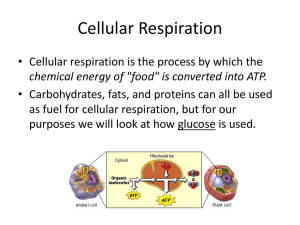
Cellular Respiration 1. To perform cell work, cells require energy. a
... The electron transport chain generates no ATP directly. Its function is to break the large amount of energy in food in manageable amounts. Each component of the chain becomes reduced when it accepts electrons from its Auphill@ neighbor, which is less electronegative. It then returns to its oxidized ...
... The electron transport chain generates no ATP directly. Its function is to break the large amount of energy in food in manageable amounts. Each component of the chain becomes reduced when it accepts electrons from its Auphill@ neighbor, which is less electronegative. It then returns to its oxidized ...
No Slide Title
... 1. BREATHING OR EXTERNAL RESPIRATION 2. CELLULAR RESPIRATION - Process by which organic compounds are broken down to yield energy for work • This energy molecule is _________ ...
... 1. BREATHING OR EXTERNAL RESPIRATION 2. CELLULAR RESPIRATION - Process by which organic compounds are broken down to yield energy for work • This energy molecule is _________ ...
1. Diagram energy flow through the biosphere
... 6. Define coenzyme and list those involved in respiration. Coenzyme small nonprotein organic molecule that is required for certain enzymes to function NAD+(nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) found in all cells that assists electron transfer NADH reduced coenzyme FADH2 reduced coenzyme FAD( ...
... 6. Define coenzyme and list those involved in respiration. Coenzyme small nonprotein organic molecule that is required for certain enzymes to function NAD+(nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) found in all cells that assists electron transfer NADH reduced coenzyme FADH2 reduced coenzyme FAD( ...
cellular-respiration-notes-2016
... compressing a spring. The tightly coiled spring has potential energy. When the compressed spring relaxes, its potential energy is released. The spring's kinetic energy can be used to perform work such as pushing a block attached to one end of the spring. The phosphate bonds are symbolized by springs ...
... compressing a spring. The tightly coiled spring has potential energy. When the compressed spring relaxes, its potential energy is released. The spring's kinetic energy can be used to perform work such as pushing a block attached to one end of the spring. The phosphate bonds are symbolized by springs ...
Section 3.6
... the investigation of bright line spectra and of magnetic effects upon these spectra—both of which preceded the theory that attempts to explain them in terms of atomic structure. ...
... the investigation of bright line spectra and of magnetic effects upon these spectra—both of which preceded the theory that attempts to explain them in terms of atomic structure. ...
cellular respiration
... and different environmental conditions. In wine-making, grapes are crushed to release the juice which contains sugars. Yeasts are added to this fluid, fermentation occurs which produces alcohol. When the alcohol concentration reaches about 12 per cent (v/v), this kills the yeast cells and fermentati ...
... and different environmental conditions. In wine-making, grapes are crushed to release the juice which contains sugars. Yeasts are added to this fluid, fermentation occurs which produces alcohol. When the alcohol concentration reaches about 12 per cent (v/v), this kills the yeast cells and fermentati ...
BIOLOGY
... in the mitochondria. In this chain, electrons are transferred from one protein to another, RELEASING energy in the process. OXYGEN is the final electron acceptor in this process. Oxygen reacts with hydrogen and electrons to form water (H2O). Oxygen is important in the body since without it the prote ...
... in the mitochondria. In this chain, electrons are transferred from one protein to another, RELEASING energy in the process. OXYGEN is the final electron acceptor in this process. Oxygen reacts with hydrogen and electrons to form water (H2O). Oxygen is important in the body since without it the prote ...
Cellular respiration
... oxaloacetate. The net energy gain from one cycle is 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 GTP; the GTP may subsequently be used to produce ATP. Thus, the total energy yield from one whole glucose molecule (2 pyruvate molecules) is 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, and 2 ATP. ...
... oxaloacetate. The net energy gain from one cycle is 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 GTP; the GTP may subsequently be used to produce ATP. Thus, the total energy yield from one whole glucose molecule (2 pyruvate molecules) is 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, and 2 ATP. ...
Final Review
... 11. In steps 5-8 of the citric acid cycle, the high-energy molecules ___GTP, NADH_____, produced, and ___oxaloacetate___ is regenerated to begin another turn of the cycle. ...
... 11. In steps 5-8 of the citric acid cycle, the high-energy molecules ___GTP, NADH_____, produced, and ___oxaloacetate___ is regenerated to begin another turn of the cycle. ...
