Exploring the Ichetucknee River System: A Stoichiometric
... stoichiometric signatures; yet these signatures exhibit daily, seasonal and episodic variation. ...
... stoichiometric signatures; yet these signatures exhibit daily, seasonal and episodic variation. ...
Introduction to the Earth
... especially in loss of biological diversity (biodiversity) Rapid expansion of urban and suburban areas decreases available habitat Deforestation Expansion of farming into marginal environments Land use that is insensitive to long term changes • Salinization ...
... especially in loss of biological diversity (biodiversity) Rapid expansion of urban and suburban areas decreases available habitat Deforestation Expansion of farming into marginal environments Land use that is insensitive to long term changes • Salinization ...
Outline 7
... Outline of Lecture 7 A. Views of communities B. Coevolution C. If there are so many herbivores why are there any plants left? D. Animal defenses E. Mimicry 1. Batesian 2. Mullerian F. Community diveristy G. Are all species equally important to community functioning? H. Succession types I. Succession ...
... Outline of Lecture 7 A. Views of communities B. Coevolution C. If there are so many herbivores why are there any plants left? D. Animal defenses E. Mimicry 1. Batesian 2. Mullerian F. Community diveristy G. Are all species equally important to community functioning? H. Succession types I. Succession ...
dependance
... The concept of paradigm (Kuhn) is more often used in ecology tthan research programme We will first discuss the differences between the two concepts, and their usefulness to assess the plurality of science ...
... The concept of paradigm (Kuhn) is more often used in ecology tthan research programme We will first discuss the differences between the two concepts, and their usefulness to assess the plurality of science ...
8 questions - University of San Diego
... a. Life expectancy of less than 45 years versus greater than 75 years b. Total fertility rate of about 5 versus less than 2 children c. Adult literacy of 60% versus 100% d. CO2 emissions of less than 500 lbs per person per year versus more than 10 tons per person per year e. Annual GDP of about $3,0 ...
... a. Life expectancy of less than 45 years versus greater than 75 years b. Total fertility rate of about 5 versus less than 2 children c. Adult literacy of 60% versus 100% d. CO2 emissions of less than 500 lbs per person per year versus more than 10 tons per person per year e. Annual GDP of about $3,0 ...
help maintain balance & stability in an ecosystem?
... • Create a NEW Table of Contents for this section, call it “Ecology” • Write your homework – leave it to be stamped! • Get your folder off the counter so we can file all of the quizzes & tests from 3rd quarter! Date ...
... • Create a NEW Table of Contents for this section, call it “Ecology” • Write your homework – leave it to be stamped! • Get your folder off the counter so we can file all of the quizzes & tests from 3rd quarter! Date ...
Ecosystem
... Limiting factor - anything that can restrict the size of a population, including living and nonliving features of an ecosystem, such as predators or drought ...
... Limiting factor - anything that can restrict the size of a population, including living and nonliving features of an ecosystem, such as predators or drought ...
6. glossary of terms
... The variety of species on the planet. A species is a group of organisms, which shares a combination of genetic variations that make its members different to all other species. Members of a species can breed only with other members of the same species; they cannot breed with members of other species. ...
... The variety of species on the planet. A species is a group of organisms, which shares a combination of genetic variations that make its members different to all other species. Members of a species can breed only with other members of the same species; they cannot breed with members of other species. ...
Lecture - Chapter 4 - Biotic Components of Ecosystems
... They are often nestled within each other, and dependent upon the abiotic resources in an area. Q: How might changes in resource abundance affect communities? ...
... They are often nestled within each other, and dependent upon the abiotic resources in an area. Q: How might changes in resource abundance affect communities? ...
such as an alligator.
... • A biome is a major regional or global community of organisms _______________________________ ______________________ and plant communities that thrive there. 13.2: Biotic & Abiotic Factors Ecology is the study of the relationships among organisms and their environment. • An ecosystem includes both ...
... • A biome is a major regional or global community of organisms _______________________________ ______________________ and plant communities that thrive there. 13.2: Biotic & Abiotic Factors Ecology is the study of the relationships among organisms and their environment. • An ecosystem includes both ...
Grade 9 Science – Biology - Frontenac Secondary School
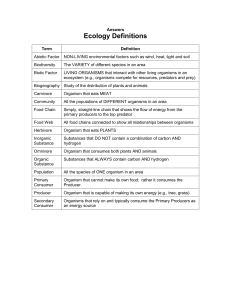
... Definitions Abiotic Factor NON-LIVING environmental factors such as wind, heat, light and soil Biotic Factor LIVING ORGANISMS that interact with other living organisms in an ecosystem (e.g., organisms compete for resources, predators and prey) Habitat Environmental area that is inhabited by a ...
... Definitions Abiotic Factor NON-LIVING environmental factors such as wind, heat, light and soil Biotic Factor LIVING ORGANISMS that interact with other living organisms in an ecosystem (e.g., organisms compete for resources, predators and prey) Habitat Environmental area that is inhabited by a ...
