Anul 2010
... the control, consisting in significantly lower percentage of viable cells and higher cellular death in the control group as compared to the pre-treated cells, suggesting an Oxaliplatin resistant phenotype. These differences were the most noticeable in the cell group treated with clinically relevant ...
... the control, consisting in significantly lower percentage of viable cells and higher cellular death in the control group as compared to the pre-treated cells, suggesting an Oxaliplatin resistant phenotype. These differences were the most noticeable in the cell group treated with clinically relevant ...
Cells
... Functions: directs all cell activities “the Boss,” contains DNA Descriptions: Generally located in the center of the cell, surrounded by a membrane Chromosomes- Threadlike material of DNA that contains genes Gene- Piece of DNA that Contains information about organisms characteristics – Eye color, he ...
... Functions: directs all cell activities “the Boss,” contains DNA Descriptions: Generally located in the center of the cell, surrounded by a membrane Chromosomes- Threadlike material of DNA that contains genes Gene- Piece of DNA that Contains information about organisms characteristics – Eye color, he ...
Animal vs Plant Cells- Information for Diagrams
... Animal cells contain organelles known as centrioles, which are not present in plant cells. Centrioles, which help move chromosomes during cell division, are generally only visible when an animal cell is actually dividing. It is believed that because animal cells, which are softer than plant cells, c ...
... Animal cells contain organelles known as centrioles, which are not present in plant cells. Centrioles, which help move chromosomes during cell division, are generally only visible when an animal cell is actually dividing. It is believed that because animal cells, which are softer than plant cells, c ...
Chapter 7
... Cell Categories Prokaryotes: Prokaryotic cells have genetic material (e.g. DNA) that is not contained in the nucleus. On the right is a bacteria. It is an example of a prokaryotic cell. What makes a bacteria a prokaryote? It does not have a nucleus. ...
... Cell Categories Prokaryotes: Prokaryotic cells have genetic material (e.g. DNA) that is not contained in the nucleus. On the right is a bacteria. It is an example of a prokaryotic cell. What makes a bacteria a prokaryote? It does not have a nucleus. ...
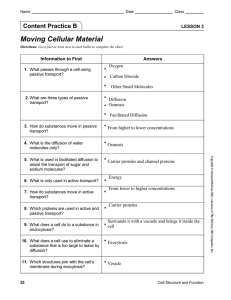
Moving Cellular Material
... 6. What is only used in active transport? 7. How do substances move in active transport? 8. Which proteins are used in active and passive transport? 9. What does a cell do to a substance in endocytosis? 10. What does a cell use to eliminate a substance that is too large to leave by diffusion? 11. Wh ...
... 6. What is only used in active transport? 7. How do substances move in active transport? 8. Which proteins are used in active and passive transport? 9. What does a cell do to a substance in endocytosis? 10. What does a cell use to eliminate a substance that is too large to leave by diffusion? 11. Wh ...
Goal 2.03 Quiz 1
... liver, which causes less water to be absorbed from the nephrons. C. The pituitary gland releases a hormone to the kidneys, which causes more water to be reabsorbed from the nephrons. D. The hypothalamus increases water available to the body, and the pituitary gland decreases the amount of water avai ...
... liver, which causes less water to be absorbed from the nephrons. C. The pituitary gland releases a hormone to the kidneys, which causes more water to be reabsorbed from the nephrons. D. The hypothalamus increases water available to the body, and the pituitary gland decreases the amount of water avai ...
Biology EOC Review - Dr. Annette M. Parrott
... is maternal and one is paternal The cell cycle – Interphase (G1, S, G2) – growth -- Mitosis – cell division Mitosis creates 2 identical diploid cells and is for the purpose of tissue repair and growth DNA condenses to form chromosomes during cell division Stages of the cell cycle ( see diagram) Inte ...
... is maternal and one is paternal The cell cycle – Interphase (G1, S, G2) – growth -- Mitosis – cell division Mitosis creates 2 identical diploid cells and is for the purpose of tissue repair and growth DNA condenses to form chromosomes during cell division Stages of the cell cycle ( see diagram) Inte ...
SBI 3CI
... It is rough or smooth& transports material through tubes thast are connected together in the cytoplasm It has tubes that are NOT connected together in the cytoplasm and it packages material like protein to be excreted from the cell. They’re vacuoles with digestive enzymes & found only in animal cell ...
... It is rough or smooth& transports material through tubes thast are connected together in the cytoplasm It has tubes that are NOT connected together in the cytoplasm and it packages material like protein to be excreted from the cell. They’re vacuoles with digestive enzymes & found only in animal cell ...
CELL PROBLEMS
... 17. Assume that two plant cells have identical volumes in water. When the cells are placed in 0.3 M sucrose (table sugar, consisting of linked glucose and fructose molecules), cell A shrinks very little and is still turgid; cell B shrinks more and is flaccid (no turgor pressure). A. When they were i ...
... 17. Assume that two plant cells have identical volumes in water. When the cells are placed in 0.3 M sucrose (table sugar, consisting of linked glucose and fructose molecules), cell A shrinks very little and is still turgid; cell B shrinks more and is flaccid (no turgor pressure). A. When they were i ...
Extra cellular components 15
... Plasmodesmata consists of a canal, lined by plasmamembrane. It has a simple or branched tubule known as desmotubule which is an extension of endoplasmic reticulum. ...
