Laboratory Safety
... • All Class II cabinets are designed for work with BSL-1,2,and 3. • not for use with volatile or toxic chemicals. Patient Safety Monitoring in International Laboratories (SMILE) ...
... • All Class II cabinets are designed for work with BSL-1,2,and 3. • not for use with volatile or toxic chemicals. Patient Safety Monitoring in International Laboratories (SMILE) ...
biosafety manual
... are: Creutzfeld-Jakob disease in humans, Mad Cow Disease and scrapie in sheep and goats). These agents are resistant to destruction by chemical (10% formalin, gluteraldehyde, 70% ethanol, iodine) and physical (UV light, ionizing radiation, boiling) procedures that normally inactivate viruses. While ...
... are: Creutzfeld-Jakob disease in humans, Mad Cow Disease and scrapie in sheep and goats). These agents are resistant to destruction by chemical (10% formalin, gluteraldehyde, 70% ethanol, iodine) and physical (UV light, ionizing radiation, boiling) procedures that normally inactivate viruses. While ...
Biosafety Plan - The University of Scranton
... The University's IBC requires that all BSCs be tested and certified prior to initial use, relocation, after HEPA filters are changed, and at least annually. 2.8 Permits Importation of infectious materials, etiologic agents and vectors that may contain them is governed by federal regulation. In gener ...
... The University's IBC requires that all BSCs be tested and certified prior to initial use, relocation, after HEPA filters are changed, and at least annually. 2.8 Permits Importation of infectious materials, etiologic agents and vectors that may contain them is governed by federal regulation. In gener ...
Global Monitoring of Emerging Diseases
... The goal would be to achieve full competence at each Center within, at most, five years, and then begin to expand the number of syndromes monitored. If successful, the number of Centers could also be increased, as resources permit, to cover more areas of the world. Concentration on a small number o ...
... The goal would be to achieve full competence at each Center within, at most, five years, and then begin to expand the number of syndromes monitored. If successful, the number of Centers could also be increased, as resources permit, to cover more areas of the world. Concentration on a small number o ...
Biosafety Manual - UCLA Office of Environment, Health and Safety
... screening and assignment to the IBC or special subcommittee thereof for review. 2. Arranging for initial and periodic inspections of laboratories used in biohazardous research to ensure that standards set by the IBC are followed. 3. Providing technical advice to PIs and to the IBC on research safety ...
... screening and assignment to the IBC or special subcommittee thereof for review. 2. Arranging for initial and periodic inspections of laboratories used in biohazardous research to ensure that standards set by the IBC are followed. 3. Providing technical advice to PIs and to the IBC on research safety ...
RPI Biosafety Plan - Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
... biosafety levels; the level recommended for work with a particular infectious agent depends upon many factors including its virulence and means of infection. Descriptions of each biosafety level are listed below: Biosafety Level 1: The least stringent level; recommended for work performed on defined ...
... biosafety levels; the level recommended for work with a particular infectious agent depends upon many factors including its virulence and means of infection. Descriptions of each biosafety level are listed below: Biosafety Level 1: The least stringent level; recommended for work performed on defined ...
Biosafety Application
... 2. Toxins, Microbiological, or Chemical to be used in animal or human studies, or used in the laboratories of teaching, testing, or research. (Refer to attached references) Biosafety Level determinations are based on the Recommendations outlined by the CDC-NIH Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomed ...
... 2. Toxins, Microbiological, or Chemical to be used in animal or human studies, or used in the laboratories of teaching, testing, or research. (Refer to attached references) Biosafety Level determinations are based on the Recommendations outlined by the CDC-NIH Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomed ...
biosafety manual - University Research Services Administration
... screening and assignment to the IBC or special subcommittee thereof for review. 2. Arranging for initial and periodic inspections of laboratories used in biohazardous research to ensure that standards set by the IBC are followed. 3. Providing technical advice to PIs and to the IBC on research safety ...
