Changes Over Time
... • Biotic-living (plants, worms, bacteria, etc.) -Abiotic-nonliving (soil, water, oxygen, etc.) ...
... • Biotic-living (plants, worms, bacteria, etc.) -Abiotic-nonliving (soil, water, oxygen, etc.) ...
Includes interspecific interactions
... 1. Interspecific Competition (-/-) can lead to the competitive exclusion principle or one species will out compete another and can lead to character displacement Fundimental Niche – Niche a species could have Realized Niche – Portion of the Fundimental Niche a species lives in ...
... 1. Interspecific Competition (-/-) can lead to the competitive exclusion principle or one species will out compete another and can lead to character displacement Fundimental Niche – Niche a species could have Realized Niche – Portion of the Fundimental Niche a species lives in ...
SCIENCE NOTES - ECOSYSTEMS LESSON 1 What is an
... - An ecosystem is all the living and nonliving things in an area. Some ecosystems are small and some are large. - All living things need nonliving things (called abiotic factors) to survive. Some examples of this are water, soil, sunlight, and air. - The living things in an ecosystem are biotic fact ...
... - An ecosystem is all the living and nonliving things in an area. Some ecosystems are small and some are large. - All living things need nonliving things (called abiotic factors) to survive. Some examples of this are water, soil, sunlight, and air. - The living things in an ecosystem are biotic fact ...
1.1 Safety in the Science Classroom
... Predators have adaptations to help them catch their prey. Prey have adaptations to help avoid predators. Examples include spines and shells, camoflage and mimicry. The number of predators and prey influence each other. See pages 44 - 47 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 ...
... Predators have adaptations to help them catch their prey. Prey have adaptations to help avoid predators. Examples include spines and shells, camoflage and mimicry. The number of predators and prey influence each other. See pages 44 - 47 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 ...
Ecosystems
... Predators have adaptations to help them catch their prey. Prey have adaptations to help avoid predators. Examples include spines and shells, camoflage and mimicry. The number of predators and prey influence each other. See pages 44 - 47 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 ...
... Predators have adaptations to help them catch their prey. Prey have adaptations to help avoid predators. Examples include spines and shells, camoflage and mimicry. The number of predators and prey influence each other. See pages 44 - 47 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 ...
1) Chapter 21 - Ecology Vocabulary
... Population – a group of the same type of organisms living in the same place at the same time. Community – all the populations that live in an ecosystem. Habitat – place where an organism lives, provides the food, shelter, moisture, temperature, and other factors required for the organism’s survival. ...
... Population – a group of the same type of organisms living in the same place at the same time. Community – all the populations that live in an ecosystem. Habitat – place where an organism lives, provides the food, shelter, moisture, temperature, and other factors required for the organism’s survival. ...
Ecology - Science
... Natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area; can be primary or secondary. Primary – begins in a place without soil Secondary – where soil already exists ...
... Natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area; can be primary or secondary. Primary – begins in a place without soil Secondary – where soil already exists ...
Life Science Notes - School City of Hobart
... formed. The pond begins to change almost as soon as it is formed. What is the first change to take place? Mud and sand wash in to make the pond shallower. 4. How do invasive species, like zebra muscles affect an ecosystem? The invasive species use up the resources that the native species need. Lesso ...
... formed. The pond begins to change almost as soon as it is formed. What is the first change to take place? Mud and sand wash in to make the pond shallower. 4. How do invasive species, like zebra muscles affect an ecosystem? The invasive species use up the resources that the native species need. Lesso ...
Ecosystems
... • Everything that exists in a particular environment. • An ecosystem includes living things, such as plants and animals, and things that are not living, such as rocks, soil, sunlight, and water. ...
... • Everything that exists in a particular environment. • An ecosystem includes living things, such as plants and animals, and things that are not living, such as rocks, soil, sunlight, and water. ...
ecosystems and agroecosystems
... and abundance of organisms. • Ecosytem: The assemblages of individuals, communities, and physical environments. – Ex. Ponds, lakes, forests etc. ...
... and abundance of organisms. • Ecosytem: The assemblages of individuals, communities, and physical environments. – Ex. Ponds, lakes, forests etc. ...
BIOLOGY 9-4 Aim: What shapes an ecosystem?
... Together, they determine the survival and growth of an organism and the productivity of the ecosystem. Habitat: where an organism lives Niche: the way an organism uses all the biotic and abiotic things in its habitat. Ex: what it eats, how it gets food…. (C) COMMUNITY INTERACTIONS The way co ...
... Together, they determine the survival and growth of an organism and the productivity of the ecosystem. Habitat: where an organism lives Niche: the way an organism uses all the biotic and abiotic things in its habitat. Ex: what it eats, how it gets food…. (C) COMMUNITY INTERACTIONS The way co ...
