osb week02 Lab2
... Bacteria and the cyanobacteria (commonly known as blue-green algae) are prokaryotes. All other organisms are eukaryotes. The prefix eu- means "true." The cells of eukaryotes have true, membrane-bound nuclei containing their genetic material. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells also differ in several ot ...
... Bacteria and the cyanobacteria (commonly known as blue-green algae) are prokaryotes. All other organisms are eukaryotes. The prefix eu- means "true." The cells of eukaryotes have true, membrane-bound nuclei containing their genetic material. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells also differ in several ot ...
Viruses - Teacher Note
... Ex. HIV - only infects certain types of white blood cells (both have a narrow range) ...
... Ex. HIV - only infects certain types of white blood cells (both have a narrow range) ...
- mrsolson.com
... 5. I know the major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Parts of a cell: 1. I know the three basic parts of a cell and their functions. I can identify the following organelles on a diagram and describe their functions: nucleus, nucleolus, mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticu ...
... 5. I know the major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Parts of a cell: 1. I know the three basic parts of a cell and their functions. I can identify the following organelles on a diagram and describe their functions: nucleus, nucleolus, mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticu ...
Chapter 13
... Have nucleus Have internal membrane-bound organelles Are larger (10–100 µm in diameter) Have more complex structure Include algae, protozoa, fungi, animals, and plants ...
... Have nucleus Have internal membrane-bound organelles Are larger (10–100 µm in diameter) Have more complex structure Include algae, protozoa, fungi, animals, and plants ...
3.5 Active Transport, Endocytosis, and Exocytosis TEKS 4B, 9A A
... 4B investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules and 9A compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids ...
... 4B investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules and 9A compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids ...
Active Transport
... Active transport is a lot like rolling boulder up a hill. The natural tendency is for the boulder to roll down the hill, just as the natural tendency of molecules is to equally distribute themselves on either side of a membrane. However, by spending some energy to push the boulder higher and highe ...
... Active transport is a lot like rolling boulder up a hill. The natural tendency is for the boulder to roll down the hill, just as the natural tendency of molecules is to equally distribute themselves on either side of a membrane. However, by spending some energy to push the boulder higher and highe ...
Cell Review for Semester 1 Final
... Part 1: Use the following plant cell diagram to answer questions regarding organelles and their functions. ...
... Part 1: Use the following plant cell diagram to answer questions regarding organelles and their functions. ...
3.4 Diffusion and Osmosis - Greenall
... Cells are constantly taking in and sending out substances. If they had to use energy to move every molecule, it would require a massive amount of energy. Some molecules do not have to use energy to move. ...
... Cells are constantly taking in and sending out substances. If they had to use energy to move every molecule, it would require a massive amount of energy. Some molecules do not have to use energy to move. ...
PPT - Hss-1.us
... a cell nucleus. Most are unicellular, but a few prokaryotes such as myxobacteria have multicellular stages in their life cycles.[ It is also spelled "procaryote". • The prokaryotes are divided into two domains: the bacteria and the archaea. Archaea were recognized as a domain of life in 1990. These ...
... a cell nucleus. Most are unicellular, but a few prokaryotes such as myxobacteria have multicellular stages in their life cycles.[ It is also spelled "procaryote". • The prokaryotes are divided into two domains: the bacteria and the archaea. Archaea were recognized as a domain of life in 1990. These ...
- Wiley Online Library
... explanation of the phenomenon of replicative ageing of yeast’ (Bilinski et al., 2012). Our response to those letters, because of its limited length will concentrate only on the most important issues raised. The main experimental argument against the hypertrophy hypothesis was that ‘yeast mothers sto ...
... explanation of the phenomenon of replicative ageing of yeast’ (Bilinski et al., 2012). Our response to those letters, because of its limited length will concentrate only on the most important issues raised. The main experimental argument against the hypertrophy hypothesis was that ‘yeast mothers sto ...
StudyIsland cell division
... chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containing one chromosome of each pair. 2. During the cell cycle, DNA is replicated before mitosis begins, in what is known as the S phase or synthesis phase. ...
... chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containing one chromosome of each pair. 2. During the cell cycle, DNA is replicated before mitosis begins, in what is known as the S phase or synthesis phase. ...
Laboratory of cell physiology
... Membrane Biol. 208: 251-263. Tuvia S., Almagor A., Bitler A., Levin S., Korenstein R., Yedgar S. 1997. Cell membrane fluctuations are regulated by medium macroviscosity: evidence for a metabolic driving force. PNAS USA. 94 : 5045-5049. Tuvia S., Levin S., Bitler A., Korenstein R. 1998. Mechanical fl ...
... Membrane Biol. 208: 251-263. Tuvia S., Almagor A., Bitler A., Levin S., Korenstein R., Yedgar S. 1997. Cell membrane fluctuations are regulated by medium macroviscosity: evidence for a metabolic driving force. PNAS USA. 94 : 5045-5049. Tuvia S., Levin S., Bitler A., Korenstein R. 1998. Mechanical fl ...
Biology semester 1 study guide
... Biology semester 1 study guide Semester 1 is coming to an end, so that means final exams are fast approaching. Therefore, I have decided to put together a study guide to help review (not study)!! ...