... screening and assignment to the IBC or special subcommittee thereof for review. 2. Arranging for initial and periodic inspections of laboratories used in biohazardous research to ensure that standards set by the IBC are followed. 3. Providing technical advice to PIs and to the IBC on research safety ...
UH-Biological Safety Manual - University of Houston
... Biological agents are those pathogenic bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites that can be transmitted to a person or animal, directly or indirectly, and are capable of causing disease in the new host. Biological agents classified according to risk are listed in section III and Appendix B. If the ag ...
... Biological agents are those pathogenic bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites that can be transmitted to a person or animal, directly or indirectly, and are capable of causing disease in the new host. Biological agents classified according to risk are listed in section III and Appendix B. If the ag ...
Steve Perfetto and Kevin Holmes - ISAC-NET
... through infectivity, allergenicity, toxicity, pharmacological or other processes. • Aerodynamic particle size of 0.5 to 100 μm ...
... through infectivity, allergenicity, toxicity, pharmacological or other processes. • Aerodynamic particle size of 0.5 to 100 μm ...
GWU Biosafety Manual - George Washington University School of
... Authority – The BSO has been approved by the Associate Vice President for Research to administer the biosafety program for GWU. The BSO may enter any space at any time to ensure compliance. Principal Investigators – It is the responsibility of the Principal Investigator to do the following: comply w ...
... Authority – The BSO has been approved by the Associate Vice President for Research to administer the biosafety program for GWU. The BSO may enter any space at any time to ensure compliance. Principal Investigators – It is the responsibility of the Principal Investigator to do the following: comply w ...
Why Biosafety Practices?
... – Work in certified BSC – Use bioaerosolcontaining equipment – Decontaminate spills promptly ...
... – Work in certified BSC – Use bioaerosolcontaining equipment – Decontaminate spills promptly ...
Containment overview
... Global Action Plan for Laboratory Containment of Wild Polioviruses Purpose: To provide a systematic, world-wide Action Plan to minimise the risk of reintroduction of wild polioviruses from the laboratory into the community. ...
... Global Action Plan for Laboratory Containment of Wild Polioviruses Purpose: To provide a systematic, world-wide Action Plan to minimise the risk of reintroduction of wild polioviruses from the laboratory into the community. ...
4. standard operating procedures
... Laminar flow cabinets (LFC) are similar in appearance, but are not Biological Safety Cabinets: •only protect the product • intake room air which is passed through a pre-filter and a HEPA filter to remove contaminants, dust and other particles •purified air then enters the work surface in a laminar f ...
... Laminar flow cabinets (LFC) are similar in appearance, but are not Biological Safety Cabinets: •only protect the product • intake room air which is passed through a pre-filter and a HEPA filter to remove contaminants, dust and other particles •purified air then enters the work surface in a laminar f ...
Vol. 36, No. 3: September 2011 - National Foundation for Infectious
... Category 1 CreditsTM and Continuing Education credits. The National Foundation for Infectious Diseases is an approved provider of continuing nursing education by the Maryland Nurses Association, an accredited approver by the American Nurses Credentialing Center’s Commission on Accreditation. For mor ...
... Category 1 CreditsTM and Continuing Education credits. The National Foundation for Infectious Diseases is an approved provider of continuing nursing education by the Maryland Nurses Association, an accredited approver by the American Nurses Credentialing Center’s Commission on Accreditation. For mor ...
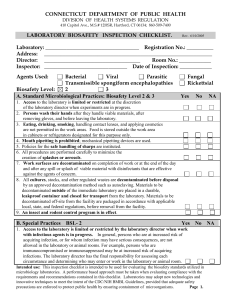
connecticut department of public health
... specific training program provided by the laboratory director or other competent scientist proficient in safe microbiological practices and techniques. 10. A high degree of precaution must always be taken with any contaminated sharp items, including needles and syringes, slides, pipettes, capillary ...
