16 Chapter
... food is stored until it is released by the mitochondria. • Mitochondria (mi tuh KAHN dree uh) (singular, mitochondrion) are organelles where energy is released from breaking down food into carbon dioxide and water. ...
... food is stored until it is released by the mitochondria. • Mitochondria (mi tuh KAHN dree uh) (singular, mitochondrion) are organelles where energy is released from breaking down food into carbon dioxide and water. ...
Slide 1
... food is stored until it is released by the mitochondria. • Mitochondria (mi tuh KAHN dree uh) (singular, mitochondrion) are organelles where energy is released from breaking down food into carbon dioxide and water. ...
... food is stored until it is released by the mitochondria. • Mitochondria (mi tuh KAHN dree uh) (singular, mitochondrion) are organelles where energy is released from breaking down food into carbon dioxide and water. ...
VascDev
... One autosomal dominant FEVR gene identified by Robaitaille et al [Nature Genetics 32: 326-330 (2002)] encodes Frizzled4, a putative Wnt receptor. A second autosomal dominant FEVR locus encodes the Wnt co-receptor Lrp5 [Toomes et al [IOVS 45: 20832090 (2004)]; Jiao et al [Am J Hum Genet 75: 878-884 ( ...
... One autosomal dominant FEVR gene identified by Robaitaille et al [Nature Genetics 32: 326-330 (2002)] encodes Frizzled4, a putative Wnt receptor. A second autosomal dominant FEVR locus encodes the Wnt co-receptor Lrp5 [Toomes et al [IOVS 45: 20832090 (2004)]; Jiao et al [Am J Hum Genet 75: 878-884 ( ...
Polyamine dependence of normal cell
... step of DNA replication is negatively affected when polyamine pools are not allowed to increase normally during cell proliferation. Cyclin A is expressed during the S phase and cyclin A/CDK2 is important for a normal rate of DNA elongation. Cyclin A expression is lowered in cells treated with polyam ...
... step of DNA replication is negatively affected when polyamine pools are not allowed to increase normally during cell proliferation. Cyclin A is expressed during the S phase and cyclin A/CDK2 is important for a normal rate of DNA elongation. Cyclin A expression is lowered in cells treated with polyam ...
Tour of Cell Organelles
... sunlight ATP & sugar ATP = active energy sugar = stored energy ...
... sunlight ATP & sugar ATP = active energy sugar = stored energy ...
Chapter 11: Cell Communication 10/7/2015
... Many ion channels are gated, i.e., they contain a “gate” which can block the channel. By default, the gate may be closed (or open) only to open (or close) when a soluble signaling molecule is bound to the channel. ...
... Many ion channels are gated, i.e., they contain a “gate” which can block the channel. By default, the gate may be closed (or open) only to open (or close) when a soluble signaling molecule is bound to the channel. ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... free radicals (oxygen ions that can damage cells) and detoxify alcohol and other drugs. 3. They are named for the Hydrogen Peroxide, H2O2, they produce when braking down alcohol and killing bacteria. 4. Peroxisomes also break down fatty acids, which the mitochondria can then use as an energy source. ...
... free radicals (oxygen ions that can damage cells) and detoxify alcohol and other drugs. 3. They are named for the Hydrogen Peroxide, H2O2, they produce when braking down alcohol and killing bacteria. 4. Peroxisomes also break down fatty acids, which the mitochondria can then use as an energy source. ...
Mapping the Body.indd
... type of molecule is greater outside the cell than inside, the molecule will diffuse in. What kind of molecule will be able to do this? As you might guess, it would have to be small. Size is important. What about chemical properties? Look at the phospholipid bilayer. Which area is thicker—the h ...
... type of molecule is greater outside the cell than inside, the molecule will diffuse in. What kind of molecule will be able to do this? As you might guess, it would have to be small. Size is important. What about chemical properties? Look at the phospholipid bilayer. Which area is thicker—the h ...
The push and pull of the bacterial cytoskeleton
... homolog (Figure 1b) [15]. Although they are similarly named (‘Par’ referring to a role in partitioning), ParA and ParM are different at both the sequence and structural levels (Box 1). At the beginning of the cell cycle, ParA of chromosome I (ParAI) localizes to the oldest pole of the cell with a DN ...
