a chromosome • Centromeres are attachment points for two chromatids and hold them together • Chromatin are less tightly coiled DNA-protein complex used to form chromosomes ...
... made up of DNA and proteins. • Two chromatids make up a chromosome • Centromeres are attachment points for two chromatids and hold them together • Chromatin are less tightly coiled DNA-protein complex used to form chromosomes ...
The Cell & Organization of Life
... chloroplast began as proK and were eaten by larger cells. Evidence that supports this theory: • They are about the same size as bacteria • They are surrounded by two membranes ...
... chloroplast began as proK and were eaten by larger cells. Evidence that supports this theory: • They are about the same size as bacteria • They are surrounded by two membranes ...
Section 7–1 Life Is Cellular (pages 169–173)
... made in the cell. You will find that the steps of this process are explained on pages 176–178. For more information about flowcharts, see Organizing Information in Appendix A in your textbook. Students’ flowcharts should include RNA moving out of the nucleus, the production of proteins in ribosomes, ...
... made in the cell. You will find that the steps of this process are explained on pages 176–178. For more information about flowcharts, see Organizing Information in Appendix A in your textbook. Students’ flowcharts should include RNA moving out of the nucleus, the production of proteins in ribosomes, ...
Chapter Objectives
... 33. Define osmosis and predict the direction of water movement based upon differences in solute concentration 34. Explain how bound water affects the osmotic behavior of dilute biological fluids 35. Describe how living cells with and without walls regulate water balance 36. Explain how transport pro ...
... 33. Define osmosis and predict the direction of water movement based upon differences in solute concentration 34. Explain how bound water affects the osmotic behavior of dilute biological fluids 35. Describe how living cells with and without walls regulate water balance 36. Explain how transport pro ...
Slide ()
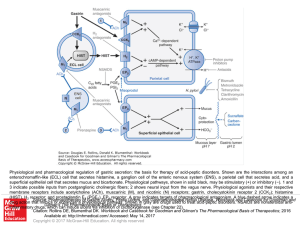
... Physiological and pharmacological regulation of gastric secretion: the basis for therapy of acid-peptic disorders. Shown are the interactions among an enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell that secretes histamine, a ganglion cell of the enteric nervous system (ENS), a parietal cell that secretes acid, an ...
... Physiological and pharmacological regulation of gastric secretion: the basis for therapy of acid-peptic disorders. Shown are the interactions among an enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell that secretes histamine, a ganglion cell of the enteric nervous system (ENS), a parietal cell that secretes acid, an ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... Organisms that cannot make their own food and must obtain energy from the foods they eat are called ________ What are the three parts of an ATP molecule? When is energy is released from ATP? Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into _______________ n the overall equation ...
... Organisms that cannot make their own food and must obtain energy from the foods they eat are called ________ What are the three parts of an ATP molecule? When is energy is released from ATP? Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into _______________ n the overall equation ...
Cell Membrane and Transport
... What are membranes? Membranes cover the surface of every cell, and also surround most organelles within cells. They have a number of functions, such as: keeping all cellular components inside the cell allowing selected molecules to move in and out of the cell isolating organelles from the res ...
... What are membranes? Membranes cover the surface of every cell, and also surround most organelles within cells. They have a number of functions, such as: keeping all cellular components inside the cell allowing selected molecules to move in and out of the cell isolating organelles from the res ...
Cells
... Why do you think it’s important that cell membranes are selectively permeable? Allows needed substances to enter and wastes to leave, while keeping molecules that are not needed out ...
... Why do you think it’s important that cell membranes are selectively permeable? Allows needed substances to enter and wastes to leave, while keeping molecules that are not needed out ...
Chapter 3 Quizzes
... 2. According to the Bible, what do all living things do “after their kind”? 3. A living thing that is made of only one cell is described as being ...
... 2. According to the Bible, what do all living things do “after their kind”? 3. A living thing that is made of only one cell is described as being ...
