Kaitlyn Kraybill-Voth Period 3 Investigation 2: Scientific Essay: Cells
... There are two main types of cells. The Prokaryote Cell and the Eukaryote Cell. The Prokaryote Cell is a single celled organism that does not have a nucleus so their genetic material is not stored in the nucleus. They have some organelles but not many. They are less complicated that eukaryotes. All b ...
... There are two main types of cells. The Prokaryote Cell and the Eukaryote Cell. The Prokaryote Cell is a single celled organism that does not have a nucleus so their genetic material is not stored in the nucleus. They have some organelles but not many. They are less complicated that eukaryotes. All b ...
Building a Knowledge Base by Telling a Story: An example
... When you say that Penetrate, for example, is a step of the process, SHAKEN will ask you to describe that step, as illustrated with this dialogue: Shaken: What is the barrier that is penetrated? User: The cell membrane of the cell. Shaken: What is the penetrator? ...
... When you say that Penetrate, for example, is a step of the process, SHAKEN will ask you to describe that step, as illustrated with this dialogue: Shaken: What is the barrier that is penetrated? User: The cell membrane of the cell. Shaken: What is the penetrator? ...
Cells and Cell Membranes
... o Stimulus usually different from transported molecule. • ex: ion-gated channels when neurotransmitters bind to a specific gated channels on a neuron, these channels open = allows Na+ ions to enter nerve cell. • ex: voltage-gated channels change in electrical charge across nerve cell membrane ...
... o Stimulus usually different from transported molecule. • ex: ion-gated channels when neurotransmitters bind to a specific gated channels on a neuron, these channels open = allows Na+ ions to enter nerve cell. • ex: voltage-gated channels change in electrical charge across nerve cell membrane ...
3:5
... 3.5 Active Transport, Endocytosis, and Exocytosis Active transport requires energy input from a cell and enables a cell to move a substance against its concentration gradient. • Passive transport requires no energy from the cell. • Active transport is powered by chemical energy (ATP). • Active tran ...
... 3.5 Active Transport, Endocytosis, and Exocytosis Active transport requires energy input from a cell and enables a cell to move a substance against its concentration gradient. • Passive transport requires no energy from the cell. • Active transport is powered by chemical energy (ATP). • Active tran ...
Biology Slide 1 of 18 End Show
... Once a multicellular organism reaches adult size, the cells in its body ...
... Once a multicellular organism reaches adult size, the cells in its body ...
Plant vs. Animal Cell Lab
... 2. Get a clean slide. Place a drop of water on the slide. Take a piece of onion and obtain one layer of epidermal tissue (your teacher will demonstrate this in class). Place the layer of tissue on a slide and then add a small drop of iodine to the slide. Place a coverslip on the slide, slowly loweri ...
... 2. Get a clean slide. Place a drop of water on the slide. Take a piece of onion and obtain one layer of epidermal tissue (your teacher will demonstrate this in class). Place the layer of tissue on a slide and then add a small drop of iodine to the slide. Place a coverslip on the slide, slowly loweri ...
10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle
... Once a multicellular organism reaches adult size, the cells in its body ...
... Once a multicellular organism reaches adult size, the cells in its body ...
No Slide Title
... What might this suggest about the structure of the cell membrane? Answer: This suggests that the cell membrane’s inner and outer layers have essentially the same structure and are, therefore, interchangeable. ...
... What might this suggest about the structure of the cell membrane? Answer: This suggests that the cell membrane’s inner and outer layers have essentially the same structure and are, therefore, interchangeable. ...
Chapter 3, Section 1
... • Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that hold materials. • Lysosomes contain enzymes to digest material. • Centrioles are tubes found in the – Centrioles help divide DNA during mitosis ...
... • Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that hold materials. • Lysosomes contain enzymes to digest material. • Centrioles are tubes found in the – Centrioles help divide DNA during mitosis ...
Chapter 5:
... Following interphase is the M stage, including mitosis and cytokinesis. During mitosis, sister chromatids of each chromosome separate, and become the nuclei of the two daughter cells. The cell cycle ends when cytokinesis, the cleaving of the cytoplasm, is complete. ...
... Following interphase is the M stage, including mitosis and cytokinesis. During mitosis, sister chromatids of each chromosome separate, and become the nuclei of the two daughter cells. The cell cycle ends when cytokinesis, the cleaving of the cytoplasm, is complete. ...
PLASMOLYZED CELLS
... run together. If they do, discard leaves and start over using fewer drops of liquid. 2. Wait 2 or 3 minutes. Observe each leaf under both low and high powers. To observe both leaves, simply move the slide back and forth across the microscope stage. a) Carefully observe the location of the chloroplas ...
... run together. If they do, discard leaves and start over using fewer drops of liquid. 2. Wait 2 or 3 minutes. Observe each leaf under both low and high powers. To observe both leaves, simply move the slide back and forth across the microscope stage. a) Carefully observe the location of the chloroplas ...