Ecology Domain Notes
... "Unless someone like you cares a whole awful lot, nothing s going to get better. It s not." - The Once-ler SB4a How do different groups of living things affect one another? Many organisms live together in extremely close relationships within an ecosystem. Symbiosis is the term for any biological rel ...
... "Unless someone like you cares a whole awful lot, nothing s going to get better. It s not." - The Once-ler SB4a How do different groups of living things affect one another? Many organisms live together in extremely close relationships within an ecosystem. Symbiosis is the term for any biological rel ...
Chapter 2: Living Things in Ecosystems Name: 2.1 Everything is
... The unfortunate chain of events on Borneo occured because the living things were connected to each other What is an Ecosystem? An ecosystem includes all the different organisms living in a certain area, along with their physical evironment (ex: coral reef, wetlands) Ecologists think of an ecos ...
... The unfortunate chain of events on Borneo occured because the living things were connected to each other What is an Ecosystem? An ecosystem includes all the different organisms living in a certain area, along with their physical evironment (ex: coral reef, wetlands) Ecologists think of an ecos ...
Chapter 5, Lesson 1 Interactions in an Ecosystem
... community – all the populations living in an area ...
... community – all the populations living in an area ...
Red Wolf Reintroduction Debate
... Social or economic threat Diseases captive breeding populations Human/pet safety Genetic homogeneity of the wolves bred in captivity for reintroduction. Due to controversy of its status as a true species, it may not be the same species as what was once in the region. If it isn't, it may not fill the ...
... Social or economic threat Diseases captive breeding populations Human/pet safety Genetic homogeneity of the wolves bred in captivity for reintroduction. Due to controversy of its status as a true species, it may not be the same species as what was once in the region. If it isn't, it may not fill the ...
Human Ecology Lecture 1
... ecosystem Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it is lost as heat when energy is transformed from one form to another form. ...
... ecosystem Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it is lost as heat when energy is transformed from one form to another form. ...
Ecosystems
... Organisms within an ecosystem constantly interact in order to obtain resources for life, such as water, sunlight or even habitat (a place to live). Because of these constant interactions, organisms develop certain roles or niches in their ecosystems. A niche is the way in which a particular organism ...
... Organisms within an ecosystem constantly interact in order to obtain resources for life, such as water, sunlight or even habitat (a place to live). Because of these constant interactions, organisms develop certain roles or niches in their ecosystems. A niche is the way in which a particular organism ...
Ecosystem Stability
... • People chopping down forests to make farmland, build roads, shopping malls, etc… • deforestation ...
... • People chopping down forests to make farmland, build roads, shopping malls, etc… • deforestation ...
Ecosystem
... • Ecosystem-The community of organisms that live in a particular area, along with their nonliving surroundings, make up an ecosystem. • The order of organization within an ecosystem from smallest to largest: Organism, which belongs to a population that includes other members of its species, populati ...
... • Ecosystem-The community of organisms that live in a particular area, along with their nonliving surroundings, make up an ecosystem. • The order of organization within an ecosystem from smallest to largest: Organism, which belongs to a population that includes other members of its species, populati ...
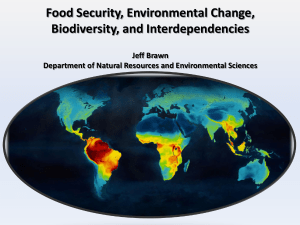
Food Security, Environmental Change, Biodiversity, and
... • The integrity of ecological systems can determine the diversity and the quality of ecological services • Environmental changes alter ecological services and dis-services to food systems and food security • The spatial scale of this dynamic can be local to ...
... • The integrity of ecological systems can determine the diversity and the quality of ecological services • Environmental changes alter ecological services and dis-services to food systems and food security • The spatial scale of this dynamic can be local to ...
a small but mighty tool for education and research in ecosystem
... Habitat for numerous invertebrates, fungi and bacteria ...
... Habitat for numerous invertebrates, fungi and bacteria ...
Ecosystem services
Humankind benefits in a multitude of ways from ecosystems. Collectively, these benefits are becoming known as ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are regularly involved in the provisioning of clean drinking water and the decomposition of wastes. While scientists and environmentalists have discussed ecosystem services implicitly for decades, the ecosystem services concept itself was popularized by the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) in the early 2000s. This grouped ecosystem services into four broad categories: provisioning, such as the production of food and water; regulating, such as the control of climate and disease; supporting, such as nutrient cycles and crop pollination; and cultural, such as spiritual and recreational benefits. To help inform decision-makers, many ecosystem services are being assigned economic values.