Keyword/concepts: Definition: Darwin Charles Darwin theorised
... Interior of the cell. The cytosol and organelles of eukaryotic cells, excluding the nucleus. ...
... Interior of the cell. The cytosol and organelles of eukaryotic cells, excluding the nucleus. ...
Cell Division (aka Mitosis)
... – A larger cell places more demands on its DNA (more things to control and not enough DNA) – Surface-to-volume ratio decreases as size increases ...
... – A larger cell places more demands on its DNA (more things to control and not enough DNA) – Surface-to-volume ratio decreases as size increases ...
CELLULAR ORGANIZATION
... Nucleolus - site of ribosome assembly Multinucleate - many nuclei Anucleate - no nucleus ...
... Nucleolus - site of ribosome assembly Multinucleate - many nuclei Anucleate - no nucleus ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Testes cells smooth ER produces steroids • Liver cells smooth ER detoxifies alcohol • All cells smooth ER produces vesicles for transportation of proteins to the golgi bodies ...
... • Testes cells smooth ER produces steroids • Liver cells smooth ER detoxifies alcohol • All cells smooth ER produces vesicles for transportation of proteins to the golgi bodies ...
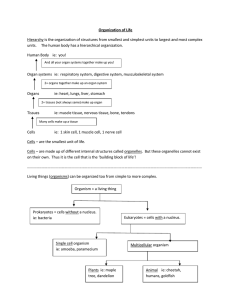
Organization of Life Hierarchy is the organization of structures from
... Organ systems ie: respiratory system, digestive system, musculoskeletal system 2+ organs together make up an organ system ...
... Organ systems ie: respiratory system, digestive system, musculoskeletal system 2+ organs together make up an organ system ...
Cell Division
... •The first phase and longest of mitosis; occurs when chromatin condenses becoming chromosomes and the mitotic spindle begins to form. •Spindles; fanlike microtuble structures which help to separate chromosomes. •The centrioles separate to opposite sides of the nucleus organizing ...
... •The first phase and longest of mitosis; occurs when chromatin condenses becoming chromosomes and the mitotic spindle begins to form. •Spindles; fanlike microtuble structures which help to separate chromosomes. •The centrioles separate to opposite sides of the nucleus organizing ...
Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle
... twisted into a condensed structure Bacterial DNA differs in ...
... twisted into a condensed structure Bacterial DNA differs in ...
1. Cells PPT
... What is around our cells? Our cells are surrounded by extracellular fluid frequently called interstitial fluid ...
... What is around our cells? Our cells are surrounded by extracellular fluid frequently called interstitial fluid ...
Six Kingdoms of Life
... S7L3. Students will recognize how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. a. Explain the role of genes and chromosomes in the process of inheriting a specific trait. Complete the cross between a heterozygous tall pea plant and a homozygous short pea plant. Tall is dominant to sho ...
... S7L3. Students will recognize how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. a. Explain the role of genes and chromosomes in the process of inheriting a specific trait. Complete the cross between a heterozygous tall pea plant and a homozygous short pea plant. Tall is dominant to sho ...
Cell membrane structure File
... • MOST COMMON MATERIAL IN THE CELL MEMBRANE • TWO LAYERS THICK • EACH LAYER HAS A ROUNDED HEAD END (HYDROPHILIC = LOVES WATER) THAT ALWAYS FACES THE WATER BASED SOLUTION (EITHER THE CELL’S ENVIRONMENT OR THE CELL’S CYTOPLASM. • EACH PHOSPHOLIPID HAS TWO TAILS ON ONE END (HYDROPHOBIC = FEARS WATER) T ...
... • MOST COMMON MATERIAL IN THE CELL MEMBRANE • TWO LAYERS THICK • EACH LAYER HAS A ROUNDED HEAD END (HYDROPHILIC = LOVES WATER) THAT ALWAYS FACES THE WATER BASED SOLUTION (EITHER THE CELL’S ENVIRONMENT OR THE CELL’S CYTOPLASM. • EACH PHOSPHOLIPID HAS TWO TAILS ON ONE END (HYDROPHOBIC = FEARS WATER) T ...
Cell Theory Rap
... And don’t forget those ribosomes This is where proteins come from These protein factories are so small you’ll agree You’ll need an electron microscope to see Just when you thought you weren’t havin’ any fun Along comes endoplasmic reticulum These tube-like structures serve as a track To carry stuff ...
... And don’t forget those ribosomes This is where proteins come from These protein factories are so small you’ll agree You’ll need an electron microscope to see Just when you thought you weren’t havin’ any fun Along comes endoplasmic reticulum These tube-like structures serve as a track To carry stuff ...
