Label the organelles in the animal cell (see page 175
... 1. Cells are ______________________________________________________ 2. All organisms are _______________________________________________ 3. All cells _______________________________________________________ Prokaryotic Cells: Pro- means “ ____________” karyo- means “ _____________” ...
... 1. Cells are ______________________________________________________ 2. All organisms are _______________________________________________ 3. All cells _______________________________________________________ Prokaryotic Cells: Pro- means “ ____________” karyo- means “ _____________” ...
Cells Organelle Practice
... Name:_____________________________________P:_________________Date:____________________ ...
... Name:_____________________________________P:_________________Date:____________________ ...
No Slide Title
... A jellyfish is a multicellular organism that lives in the ocean. It obtains nourishment mostly by eating small fish. Its cells do not have a cell wall and it moves by pushing water outward. What type of organism is a jellyfish? a. plant b. animal c. fungi d. protist ...
... A jellyfish is a multicellular organism that lives in the ocean. It obtains nourishment mostly by eating small fish. Its cells do not have a cell wall and it moves by pushing water outward. What type of organism is a jellyfish? a. plant b. animal c. fungi d. protist ...
Print here - Ecosystemforkids.com
... Identify an organism below that has cells that have a cell wall. a. ...
... Identify an organism below that has cells that have a cell wall. a. ...
cell test review 15-16 - Mercer Island School District
... Instructions: Review your notes, labs and homework to study for your test (chapter 3). A. Structures and Function of Cells- Know the function of each and be able to apply an analogy (Like your cell factory). Also be able to label a picture. nucleus cell membrane golgi bodies vacuoles ...
... Instructions: Review your notes, labs and homework to study for your test (chapter 3). A. Structures and Function of Cells- Know the function of each and be able to apply an analogy (Like your cell factory). Also be able to label a picture. nucleus cell membrane golgi bodies vacuoles ...
Cell Cycle
... C. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell D. Damaged sister chromatids are replaced by new ones 10. What happens in a cell during metaphase? A. The nuclear membrane breaks up B. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell C. Sister chromatids are pulled to opposite ends of the cell D. All o ...
... C. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell D. Damaged sister chromatids are replaced by new ones 10. What happens in a cell during metaphase? A. The nuclear membrane breaks up B. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell C. Sister chromatids are pulled to opposite ends of the cell D. All o ...
Cell Cycle
... C. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell D. Damaged sister chromatids are replaced by new ones 10. What happens in a cell during metaphase? A. The nuclear membrane breaks up B. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell C. Sister chromatids are pulled to opposite ends of the cell D. All o ...
... C. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell D. Damaged sister chromatids are replaced by new ones 10. What happens in a cell during metaphase? A. The nuclear membrane breaks up B. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell C. Sister chromatids are pulled to opposite ends of the cell D. All o ...
What`s Inside the Cell
... Found ONLY in Plant Cells Cell Wall – provides structure to the plant cell. Chloroplasts – contain chlorophyll that makes food for the plant cell. ...
... Found ONLY in Plant Cells Cell Wall – provides structure to the plant cell. Chloroplasts – contain chlorophyll that makes food for the plant cell. ...
Click Here For Review Sheet
... 2. They perform thousands of different _____________________ in the life forms of Earth. ...
... 2. They perform thousands of different _____________________ in the life forms of Earth. ...
Plant Cell
... "microtubule organizing center", is an area in the cell where microtubles are produced from each centrosome, microtubules grow into a "spindle" which is responsible for separating replicated chromosomes into the two daughter cells Plant cells have centrosomes, but they do not have centrioles ...
... "microtubule organizing center", is an area in the cell where microtubles are produced from each centrosome, microtubules grow into a "spindle" which is responsible for separating replicated chromosomes into the two daughter cells Plant cells have centrosomes, but they do not have centrioles ...
The Cellular Organelles include: Cell Membrane: is like the skin that
... Cytoplasm- is the jelly-like center that helps support other structures in the cell. Nucleus- is a large dark and round and is easily found. It contains Chromosomes,or DNA. The nucleus is the brain of the cell. Vacuoles- are balloon like spaces within the cytoplasm which are used for food storage an ...