Medical Interventions
... Circular DOUBLE stranded DNA molecules Can have many in a bacterial cell Normal function of the cell not dependent on the genetic information in this DNA, but it often codes for advantageous proteins Can be transferred from one bacterial cell to another ...
... Circular DOUBLE stranded DNA molecules Can have many in a bacterial cell Normal function of the cell not dependent on the genetic information in this DNA, but it often codes for advantageous proteins Can be transferred from one bacterial cell to another ...
Plasma Membrane - Rapid City Area Schools
... charity would you give it to? Review: Name as many different parts of the inside of a cell as possible Learning Targets: How osmosis and diffusion worked in the egg lab, different cells in the body, plant vs. animal cells ...
... charity would you give it to? Review: Name as many different parts of the inside of a cell as possible Learning Targets: How osmosis and diffusion worked in the egg lab, different cells in the body, plant vs. animal cells ...
Cell Physiology
... substances against concentration gradients (from low to high, or up a gradient concentration. ...
... substances against concentration gradients (from low to high, or up a gradient concentration. ...
What do cells do with all that energy?
... The cell theory applies to all living things, including you. State the three main parts of the cell theory and briefly describe how they relate to you. Which chemical compound stores energy a cell needs to carry out its processes? Name two functions of the cell membrane. ...
... The cell theory applies to all living things, including you. State the three main parts of the cell theory and briefly describe how they relate to you. Which chemical compound stores energy a cell needs to carry out its processes? Name two functions of the cell membrane. ...
Male Anatomy
... sister chromatids joined at their centromeres. During telophase I the spindle disappears, nuclear membranes may re-form and the two nuclei, each containing a haploid set of chromosomes, are separated as cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. Prophase II begins with the formation of a spindle and the sti ...
... sister chromatids joined at their centromeres. During telophase I the spindle disappears, nuclear membranes may re-form and the two nuclei, each containing a haploid set of chromosomes, are separated as cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. Prophase II begins with the formation of a spindle and the sti ...
a. Cell Membrane
... that the student sees has DIFFERENT cells than the rest, and how are the cells different? a. The flower is DIFFERENT because its cells are the only ones WITHOUT a nucleus. b. The apple is DIFFERENT because its cells are the only ones WITH a cell ...
... that the student sees has DIFFERENT cells than the rest, and how are the cells different? a. The flower is DIFFERENT because its cells are the only ones WITHOUT a nucleus. b. The apple is DIFFERENT because its cells are the only ones WITH a cell ...
Chapter 10 - IRSC Biology Department
... – Phosphorylation at one site (red) inactivates Cdk – Phosphorylation at another site (green) activates Cdk ...
... – Phosphorylation at one site (red) inactivates Cdk – Phosphorylation at another site (green) activates Cdk ...
.. Golgi Bodies
... Vesicles are tiny, membranous sacs that move through the cytoplasm or take up positions in it. A common type, the lysosome, buds from Golgi membranes of animal cells and certain fungal cells. Lysosomes are organelles of intracellular digestion. They contain a potent brew, rich with diverse enzymes t ...
... Vesicles are tiny, membranous sacs that move through the cytoplasm or take up positions in it. A common type, the lysosome, buds from Golgi membranes of animal cells and certain fungal cells. Lysosomes are organelles of intracellular digestion. They contain a potent brew, rich with diverse enzymes t ...
The Cell Lab
... Kingdom Plantae: This kingdom includes mosses, ferns, horsetails, club mosses, conifers, angiosperms (flowering plants). To examine cell structure of a typical plant we will use Elodea, an aquatic plant. Place a leaf of Elodea on a slide. Use one drop of water and place the cover slip on the drop. E ...
... Kingdom Plantae: This kingdom includes mosses, ferns, horsetails, club mosses, conifers, angiosperms (flowering plants). To examine cell structure of a typical plant we will use Elodea, an aquatic plant. Place a leaf of Elodea on a slide. Use one drop of water and place the cover slip on the drop. E ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.