... homolog (Figure 1b) [15]. Although they are similarly named (‘Par’ referring to a role in partitioning), ParA and ParM are different at both the sequence and structural levels (Box 1). At the beginning of the cell cycle, ParA of chromosome I (ParAI) localizes to the oldest pole of the cell with a DN ...
Common Mistakes in Battery Pack Development (And how to avoid
... headroom to accommodate for pulse currents and low temperature usage. Preventing the Most Common Mistakes in Designing Batteries: How do skilled engineers avoid these common pitfalls? Follow these common sense tips: Tip 1: Design in Early Go beyond merely specifying the battery on paper. Early in yo ...
... headroom to accommodate for pulse currents and low temperature usage. Preventing the Most Common Mistakes in Designing Batteries: How do skilled engineers avoid these common pitfalls? Follow these common sense tips: Tip 1: Design in Early Go beyond merely specifying the battery on paper. Early in yo ...
review_for_midterm_april_2016
... What are the characteristics of living things? Label a microscope and describe the function of each of its parts. What three statements make up the cell theory? Who are the 3 scientists who contributed to cell theory and what did each contribute? Describe the theory of abiogenesis (spontaneous gener ...
... What are the characteristics of living things? Label a microscope and describe the function of each of its parts. What three statements make up the cell theory? Who are the 3 scientists who contributed to cell theory and what did each contribute? Describe the theory of abiogenesis (spontaneous gener ...
Minireview - Biologie am KIT
... members of the PAR complex alter their uniform cellular distribution and relocalize to the plasma membrane at one end of the cell. This allows for the formation of a different protein complex at the other end of the cell. The resulting distinct and mutually exclusive membrane domains at either end o ...
... members of the PAR complex alter their uniform cellular distribution and relocalize to the plasma membrane at one end of the cell. This allows for the formation of a different protein complex at the other end of the cell. The resulting distinct and mutually exclusive membrane domains at either end o ...
Ovarian Cancer Case Study - Mrs. Felker`s Science Site
... during mitosis. With the spindle still in place, the cell can't divide into daughter cells and therefore the cancer can’t grow. ...
... during mitosis. With the spindle still in place, the cell can't divide into daughter cells and therefore the cancer can’t grow. ...
Welcome to BISC 220 Cell Physiology Lab
... amounts of 6xHis-b-gal. (The 6xHis tag will be used in the purification process.) ...
... amounts of 6xHis-b-gal. (The 6xHis tag will be used in the purification process.) ...
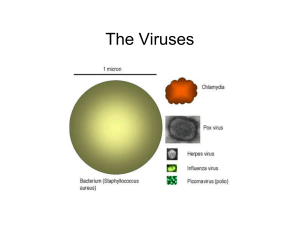
Introduction to Agricultural Biotechnology AGR 0150 Viruses Part 3
... • obligately replicate inside host cells using host metabolic machinery and ribosomes to form a pool of components • which assemble into particles called VIRIONS, which serve to protect the genome and to transfer it to other cells. • They are distinct from other so-called VIRUS-LIKE AGENTS such as V ...
... • obligately replicate inside host cells using host metabolic machinery and ribosomes to form a pool of components • which assemble into particles called VIRIONS, which serve to protect the genome and to transfer it to other cells. • They are distinct from other so-called VIRUS-LIKE AGENTS such as V ...
Hurthle Cell Neoplasm of the Thyroid: Still a Dilemma?
... have been treated with head and neck irradiation and systemic chemotherapy (1,2,3,8,9). Diffuse or focal Hurthle cell changes can be seen in the thyroids of patients who have hyperthyroidism for a long time. In many of these nonneoplastic conditions, Hurthle cells are found as isolated cells but in ...
... have been treated with head and neck irradiation and systemic chemotherapy (1,2,3,8,9). Diffuse or focal Hurthle cell changes can be seen in the thyroids of patients who have hyperthyroidism for a long time. In many of these nonneoplastic conditions, Hurthle cells are found as isolated cells but in ...