... specific training program provided by the laboratory director or other competent scientist proficient in safe microbiological practices and techniques. 10. A high degree of precaution must always be taken with any contaminated sharp items, including needles and syringes, slides, pipettes, capillary ...
noninfectious vaccines - Extension Veterinary Medicine
... Educational programs of Texas Cooperative Extension serve people of all ages regardless of socioeconomic level, race, color, sex, religion, handicap or national origin. Issued in furtherance of Cooperative Extension Work in Agriculture and Home Economics, Acts of Congress of May 8, 1914, as amended, ...
... Educational programs of Texas Cooperative Extension serve people of all ages regardless of socioeconomic level, race, color, sex, religion, handicap or national origin. Issued in furtherance of Cooperative Extension Work in Agriculture and Home Economics, Acts of Congress of May 8, 1914, as amended, ...
Occupational Safety - College of Agriculture and Life Sciences
... Work with dangerous and exotic agents which pose a high risk of aerosoltransmitted laboratory infectious and life threatening disease. Ebola, Marburg, – Special facility design features required – All activities confined to Class III biosafety cabinets (glove boxes), or Class II BSC’s used by worker ...
... Work with dangerous and exotic agents which pose a high risk of aerosoltransmitted laboratory infectious and life threatening disease. Ebola, Marburg, – Special facility design features required – All activities confined to Class III biosafety cabinets (glove boxes), or Class II BSC’s used by worker ...
biosafety levels and risk assessment policy
... ABSL – Vertebrate animal biosafety level (ABSL) criteria are established for the use of experimentally infected animals in animal care facilities, as well as for animals that may harbor zoonotic infectious agents. In general, the animal biosafety level for working with any given infectious agent in ...
... ABSL – Vertebrate animal biosafety level (ABSL) criteria are established for the use of experimentally infected animals in animal care facilities, as well as for animals that may harbor zoonotic infectious agents. In general, the animal biosafety level for working with any given infectious agent in ...
Menacing Microbes: The Threat of Bioterrorism
... warfare – Did not address production of such weapons – Had no provisions for enforcement – Active programs to develop bioweapons in the US, USSR, UK, France, and Japan ...
... warfare – Did not address production of such weapons – Had no provisions for enforcement – Active programs to develop bioweapons in the US, USSR, UK, France, and Japan ...
49i27r6 - NSF International
... A Suit Laboratory where personnel must wear a positive pressure protective suit. BSL-4 Cabinet and Suit Laboratories have special engineering and design features to prevent microorganisms from being disseminated into the environment. Practices, safety equipment, and facility design and constructio ...
... A Suit Laboratory where personnel must wear a positive pressure protective suit. BSL-4 Cabinet and Suit Laboratories have special engineering and design features to prevent microorganisms from being disseminated into the environment. Practices, safety equipment, and facility design and constructio ...
Preventing Life Threatening Infections in the Asplenic and Other
... older. This age-specific approval and the unavailability of JE-VAX®* creates a substantial problem in providing vaccineinduced protection for those under 18 years of age. There is currently no satisfactory solution for protection of persons under 18 years of age against JE. ...
... older. This age-specific approval and the unavailability of JE-VAX®* creates a substantial problem in providing vaccineinduced protection for those under 18 years of age. There is currently no satisfactory solution for protection of persons under 18 years of age against JE. ...
Biological Safety Program Manual - BioS
... blood or other body fluids. 4.19 Cryogen - A liquid or solid used as a refrigerant with a normal boiling point below -150° C (-238° F) as defined by the U.S. National Bureau of Standards and having large liquid-to-gas expansion ratios (generally greater than 700). 4.20 Cryostat - An apparatus for ma ...
... blood or other body fluids. 4.19 Cryogen - A liquid or solid used as a refrigerant with a normal boiling point below -150° C (-238° F) as defined by the U.S. National Bureau of Standards and having large liquid-to-gas expansion ratios (generally greater than 700). 4.20 Cryostat - An apparatus for ma ...