Name: - thalerscience
... The rusty crayfish disrupts an aquatic ecosystem by o _____________________ for the food eaten by the _____________________________ o _______________________ and young of bass and pickerel o Fewer worms and snails may cause ____________________________________ o Fewer minnows means less food for the ...
... The rusty crayfish disrupts an aquatic ecosystem by o _____________________ for the food eaten by the _____________________________ o _______________________ and young of bass and pickerel o Fewer worms and snails may cause ____________________________________ o Fewer minnows means less food for the ...
4-2 Assessment
... species compete for resources. • Predation: one animal hunts & feeds on another. ...
... species compete for resources. • Predation: one animal hunts & feeds on another. ...
Name Science Period ______ TEST Review Ecology #2 (30 pts
... 14. The largest population that an environment can support is called its carrying capacity. 15. An organism’s particular role in its habitat, or how it makes its living, is called its niche. 16. The behaviors and physical characteristics of species that allow them to live successfully in their envir ...
... 14. The largest population that an environment can support is called its carrying capacity. 15. An organism’s particular role in its habitat, or how it makes its living, is called its niche. 16. The behaviors and physical characteristics of species that allow them to live successfully in their envir ...
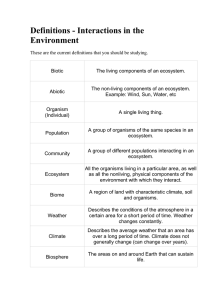
Definitions - Interactions in the Environment These are the current
... A group of organisms of the same species in an ecosystem. ...
... A group of organisms of the same species in an ecosystem. ...
Chapters 4 and 5 Review
... 34. Which characteristic of a population increases the effects of starvation, predators, and disease? a. increasing density b. exponential growth c. logistic growth d. increasing death rate 35. In the human population, better sanitation and hygiene, disease control, and agricultural technology are a ...
... 34. Which characteristic of a population increases the effects of starvation, predators, and disease? a. increasing density b. exponential growth c. logistic growth d. increasing death rate 35. In the human population, better sanitation and hygiene, disease control, and agricultural technology are a ...
4.1 Ecosystems: Everything is Connected Objectives
... • An ecosystem is made up of both living and nonliving things. – Biotic factors are the living (and once living) components of an ecosystem including all of the plants, animals, dead organisms and their parts, and waste products – Abiotic factors are the nonliving parts of an ecosystem which include ...
... • An ecosystem is made up of both living and nonliving things. – Biotic factors are the living (and once living) components of an ecosystem including all of the plants, animals, dead organisms and their parts, and waste products – Abiotic factors are the nonliving parts of an ecosystem which include ...
Chapter 13 How Ecosystems Change
... Developing Ecosystem • Secondary succession = Succession taking place in areas where there has been previous growth like an abandoned farm filed or forest clearing. ...
... Developing Ecosystem • Secondary succession = Succession taking place in areas where there has been previous growth like an abandoned farm filed or forest clearing. ...
Chapter 14 - Ecosystems
... • Ecology – means “study of the house” or the place where one lives. It is the study of the interactions of organisms with one another and with their physical environment. • Community – the organisms that live in a particular place, such as a forest. • Habitat – the physical location of a community. ...
... • Ecology – means “study of the house” or the place where one lives. It is the study of the interactions of organisms with one another and with their physical environment. • Community – the organisms that live in a particular place, such as a forest. • Habitat – the physical location of a community. ...
Interactions and Ecosystems Study Guide 1. Describe the difference
... Is the first species to arrive to an ecosystem that was devoid of life before it arrived. These species tend to be plants that can survive in harsh conditions and have adaptations that allow to grow when little soil is present 18. Explain how things like pesticides can have ‘unintended consequences’ ...
... Is the first species to arrive to an ecosystem that was devoid of life before it arrived. These species tend to be plants that can survive in harsh conditions and have adaptations that allow to grow when little soil is present 18. Explain how things like pesticides can have ‘unintended consequences’ ...
Benefits of Marine Protected Areas
... outside the boundaries- or spillover. The amount of spillover depends on the particular species and will change based on the extend of their home range, or how far they will travel in a lifetime. Through spillover, MPA benefits will not only be seen inside the boundaries, but also exported outside M ...