... Cytoplasm- is the jelly-like center that helps support other structures in the cell. Nucleus- is a large dark and round and is easily found. It contains Chromosomes,or DNA. The nucleus is the brain of the cell. Vacuoles- are balloon like spaces within the cytoplasm which are used for food storage an ...
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
... the middle of the cell with sister chromatid at equator Spindle fibers attach to centromere metaphase duplicated chromosomes lined up in middle of cell ...
... the middle of the cell with sister chromatid at equator Spindle fibers attach to centromere metaphase duplicated chromosomes lined up in middle of cell ...
AQA B2 ESQ - Mitosis and Meiosis 1
... What happens to the genetic material before the cell divides? ...
... What happens to the genetic material before the cell divides? ...
CelI/DNA Review 6-
... 13.What type of bond hold the two strands of a DNA molecule together? lX°,oOÿ-Jÿ 14.The backbone of the DNA helix is composed of alternating ? and ? ,.ÿOOtO.X' ÿ ÿOf:'l2:r-aÿ'X'O--ÿ 15. In the DNA, each nucleotide is composed of (3 things) Ak)ÿXOo.g") ÿ'ÿkÿkÿa.ÿ"- --ÿ_ÿ','ÿA--xk,(ÿ.ÿ, 16. The strand ...
... 13.What type of bond hold the two strands of a DNA molecule together? lX°,oOÿ-Jÿ 14.The backbone of the DNA helix is composed of alternating ? and ? ,.ÿOOtO.X' ÿ ÿOf:'l2:r-aÿ'X'O--ÿ 15. In the DNA, each nucleotide is composed of (3 things) Ak)ÿXOo.g") ÿ'ÿkÿkÿa.ÿ"- --ÿ_ÿ','ÿA--xk,(ÿ.ÿ, 16. The strand ...
The Cell Cycle
... ● Cytoplasm begins to divide ● Animal cells: furrow develops, pinches off the cell into two parts (TWO daughter cells) - marks end of cell division ● Plant cells: cell plate forms between two chromatin masses - develops into new cell wall Mitosis and Cytokinesis cell division on contrast microscop ...
... ● Cytoplasm begins to divide ● Animal cells: furrow develops, pinches off the cell into two parts (TWO daughter cells) - marks end of cell division ● Plant cells: cell plate forms between two chromatin masses - develops into new cell wall Mitosis and Cytokinesis cell division on contrast microscop ...
MITOTIC CELL DIVISION
... pulled to the poll by the contraction of the spindle fibers • chromatids are separated at the centromere ...
... pulled to the poll by the contraction of the spindle fibers • chromatids are separated at the centromere ...
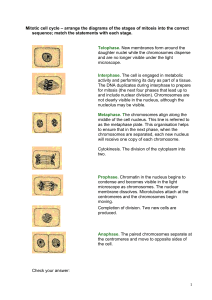
Mitotic cell cycle – arrange the diagrams of the stages of mitosis into
... Interphase. The cell is engaged in metabolic activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleol ...
... Interphase. The cell is engaged in metabolic activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleol ...
The Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis
... the sister chromatids apart to opposite ends of the cell. Once apart they are now each called Chromosomes. ...
... the sister chromatids apart to opposite ends of the cell. Once apart they are now each called Chromosomes. ...
Cell Wall
... What is an organelle? Organelles are structures specialized to perform distinct processes within a cell. ...
... What is an organelle? Organelles are structures specialized to perform distinct processes within a cell. ...
Meiosis - SchoolNotes
... • In the S stage of Interphase: – Each DNA Strand makes an exact copy of itself • The two identical strands are joined together by a centomere. • The joined strands are called sister chromatids ...
... • In the S stage of Interphase: – Each DNA Strand makes an exact copy of itself • The two identical strands are joined together by a centomere. • The joined strands are called sister chromatids ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.