Chem 2B
... 11. In steps 5-8 of the citric acid cycle, the high-energy molecules ___GTP, NADH_____, produced, and ___oxaloacetate___ is regenerated to begin another turn of the cycle. ...
... 11. In steps 5-8 of the citric acid cycle, the high-energy molecules ___GTP, NADH_____, produced, and ___oxaloacetate___ is regenerated to begin another turn of the cycle. ...
APBioReview
... Pyruvate (See last slide) goes into the Krebs cycle (AKA the Citric Acid Cycle). In a series of steps enzymes transfer electrons to coenzyme acceptors NAD+ and FAD, CO2 released. ...
... Pyruvate (See last slide) goes into the Krebs cycle (AKA the Citric Acid Cycle). In a series of steps enzymes transfer electrons to coenzyme acceptors NAD+ and FAD, CO2 released. ...
Physiology for Coaches
... exercise, in sporting terms is primarily used in short high intensity activities such as weight lifting and sprinting. In this system two reactions occur ...
... exercise, in sporting terms is primarily used in short high intensity activities such as weight lifting and sprinting. In this system two reactions occur ...
Metabolism Teaching Notes ***Print off slides 7,12,13, 16, 20, 23, 24
... by gaining electrons (i.e. they converted from NAD+ or FADH respectively by being reduced) during glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation and Kreb’s Cycle. o NADH and FADH2 are then fed into electron transport system where they are oxidized slowly and thus lose their electrons slowly to create proton m ...
... by gaining electrons (i.e. they converted from NAD+ or FADH respectively by being reduced) during glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation and Kreb’s Cycle. o NADH and FADH2 are then fed into electron transport system where they are oxidized slowly and thus lose their electrons slowly to create proton m ...
Chapter 9 Presentation
... • The numerous steps of the ETC harness the energy released from the glucose metabolism. Each intermediate is more electronegative than the previous one and eventually the electrons reach O2 forming water. During the electron transfers, small amounts of energy are transferred and energy is released ...
... • The numerous steps of the ETC harness the energy released from the glucose metabolism. Each intermediate is more electronegative than the previous one and eventually the electrons reach O2 forming water. During the electron transfers, small amounts of energy are transferred and energy is released ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 Part A
... 1. What are cytochromes? 2. Write a note on the amphoteric nature of proteins. 3. Comment on the following: (i) Isomerization (ii) Tautomerization. 4. What is called line Weaker Burk equation? 5. What is V-Max? 6. Differentiate LDL from HDL. 7. What is chemi-osmotic hypothesis? 8. Comment on auto ox ...
... 1. What are cytochromes? 2. Write a note on the amphoteric nature of proteins. 3. Comment on the following: (i) Isomerization (ii) Tautomerization. 4. What is called line Weaker Burk equation? 5. What is V-Max? 6. Differentiate LDL from HDL. 7. What is chemi-osmotic hypothesis? 8. Comment on auto ox ...
Cellular Respiration
... • The electrons are eventually passed to Oxygen. This makes Oxygen very negative. It quickly bonds with H+ to form water. – The H+ that has built up in the intermembrane space wants out! It flows through a molecule called ATP synthase. As it does ATP is formed. • Each NADH that donates electrons to ...
... • The electrons are eventually passed to Oxygen. This makes Oxygen very negative. It quickly bonds with H+ to form water. – The H+ that has built up in the intermembrane space wants out! It flows through a molecule called ATP synthase. As it does ATP is formed. • Each NADH that donates electrons to ...
Microbial Metabolism
... • Anaerobic microbe – Does not use oxygen – Final electron acceptor is an inorganic molecule other than O2 ...
... • Anaerobic microbe – Does not use oxygen – Final electron acceptor is an inorganic molecule other than O2 ...
Electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of compounds that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions, and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. This creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis, or the generation of chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The final acceptor of electrons in the electron transport chain is molecular oxygen.Electron transport chains are used for extracting energy via redox reactions from sunlight in photosynthesis or, such as in the case of the oxidation of sugars, cellular respiration. In eukaryotes, an important electron transport chain is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane where it serves as the site of oxidative phosphorylation through the use of ATP synthase. It is also found in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast in photosynthetic eukaryotes. In bacteria, the electron transport chain is located in their cell membrane.In chloroplasts, light drives the conversion of water to oxygen and NADP+ to NADPH with transfer of H+ ions across chloroplast membranes. In mitochondria, it is the conversion of oxygen to water, NADH to NAD+ and succinate to fumarate that are required to generate the proton gradient. Electron transport chains are major sites of premature electron leakage to oxygen, generating superoxide and potentially resulting in increased oxidative stress.