... outside the boundaries- or spillover. The amount of spillover depends on the particular species and will change based on the extend of their home range, or how far they will travel in a lifetime. Through spillover, MPA benefits will not only be seen inside the boundaries, but also exported outside M ...
Ecology Powerpoint Review
... Population – group of a single species living in the same place Communities - group of interacting populations Ecosystem – the community and its environment Biome – group of ecosystems with the same communities Biosphere – the circle of life ...
... Population – group of a single species living in the same place Communities - group of interacting populations Ecosystem – the community and its environment Biome – group of ecosystems with the same communities Biosphere – the circle of life ...
16 Palmer Globalization Grand Challenge
... are currently highly distributed and vary dramatically in their quality (e.g., export/import data, rates of extraction and consumption, local dependence on the resource, link between cultural preferences and ecosystem services). It will also require new models that can serve as local to global ‘acco ...
... are currently highly distributed and vary dramatically in their quality (e.g., export/import data, rates of extraction and consumption, local dependence on the resource, link between cultural preferences and ecosystem services). It will also require new models that can serve as local to global ‘acco ...
Ecology Practice Questions
... 2. An ecosystem consists of biotic and abiotic factors. 3. Clearing a forest would reduce the amount of energy available to the consumers. 4. While an understanding of the interactions between organisms and their environment was very important to early hunter and gatherer humans, it is even more imp ...
... 2. An ecosystem consists of biotic and abiotic factors. 3. Clearing a forest would reduce the amount of energy available to the consumers. 4. While an understanding of the interactions between organisms and their environment was very important to early hunter and gatherer humans, it is even more imp ...
Ecology Notes
... Limiting Factor Anything that restricts the number of individuals in a population. Includes living / biotic and nonliving / abiotic features of the ecosystem i.e. water, food, light… ...
... Limiting Factor Anything that restricts the number of individuals in a population. Includes living / biotic and nonliving / abiotic features of the ecosystem i.e. water, food, light… ...
Attachment 4
... During the summer months, water temperatures are in the balmy 70's. Winter drops near shore waters to the 40's while offshore waters remain warmed by the Gulf Stream. These warm waters allow tropical species to exist offshore. The Labrador Current comes in from the north Atlantic, bringing with it c ...
... During the summer months, water temperatures are in the balmy 70's. Winter drops near shore waters to the 40's while offshore waters remain warmed by the Gulf Stream. These warm waters allow tropical species to exist offshore. The Labrador Current comes in from the north Atlantic, bringing with it c ...
AP Study Guide for Behavior/Ecology Unit Test
... Importance of Biodiversity and reasons for loss Chapter 54 – Ecosystems What is meant by an ecosystem? Heterotrophs and autotrophs (photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs) Primary, secondary consumers, etc. Roles/niches Herbivores and carnivores. Their roles/niches Matter and Energy movement through ec ...
... Importance of Biodiversity and reasons for loss Chapter 54 – Ecosystems What is meant by an ecosystem? Heterotrophs and autotrophs (photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs) Primary, secondary consumers, etc. Roles/niches Herbivores and carnivores. Their roles/niches Matter and Energy movement through ec ...
2. Biodiversity in Ecosystems Notes word
... • The ____________ of predators and prey __________________ each other. Example: the size of the prey population can be affected by the number of predators. In the example of the lynx and the hare, ...
... • The ____________ of predators and prey __________________ each other. Example: the size of the prey population can be affected by the number of predators. In the example of the lynx and the hare, ...
Chapter 56 Guided Notes Concept 56.1: Human activities threaten
... • The enormous genetic diversity of organisms has potential for great human benefit Ecosystem Services ...
... • The enormous genetic diversity of organisms has potential for great human benefit Ecosystem Services ...
Ecosystem services
Humankind benefits in a multitude of ways from ecosystems. Collectively, these benefits are becoming known as ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are regularly involved in the provisioning of clean drinking water and the decomposition of wastes. While scientists and environmentalists have discussed ecosystem services implicitly for decades, the ecosystem services concept itself was popularized by the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) in the early 2000s. This grouped ecosystem services into four broad categories: provisioning, such as the production of food and water; regulating, such as the control of climate and disease; supporting, such as nutrient cycles and crop pollination; and cultural, such as spiritual and recreational benefits. To help inform decision-makers, many ecosystem services are being assigned economic values.