Polarity and cell division orientation in the cleavage embryo: from
... paper, we describe how polarity cues, cytoskeleton and cell-to-cell communication interact with each other to regulate orientation of the early embryonic division planes in model animals such as Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila and mouse. We focus particularly on the Par pathway and the actin-driv ...
... paper, we describe how polarity cues, cytoskeleton and cell-to-cell communication interact with each other to regulate orientation of the early embryonic division planes in model animals such as Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila and mouse. We focus particularly on the Par pathway and the actin-driv ...
Mammalian Cell Line Characterization
... A variety of in-vitro and cell-based virology tests, including the general virus screens to detect adventitious and infectious virus, are available. These assays enable our highly trained personnel (including many Ph.D. level virologists) to detect the various forms of virus cytopathic effect (CPE) ...
... A variety of in-vitro and cell-based virology tests, including the general virus screens to detect adventitious and infectious virus, are available. These assays enable our highly trained personnel (including many Ph.D. level virologists) to detect the various forms of virus cytopathic effect (CPE) ...
A novel checkpoint mechanism regulating the G1/S transition
... occurs in G1 and not in S phase, which is further supported by the following: The Cdc2 inhibitor Rum1, which is only expressed in G1 (Benito et al. 1998), was strongly expressed during the delay period (Fig. 1D). Moreover, the activity of the S-phase-specific checkpoint kinase Cds1 was not activated ...
... occurs in G1 and not in S phase, which is further supported by the following: The Cdc2 inhibitor Rum1, which is only expressed in G1 (Benito et al. 1998), was strongly expressed during the delay period (Fig. 1D). Moreover, the activity of the S-phase-specific checkpoint kinase Cds1 was not activated ...
Cell Transport and Cell Energy Study Guide Answer the following
... Cell Transport and Cell Energy Study Guide Answer the following questions to help prepare for the upcoming test. 1. During cellular respiration, food is being broken down to produce ________________ 2. Cellular respiration take place in which organelle? _________________________ 3. What are the prod ...
... Cell Transport and Cell Energy Study Guide Answer the following questions to help prepare for the upcoming test. 1. During cellular respiration, food is being broken down to produce ________________ 2. Cellular respiration take place in which organelle? _________________________ 3. What are the prod ...
Read more - Embrace Kids Foundation
... Devin and Jason McCourty are The primary focus of the Pediatric Sickle Cell and Hemoglobinopathies Nurse Navigator is to enhance patient services, remove barriers to care, and Tackling Sickle Cell. improve care coordination. The nurse navigator supports the families of infants identified by newborn ...
... Devin and Jason McCourty are The primary focus of the Pediatric Sickle Cell and Hemoglobinopathies Nurse Navigator is to enhance patient services, remove barriers to care, and Tackling Sickle Cell. improve care coordination. The nurse navigator supports the families of infants identified by newborn ...
Gen. Bio. - deped catanduanes
... cell membranes and cytoplasm but do not contain nuclei. All bacteria are prokaryotes. Examples of prokaryotes include Escherichia coli which live in your intestines, and Staphylococcus aureus, which can cause skin infection. Even though they are relatively simple, prokaryotes carry out every activit ...
... cell membranes and cytoplasm but do not contain nuclei. All bacteria are prokaryotes. Examples of prokaryotes include Escherichia coli which live in your intestines, and Staphylococcus aureus, which can cause skin infection. Even though they are relatively simple, prokaryotes carry out every activit ...
Mutations in a- and/ -Tubulin Affect Spindle Chinese Hamster Ovary
... organization and function after relatively short periods at 40.5°C. At the nonpermissive temperature all the mutants had normal appearing cytoplasmic microtubules. Premature chromosome condensation analysis failed to show any discrete step in the interphase cell cycle in which these mutants are arre ...
... organization and function after relatively short periods at 40.5°C. At the nonpermissive temperature all the mutants had normal appearing cytoplasmic microtubules. Premature chromosome condensation analysis failed to show any discrete step in the interphase cell cycle in which these mutants are arre ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.