Frequently Asked Questions - Eurobodalla Shire Council
... The open woodland community, is recommended to be burnt between 5-40 years (NSW State Fire Interval Guidelines), to maintain health and diversity. Burning more frequently than this, and even burning continually at the lower interval, can lead to irreversible damage. The Threatened Species Conservati ...
... The open woodland community, is recommended to be burnt between 5-40 years (NSW State Fire Interval Guidelines), to maintain health and diversity. Burning more frequently than this, and even burning continually at the lower interval, can lead to irreversible damage. The Threatened Species Conservati ...
PDF: Printable Press Release
... “Salt marshes and seagrass beds depend largely on one or a few species of plants that create the habitat structure,” says Duffy. “When such species are lost, low diversity means there is often no one else to take their place and the effects can ripple out through the community of animals, potentiall ...
... “Salt marshes and seagrass beds depend largely on one or a few species of plants that create the habitat structure,” says Duffy. “When such species are lost, low diversity means there is often no one else to take their place and the effects can ripple out through the community of animals, potentiall ...
Ecosystem Interactions
... share the same niche they will compete for limited resources. 2.Members of the same species are adapted to the same niche. ...
... share the same niche they will compete for limited resources. 2.Members of the same species are adapted to the same niche. ...
BIODIVERSITY: WHY IT MATTERS Should it matter to humans that
... purifying the air, filtering harmful substances out of water, turning decayed matter into nutrients, preventing erosion and flooding, and moderating climate. It is not known how many species can be eliminated from an ecosystem without its functioning being impaired. It is likely that an ecosystem wi ...
... purifying the air, filtering harmful substances out of water, turning decayed matter into nutrients, preventing erosion and flooding, and moderating climate. It is not known how many species can be eliminated from an ecosystem without its functioning being impaired. It is likely that an ecosystem wi ...
Ecosystems Overview - earth science and environmental
... Biology. Second Edition. Blackwell Science, Massachusetts, U.S.A. ...
... Biology. Second Edition. Blackwell Science, Massachusetts, U.S.A. ...
Exam 4
... What is an ecosystem? What are some of the biotic and abiotic factors of an ecosystem? What are the two most important factors in determining the habitat and biome type? What type of biome is found in southern California? What factors cause the different ecosystems on Earth? Where is the concentrati ...
... What is an ecosystem? What are some of the biotic and abiotic factors of an ecosystem? What are the two most important factors in determining the habitat and biome type? What type of biome is found in southern California? What factors cause the different ecosystems on Earth? Where is the concentrati ...
Chapter 4: Ecosystems and Communities
... Ex. Biotic: food, predators, prey, autotrophs, competition Abiotic: space, water, sunlight, salt, oxygen, temperature (altitude/latitude) 2. Carrying Capacity: the maximum number of organisms an area can “hold” on a sustained basis Organisms grow exponentially (reproduce at a high rate) until the ...
... Ex. Biotic: food, predators, prey, autotrophs, competition Abiotic: space, water, sunlight, salt, oxygen, temperature (altitude/latitude) 2. Carrying Capacity: the maximum number of organisms an area can “hold” on a sustained basis Organisms grow exponentially (reproduce at a high rate) until the ...
Unit 12 Study Guide KEY
... 13. Answers will vary. A good answer might be: Particles thrown up into the atmosphere by the impact would have blocked and reduced the amount of sunlight reaching the Earth for several years. This would have adversely affected photosynthesis, disrupting the biogeochemical cycles. 14. a biogeochemic ...
... 13. Answers will vary. A good answer might be: Particles thrown up into the atmosphere by the impact would have blocked and reduced the amount of sunlight reaching the Earth for several years. This would have adversely affected photosynthesis, disrupting the biogeochemical cycles. 14. a biogeochemic ...
Community Ecology - Columbia University
... Abundance • Edge species are often invasive/exotic, anthropophilic, and are everywhere • May lead people to conserve areas that are less important • Do not take into account endemicity ...
... Abundance • Edge species are often invasive/exotic, anthropophilic, and are everywhere • May lead people to conserve areas that are less important • Do not take into account endemicity ...
The Value of Endangered Species: the Importance of Conserving
... valuable is understanding why so many kinds of plants and animals are valuable. ...
... valuable is understanding why so many kinds of plants and animals are valuable. ...
A market for ecosystem services
... Non-market input’s value can be derived from the value of the market input and the substitutability of the market and non-market inputs: ...
... Non-market input’s value can be derived from the value of the market input and the substitutability of the market and non-market inputs: ...
2-Principles of Ecology (notes)
... Abiotic Factors – nonliving parts of the environment air, temperature, light, minerals, water, soil ...
... Abiotic Factors – nonliving parts of the environment air, temperature, light, minerals, water, soil ...
Restoration ecology

Restoration ecology emerged as a separate field in ecology in the 1980s. It is the scientific study supporting the practice of ecological restoration, which is the practice of renewing and restoring degraded, damaged, or destroyed ecosystems and habitats in the environment by active human intervention and action. The term ""restoration ecology"" is therefore commonly used for the academic study of the process, whereas the term ""ecological restoration"" is commonly used for the actual project or process by restoration practitioners.