Lecture 2: How to Study Cells
... of intracellular organization: 1. Prokaryotes (no nuclear envelope) 2. Eukaryotes (nuclear envelope) ...
... of intracellular organization: 1. Prokaryotes (no nuclear envelope) 2. Eukaryotes (nuclear envelope) ...
E - Waterford Public Schools
... • Luigi Galvani • Italian physician who observed a frog’s leg twitch when it was touched with two different metals • In attempting to explain what happened, Galvani thought that the animal tissue in the frog’s leg was the source of electricity ...
... • Luigi Galvani • Italian physician who observed a frog’s leg twitch when it was touched with two different metals • In attempting to explain what happened, Galvani thought that the animal tissue in the frog’s leg was the source of electricity ...
Argumentation activity: Gene expression regulation in bacteria You
... determines the activities inside the cell. The general mechanism through which this occurs is conserved from bacteria (single cell prokaryotes without nuclei) to eukaryotes (single to multi cell organisms with a nucleus and other membraneenclosed organelles). ...
... determines the activities inside the cell. The general mechanism through which this occurs is conserved from bacteria (single cell prokaryotes without nuclei) to eukaryotes (single to multi cell organisms with a nucleus and other membraneenclosed organelles). ...
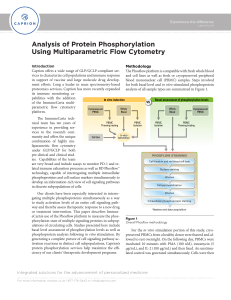
Analysis of Protein Phosphorylation Using Multiparametric Flow
... cells detects the basal level of protein phosphorylation. Assessment of basal levels leads to an understanding of the complex phosphorylation equilibrium that exists in vivo. By contrast, phosphorylation analysis done on the same clinical specimens following in vitro stimulation with PMA, ionomycin ...
... cells detects the basal level of protein phosphorylation. Assessment of basal levels leads to an understanding of the complex phosphorylation equilibrium that exists in vivo. By contrast, phosphorylation analysis done on the same clinical specimens following in vitro stimulation with PMA, ionomycin ...
Document
... CED-9 and Bcl-2 homologs serve as sensors of signals that regulate apoptosis. In the presence of a trophic factor, these regulators block the activation of adaptor proteins (CED-4 and Apaf-1) and thereby prevent effector proteins (the CED-3, Casp9, and Casp3 proteases) from becoming activated. These ...
... CED-9 and Bcl-2 homologs serve as sensors of signals that regulate apoptosis. In the presence of a trophic factor, these regulators block the activation of adaptor proteins (CED-4 and Apaf-1) and thereby prevent effector proteins (the CED-3, Casp9, and Casp3 proteases) from becoming activated. These ...
Water potential 2.0
... Water potential 2.0 The prediction of osmosis and how water is going to move! Water potential = pressure potential + solute potential Solute potential= If the concentration of “stuff” in a solution increases it binds up more water. there is less water to move in/out of a cell because it is bound alr ...
... Water potential 2.0 The prediction of osmosis and how water is going to move! Water potential = pressure potential + solute potential Solute potential= If the concentration of “stuff” in a solution increases it binds up more water. there is less water to move in/out of a cell because it is bound alr ...
3. Please give an example of a Prokaryotic cell.
... How could this relate to real life and YOU? ...
... How could this relate to real life and YOU? ...
Cells: Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
... • Using a technique called the Gram stain – Scientists can classify many bacterial species into two groups based on cell wall composition, Gram-positive and Gram-negative ...
... • Using a technique called the Gram stain – Scientists can classify many bacterial species into two groups based on cell wall composition, Gram-positive and Gram-negative ...
STIMULATION OF PORCINE BONE MARROW STROMAL CELLS
... When BMSc subcultured with HY, Dex, and/or rhBMP -2 on Day 2 and Day 7, HY, rhBMP-2, Dex-HY interaction and rhBMP-2-HY interaction significantly stimulated cellular proliferation, respectively. Specifically, cellular proliferation was significantly increased in the presence of 4.0 mg/mL HY, and in c ...
... When BMSc subcultured with HY, Dex, and/or rhBMP -2 on Day 2 and Day 7, HY, rhBMP-2, Dex-HY interaction and rhBMP-2-HY interaction significantly stimulated cellular proliferation, respectively. Specifically, cellular proliferation was significantly increased in the presence of 4.0 mg/mL HY, and in c ...
The Cell
... ◦ Exocytosis is used to export bulky molecules, such as proteins or polysaccharides. ◦ Endocytosis is used to import substances useful to the livelihood of the cell. ...
... ◦ Exocytosis is used to export bulky molecules, such as proteins or polysaccharides. ◦ Endocytosis is used to import substances useful to the livelihood of the cell. ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.