... Biology semester 1 study guide Semester 1 is coming to an end, so that means final exams are fast approaching. Therefore, I have decided to put together a study guide to help review (not study)!! ...
Diffusion, osmosis and transport of substances in cells
... Diffusion, osmosis and transport of substances in cells At the end of this CLIL lesson: • You will be able to understand and communicate using scientific terms regarding the cell. • You will see what happens and explain what is happening when cells are put into solutions with different salt or sugar ...
... Diffusion, osmosis and transport of substances in cells At the end of this CLIL lesson: • You will be able to understand and communicate using scientific terms regarding the cell. • You will see what happens and explain what is happening when cells are put into solutions with different salt or sugar ...
College 5
... contacts between residues (not all are favourable) and the number of native contacts (meaning contacts that also occur in the functional protein). The potential energy drives the system to a conformation where a certain number of native contacts has been established, but the chain is not yet folded. ...
... contacts between residues (not all are favourable) and the number of native contacts (meaning contacts that also occur in the functional protein). The potential energy drives the system to a conformation where a certain number of native contacts has been established, but the chain is not yet folded. ...
Slide 1
... Synthesis and Sidedness of Membranes • membranes have distinct inside and outside faces • asymmetrical distribution of proteins, lipids, and associated carbohydrates in the plasma membrane is determined when the membrane is built by the ER and Golgi apparatus Transmembrane glycoproteins ...
... Synthesis and Sidedness of Membranes • membranes have distinct inside and outside faces • asymmetrical distribution of proteins, lipids, and associated carbohydrates in the plasma membrane is determined when the membrane is built by the ER and Golgi apparatus Transmembrane glycoproteins ...
Diffusion Worksheet
... Define simple diffusion: ____________________________________________________________ Define dialysis: __________________________________________________________________ Define osmosis: __________________________________________________________________ Define facilitated diffusion: _________________ ...
... Define simple diffusion: ____________________________________________________________ Define dialysis: __________________________________________________________________ Define osmosis: __________________________________________________________________ Define facilitated diffusion: _________________ ...
mock exam 2 - answers
... 44. A new strain of bacteria is found that lives in strongly basic environments at very high temperatures. Which of the following are most likely the optimal pH and optimal temperature for the enzymes present in this bacteria? a. optimal pH of 3, optimal temperature of 100⁰C b. optimal pH of 3, opti ...
... 44. A new strain of bacteria is found that lives in strongly basic environments at very high temperatures. Which of the following are most likely the optimal pH and optimal temperature for the enzymes present in this bacteria? a. optimal pH of 3, optimal temperature of 100⁰C b. optimal pH of 3, opti ...
in toto dynamic imaging and modeling of chordate morphogenesis
... •genetic studies have provided insights into mechanisms driving notochord morphogenesis •models based on our genetic studies predict certain types of cellular behavior. For example, cells should be quiescent at lateral edges after intercalation. ...
... •genetic studies have provided insights into mechanisms driving notochord morphogenesis •models based on our genetic studies predict certain types of cellular behavior. For example, cells should be quiescent at lateral edges after intercalation. ...
Cell Communication
... and too large to pass through the plasma membrane • they influence cell activities by binding to receptor proteins on the plasma membrane – binding leads to change in the shape of the receptor – these trigger changes in the ...
... and too large to pass through the plasma membrane • they influence cell activities by binding to receptor proteins on the plasma membrane – binding leads to change in the shape of the receptor – these trigger changes in the ...
Mitosis -- Internet Lesson Name
... How many chromosomes are at each pole of the cell? ________________ During meiosis 2, chromosomes line up again along the cell’s _________________________________. What phase does this happen in? __________________________________ Only _____________ copy of each chromosome moves toward the poles. Wh ...
... How many chromosomes are at each pole of the cell? ________________ During meiosis 2, chromosomes line up again along the cell’s _________________________________. What phase does this happen in? __________________________________ Only _____________ copy of each chromosome moves toward the poles. Wh ...
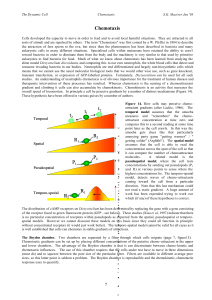
34 Chemotaxis
... where the G-protein is activated, and the kinetics of the dissociation. Thus information about the complex can be measured in living cells – completely unthinkable even a few years back!! The GFP revolution only really started in 1990(ish) when it was introduced to cell biology. GFP forms also promi ...
... where the G-protein is activated, and the kinetics of the dissociation. Thus information about the complex can be measured in living cells – completely unthinkable even a few years back!! The GFP revolution only really started in 1990(ish) when it was introduced to cell biology. GFP forms also promi ...
terminology used in tissue culture
... Mass of undifferentiated cells produced in tissue culture is called callus. The callus is highly vacuolated and unorganised cells. Clone A clone is a group of plants produced from a single explant through asexual reproduction. All the members of a clone have the same genotype as'" that of the parent ...
... Mass of undifferentiated cells produced in tissue culture is called callus. The callus is highly vacuolated and unorganised cells. Clone A clone is a group of plants produced from a single explant through asexual reproduction. All the members of a clone have the same genotype as'" that of the parent ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.