Eukaryote PowerPoint
... Functions in the collection, packaging, modification, and distribution of materials synthesized in the cell One side is always close to the rough ER (cis side) receiving products from the ER Movement occurs to discharge the product from the opposite (trans) side. Small sacs, called vesicles, can be ...
... Functions in the collection, packaging, modification, and distribution of materials synthesized in the cell One side is always close to the rough ER (cis side) receiving products from the ER Movement occurs to discharge the product from the opposite (trans) side. Small sacs, called vesicles, can be ...
Cell & Tissue Culture - Hyndland Secondary School
... Easier to produce a whole plant from single cell Nuclear totipotency – capable of producing all differentiated cell types because genome contains all genes (all cells are nuclear totipotent – in theory - DtS). Explants (cells or pieces of tissue) grown in appropriate media (light required – photoa ...
... Easier to produce a whole plant from single cell Nuclear totipotency – capable of producing all differentiated cell types because genome contains all genes (all cells are nuclear totipotent – in theory - DtS). Explants (cells or pieces of tissue) grown in appropriate media (light required – photoa ...
Bacteria are protected by a rigid cell wall composed of
... The process whereby a cell divides asexually to produce two daughter cells. ...
... The process whereby a cell divides asexually to produce two daughter cells. ...
Mitosis - Cloudfront.net
... its own chromosome and move towards the centrioles at opposite ends of the cell ...
... its own chromosome and move towards the centrioles at opposite ends of the cell ...
Name
... 31. a. Explain why the age of the mother and not that of the father is correlated with the probability of having a child with Down syndrome. Because mom’s pre-egg cells are arrested in metaphase I until ovulation. In metaphase I, the chromosome are attached to the spindle fibers. Spindle fibers dege ...
... 31. a. Explain why the age of the mother and not that of the father is correlated with the probability of having a child with Down syndrome. Because mom’s pre-egg cells are arrested in metaphase I until ovulation. In metaphase I, the chromosome are attached to the spindle fibers. Spindle fibers dege ...
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Using two successive divisions to
... chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell. Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. ...
... chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell. Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. ...
Slide 1
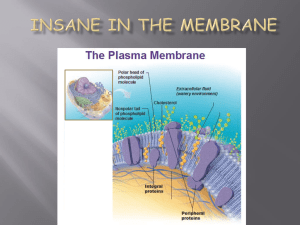
... allowing only some things in and out of the cell. Semipermiable- A membrane that can select what materials can move through. ...
... allowing only some things in and out of the cell. Semipermiable- A membrane that can select what materials can move through. ...
Meiosis Power Point
... The chromosomes line up in a similar The sister chromatids separate and way to the metaphase stage of move toward opposite ends of the ...
... The chromosomes line up in a similar The sister chromatids separate and way to the metaphase stage of move toward opposite ends of the ...
“The Cell City”
... worn-out cell parts. ► When the cell dies the lysosomes break open and break down the cell. ► Mostly found in animal cells ...
... worn-out cell parts. ► When the cell dies the lysosomes break open and break down the cell. ► Mostly found in animal cells ...
Parts of a Cell
... In a plant cell, the membrane is JUST inside the cell wall. In animal cells, the membrane is the outermost layer Contains proteins, lipids and phospholipids Decides what goes in and out of the cellnutrients goes in, waste goes out Protects the cell from the outside environment ...
... In a plant cell, the membrane is JUST inside the cell wall. In animal cells, the membrane is the outermost layer Contains proteins, lipids and phospholipids Decides what goes in and out of the cellnutrients goes in, waste goes out Protects the cell from the outside environment ...
Final Animal Organelles
... • Chloroplasts are what make plants their distinctive green color • The process of turning light into energy is called photosynthesis ...
... • Chloroplasts are what make plants their distinctive green color • The process of turning light into energy is called photosynthesis ...
Cells
... basic unit of life. All living things contain at least one cell. Cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... basic unit of life. All living things contain at least one cell. Cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
Mini-lesson on prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
... • Gram stains won’t work because of their membrane structure • Ethanol shrunk the cells in the gram stain so the cells looked like tiny dots, if you could find them • Methylene blue works great • All of your yeast should have been killed from the heat and therefore were blue ...
... • Gram stains won’t work because of their membrane structure • Ethanol shrunk the cells in the gram stain so the cells looked like tiny dots, if you could find them • Methylene blue works great • All of your yeast should have been killed from the heat and therefore were blue ...
sample exam Bio106 - KSU Faculty Member websites
... a)- Having true nucleus b)- Some move by cilia c)- They are multicellular d)- Both (a) and (b) 3. The microfilaments are made of a protein called …………… a)- Tubulin ...
... a)- Having true nucleus b)- Some move by cilia c)- They are multicellular d)- Both (a) and (b) 3. The microfilaments are made of a protein called …………… a)- Tubulin ...
Lesson Plan
... New Material: Virus Structure and Life Cycle, Cell Cycle Guided Practice: Virus Notes and Cell Cycle Notes Assessment and Closing: Virus Exit Ticket ...
... New Material: Virus Structure and Life Cycle, Cell Cycle Guided Practice: Virus Notes and Cell Cycle Notes Assessment and Closing: Virus Exit Ticket ...
CellMembranes - Mexico Central School District
... pancreas secretes insulin into your blood stream. The insulin binds insulin receptors. Some intercellular signaling happens and eventually a Glucose transporter is sent to the cell surface so that the glucose from the food you just ate can get into your cells. ...
... pancreas secretes insulin into your blood stream. The insulin binds insulin receptors. Some intercellular signaling happens and eventually a Glucose transporter is sent to the cell surface so that the glucose from the food you just ate can get into your cells. ...
Do you know that most living things start out as a single cell
... All cells are made from other cells. New cells are made when an old cell divides in two. Each of these two cells can then divide to make two more cells. This process is called cell division. As long as each new cell continues to divide, a single cell can become many cells. Cell division begins insid ...
... All cells are made from other cells. New cells are made when an old cell divides in two. Each of these two cells can then divide to make two more cells. This process is called cell division. As long as each new cell continues to divide, a single cell can become many cells. Cell division begins insid ...
Phase separation in the cell cytoplasm
... Cells exhibit a complex spatial organization, often involving organelles that are surrounded by a membrane. However, there exist many structures that are not membrane bounded. Examples are the centrosome, meiotic and mitotoc spindles as well as germ granules. An interesting question is how such stru ...
... Cells exhibit a complex spatial organization, often involving organelles that are surrounded by a membrane. However, there exist many structures that are not membrane bounded. Examples are the centrosome, meiotic and mitotoc spindles as well as germ granules. An interesting question is how such stru ...
Cells - Denbigh Baptist Christian School
... Reproduction of cells is a requirement – otherwise organism dies and becomes extinct Cell division – two different ways ...
... Reproduction of cells is a requirement – otherwise organism dies and becomes extinct Cell division – two different ways ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.