... Plasmodesmata consists of a canal, lined by plasmamembrane. It has a simple or branched tubule known as desmotubule which is an extension of endoplasmic reticulum. ...
Notes guide 2-3 Plant and Animal Cells 1. The two main types of
... 14. How are organs in the body dependent upon one another? __________________________________________________________ 15. ___________________ are composed of two or more different organs that work together to provide a common function. Examples include: _________________ ____________________________ ...
... 14. How are organs in the body dependent upon one another? __________________________________________________________ 15. ___________________ are composed of two or more different organs that work together to provide a common function. Examples include: _________________ ____________________________ ...
To assign fewer questions, you may want to skip the questions with
... vacuole—production of ATP 14. Just like complex organisms, cells are able to survive by coordinating various activities. Complex organisms have a variety of systems, and cells have a variety of organelles that work together for survival. Describe the roles of two organelles. In your answer be sure t ...
... vacuole—production of ATP 14. Just like complex organisms, cells are able to survive by coordinating various activities. Complex organisms have a variety of systems, and cells have a variety of organelles that work together for survival. Describe the roles of two organelles. In your answer be sure t ...
Model Paper
... Attempt all parts of Section – A. Section –A must be return to the superintendent after ...
... Attempt all parts of Section – A. Section –A must be return to the superintendent after ...
Cell Structures Unit
... Separate mass surrounded by a semipermeable membrane The basic structural unit of life All organisms are composed of one or more cells ...
... Separate mass surrounded by a semipermeable membrane The basic structural unit of life All organisms are composed of one or more cells ...
PRE-ASSESSMENT
... Disagree 3. Originally, people believed that life could appear suddenly from non-living materials. ...
... Disagree 3. Originally, people believed that life could appear suddenly from non-living materials. ...
File
... Homeostasis (maintain stable internal environment for cell survival) Substances need to move in and out of the cell as they are needed ...
... Homeostasis (maintain stable internal environment for cell survival) Substances need to move in and out of the cell as they are needed ...
Cell Nucleus
... The nucleus is only found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the genetic material (the DNA) of the cell. The genetic material of the nucleus is like a set of instructions. These instructions tell the cell how to build molecules needed for the cell to function properly. That is, the DNA tells t ...
... The nucleus is only found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the genetic material (the DNA) of the cell. The genetic material of the nucleus is like a set of instructions. These instructions tell the cell how to build molecules needed for the cell to function properly. That is, the DNA tells t ...
Cell Dudes From Long Ago - CCA Science
... medical doctor. He concluded that all cells come from other cells He pushed the idea that diseases usually result from problems with cells rather than from problems with other bigger parts of the ...
... medical doctor. He concluded that all cells come from other cells He pushed the idea that diseases usually result from problems with cells rather than from problems with other bigger parts of the ...
Section 3
... the DNA and organelles are copied and the cell is preparing itself to enter the mitosis phases. Mitosis Phase 1 called prophase. During prophase, the DNA begins to “twist” together and darken within the cell. (Imagine tiny, thin fibers twisting. These fibers will become thicker, shorter and more vis ...
... the DNA and organelles are copied and the cell is preparing itself to enter the mitosis phases. Mitosis Phase 1 called prophase. During prophase, the DNA begins to “twist” together and darken within the cell. (Imagine tiny, thin fibers twisting. These fibers will become thicker, shorter and more vis ...
Introduction to Cellular and Molecular Biology 205
... focus in 1859 when Charles Darwin published On ...
... focus in 1859 when Charles Darwin published On ...
Prokaryotic Cells
... •Others pass through parts of the cell not stained to form an image on a phosphorescent screen •Because the scattered electrons are lost from the beam, the stained regions show up as dark •Thus the image is a montage of light (non stained) and ...
... •Others pass through parts of the cell not stained to form an image on a phosphorescent screen •Because the scattered electrons are lost from the beam, the stained regions show up as dark •Thus the image is a montage of light (non stained) and ...
rickettsia-notes
... Most of these tiny non-motile Gram –negative Bacteria are obligate parasites able to grow only within host cells as parasites. In morphological appearance they are bacilli or cocci .Rickettsias are cultivated on yolk sac of chicken embryo are either rod like or rounded ranging from 0.5 m to 2 m. T ...
... Most of these tiny non-motile Gram –negative Bacteria are obligate parasites able to grow only within host cells as parasites. In morphological appearance they are bacilli or cocci .Rickettsias are cultivated on yolk sac of chicken embryo are either rod like or rounded ranging from 0.5 m to 2 m. T ...
Overview of Cell Organelles
... animal cell organelles (including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole). ...
... animal cell organelles (including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole). ...
CELL GROWTH, CELL REPRODUCTION AND MITOSIS
... cell. Yes, you were just one tiny cell that people needed a microscope to see. Then one day that cell underwent mitosis, which means cell division. Everything inside that cell was copied (the nucleus, the mitochondria, the vacuoles, all the DNA, etc.) so that when the cell split, both the new cell a ...
... cell. Yes, you were just one tiny cell that people needed a microscope to see. Then one day that cell underwent mitosis, which means cell division. Everything inside that cell was copied (the nucleus, the mitochondria, the vacuoles, all the DNA, etc.) so that when the cell split, both the new cell a ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.