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
... defect that prevents the formation of an essential enzyme that breaks down lipids These lipids build up in the body and can cause nerve damage; prognosis is not good ...
... defect that prevents the formation of an essential enzyme that breaks down lipids These lipids build up in the body and can cause nerve damage; prognosis is not good ...
Test - Cobb Learning
... ( performs photosynthesis) _________________ F. gel-like substance inside the cell membrane________________ G. packages substances in cell_________________________ H. stores food, water or wastes( is larger in plant cells) ______________________ I. These are found only in animal cells and have diges ...
... ( performs photosynthesis) _________________ F. gel-like substance inside the cell membrane________________ G. packages substances in cell_________________________ H. stores food, water or wastes( is larger in plant cells) ______________________ I. These are found only in animal cells and have diges ...
2.5: CELL DIVISION
... biochemical reactions are performed. Interphase is broken up into three stages: *G1 Stage (first growth stage) The cell performs its normal differentiated function. Protein synthesis mitochondria replication/ chloroplast replication. *S Stage DNA replication. At this point the mass of DNA in the cel ...
... biochemical reactions are performed. Interphase is broken up into three stages: *G1 Stage (first growth stage) The cell performs its normal differentiated function. Protein synthesis mitochondria replication/ chloroplast replication. *S Stage DNA replication. At this point the mass of DNA in the cel ...
Mitosis Notes
... one from each of two parents. – The offspring produced inherit some genetic information from both parents, therefore they are genetically different. ...
... one from each of two parents. – The offspring produced inherit some genetic information from both parents, therefore they are genetically different. ...
Mitosis
... divide about 50 times and then they lose the ability to die. This “clock” gets re-set during the formation of the gametes. Cancer cells escape this process of mortality: they are immortal and can divide endlessly. Normal cells that suffer significant chromosome damage destroy themselves due to the ...
... divide about 50 times and then they lose the ability to die. This “clock” gets re-set during the formation of the gametes. Cancer cells escape this process of mortality: they are immortal and can divide endlessly. Normal cells that suffer significant chromosome damage destroy themselves due to the ...
Mitosis
... divide about 50 times and then they lose the ability to die. This “clock” gets re-set during the formation of the gametes. Cancer cells escape this process of mortality: they are immortal and can divide endlessly. Normal cells that suffer significant chromosome damage destroy themselves due to the ...
... divide about 50 times and then they lose the ability to die. This “clock” gets re-set during the formation of the gametes. Cancer cells escape this process of mortality: they are immortal and can divide endlessly. Normal cells that suffer significant chromosome damage destroy themselves due to the ...
1. Name two functions of the cell membrane
... 19. When proteins help molecules move across the membrane, it is called______________________________________ ACTIVE TRANSPORT 20. Active transport moves molecules [ with | against ] the concentration gradient. 21. Active transport requires _____________________________ 22. Changes in protein shape ...
... 19. When proteins help molecules move across the membrane, it is called______________________________________ ACTIVE TRANSPORT 20. Active transport moves molecules [ with | against ] the concentration gradient. 21. Active transport requires _____________________________ 22. Changes in protein shape ...
A Tour of the Cell
... Tay-Sachs disease Genetic Lysosomes lack lipiddigesting enzyme Nerve cells accumulate excess lipids Die in childhood University of AZ ...
... Tay-Sachs disease Genetic Lysosomes lack lipiddigesting enzyme Nerve cells accumulate excess lipids Die in childhood University of AZ ...
Unit 3 Cells Review Name ____ Learning target 1: I can describe
... Learning Target 4. I can analyze the similarities and differences between eukaryotic & prokaryotic cells 13. Distinguish between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. What similarities do they have? Learning Target 5. I can analyze the similarities and differences between plant & animal cells 14 ...
... Learning Target 4. I can analyze the similarities and differences between eukaryotic & prokaryotic cells 13. Distinguish between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. What similarities do they have? Learning Target 5. I can analyze the similarities and differences between plant & animal cells 14 ...
eprint_12_11727_866
... common features in their cell division processes. Replication of the DNA must occur. Segregation of the "original" and its "replica" follow. Cytokinesis ends the cell division process. Whether the cell was eukaryotic or prokaryotic, these basic events must occur. Cytokinesis is the process where one ...
... common features in their cell division processes. Replication of the DNA must occur. Segregation of the "original" and its "replica" follow. Cytokinesis ends the cell division process. Whether the cell was eukaryotic or prokaryotic, these basic events must occur. Cytokinesis is the process where one ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.