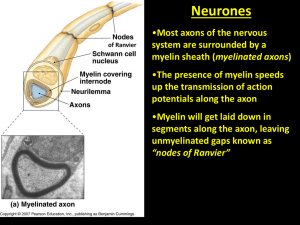
Myelin Sheaths Plant Hormone Intro
... - negative geotropism – shoots tend to grow away from pull of gravity. - positive geotropism – roots tend to grow towards the pull of gravity. ...
... - negative geotropism – shoots tend to grow away from pull of gravity. - positive geotropism – roots tend to grow towards the pull of gravity. ...
Morphology of the Cell Wall
... whereas the coextensive network of pectins provides the cell wall with the ability to resist compression. In addition to these networks, a small amount of protein can be found in all plant primary cell walls. Some of this protein is thought to increase mechanical strength and part of it consists of ...
... whereas the coextensive network of pectins provides the cell wall with the ability to resist compression. In addition to these networks, a small amount of protein can be found in all plant primary cell walls. Some of this protein is thought to increase mechanical strength and part of it consists of ...
Chapter 2 Test
... 10. Why do capillaries have such thin walls? A. So nutrients and gases have an easier time diffusing in and out. B. So it can hold more blood. C. To fit inside the human body. D. To provide structural support for the circulatory system 11. The total of all chemical reactions that happen in a cell an ...
... 10. Why do capillaries have such thin walls? A. So nutrients and gases have an easier time diffusing in and out. B. So it can hold more blood. C. To fit inside the human body. D. To provide structural support for the circulatory system 11. The total of all chemical reactions that happen in a cell an ...
AP Biology Cells Unit 2_1
... junctions) provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to an adjacent cell. Gap junctions consist of special membrane proteins that surround a pore through which ions, sugars, amino acids, and other small molecules may pass. Gap junctions are necessary for communication between cells in many types of ...
... junctions) provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to an adjacent cell. Gap junctions consist of special membrane proteins that surround a pore through which ions, sugars, amino acids, and other small molecules may pass. Gap junctions are necessary for communication between cells in many types of ...
CH 3 Outline
... Called “engines” because they move things around in a cell or even the entire cell ...
... Called “engines” because they move things around in a cell or even the entire cell ...
Bioreactors for steady state cell culture - Institute of Bio
... Quasi-VivoTM Cell Culture Systems Chamber design Minimises bubble formation and shear stress Shape & dimensions similar to 24 well plates. Facilitates cell transfer …from seeding to the bio-module Cell biologists familiar with conventional multi-well plates rapidly able to use ...the system Prop ...
... Quasi-VivoTM Cell Culture Systems Chamber design Minimises bubble formation and shear stress Shape & dimensions similar to 24 well plates. Facilitates cell transfer …from seeding to the bio-module Cell biologists familiar with conventional multi-well plates rapidly able to use ...the system Prop ...
CHAPTER 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL
... Conservation of matter states that matter cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be converted from one form to another. Conservation of energy states you cannot destroy or create energy only convert it from one form to another. Entropy is a measure of disorder or randomness- everything that hap ...
... Conservation of matter states that matter cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be converted from one form to another. Conservation of energy states you cannot destroy or create energy only convert it from one form to another. Entropy is a measure of disorder or randomness- everything that hap ...
Waste Removal - Pro and Eukaryotes
... The lysosome has digestive enzymes that will break down waste material. Vacuoles can help in this process by storing substances that need to be disposed of and sending them to the lysosome to digest The digested material will leave the cell through the cell membrane http://www.biology4kids.com/files ...
... The lysosome has digestive enzymes that will break down waste material. Vacuoles can help in this process by storing substances that need to be disposed of and sending them to the lysosome to digest The digested material will leave the cell through the cell membrane http://www.biology4kids.com/files ...
Neuroembryology as a Process of PaYern FormaVon Outline The
... • Today, we will focus on how the brain develops as a complex process of pa5ern forma8on resul8ng in large part from self-‐ organiza8on • For development, self-‐organiza8on is a process by which components ...
... • Today, we will focus on how the brain develops as a complex process of pa5ern forma8on resul8ng in large part from self-‐ organiza8on • For development, self-‐organiza8on is a process by which components ...
Cells - Building Directory
... • 1839-German Zoologist: Theodor Schwann • Cells make up all parts of animals • 1858-German Physician: Rudolph Virchow • Cells come only from other cells ...
... • 1839-German Zoologist: Theodor Schwann • Cells make up all parts of animals • 1858-German Physician: Rudolph Virchow • Cells come only from other cells ...
Cell Diagrams with Structures and Functions
... into the cell and blocking others. centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a small body located near the nucleus - it has a dense center and radiating tubules. The centrosomes is where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and the two pa ...
... into the cell and blocking others. centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a small body located near the nucleus - it has a dense center and radiating tubules. The centrosomes is where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and the two pa ...
Micr-22 Exam 1 Study Guide Revised Spring 2016
... 27. Give examples of reservoirs, and explain their relevance to disease control. 28. Describe disease transmission methods, especially vectors. 29. Interpret epidemiology graphs: Interpret axes, labels, and data; predict trends. Pathogens (various references) 30. Be familiar with the organisms below ...
... 27. Give examples of reservoirs, and explain their relevance to disease control. 28. Describe disease transmission methods, especially vectors. 29. Interpret epidemiology graphs: Interpret axes, labels, and data; predict trends. Pathogens (various references) 30. Be familiar with the organisms below ...
Micr-22 Exam 1 Study Guide Revised Spring 2016 Test Preparation
... 27. Give examples of reservoirs, and explain their relevance to disease control. 28. Describe disease transmission methods, especially vectors. 29. Interpret epidemiology graphs: Interpret axes, labels, and data; predict trends. Pathogens (various references) 30. Be familiar with the organisms below ...
... 27. Give examples of reservoirs, and explain their relevance to disease control. 28. Describe disease transmission methods, especially vectors. 29. Interpret epidemiology graphs: Interpret axes, labels, and data; predict trends. Pathogens (various references) 30. Be familiar with the organisms below ...
Name: Date - cloudfront.net
... Answer: The cell membrane is mostly made of ______________, although there are some ________________ that help bring things into and out of the cell, and some ___________________ attached to the outside of the membrane to help with identification of the cell [communication]. 8. What is a phospholipi ...
... Answer: The cell membrane is mostly made of ______________, although there are some ________________ that help bring things into and out of the cell, and some ___________________ attached to the outside of the membrane to help with identification of the cell [communication]. 8. What is a phospholipi ...
Back to the question I
... It is a membrane-bound organelle and is surrounded by a double membrane. It communicates with the surrounding cytosol via numerous nuclear pores. The nucleus houses the DNA which stores genetic information for a cell. The DNA contains instructions for the production of the cell's proteins and for re ...
... It is a membrane-bound organelle and is surrounded by a double membrane. It communicates with the surrounding cytosol via numerous nuclear pores. The nucleus houses the DNA which stores genetic information for a cell. The DNA contains instructions for the production of the cell's proteins and for re ...
Decision One: Concept Map and Learning Unit
... life cycle and its cells, and list the traits that it inherits from its parents.) Paragraph Description of Culminating Activity: Students will choose one of the following animals: chicken, butterfly, frog, turtle, grasshopper, dog, or fish. Then the students will describe the animal’s life processes ...
... life cycle and its cells, and list the traits that it inherits from its parents.) Paragraph Description of Culminating Activity: Students will choose one of the following animals: chicken, butterfly, frog, turtle, grasshopper, dog, or fish. Then the students will describe the animal’s life processes ...
A1983QP60500001
... cells as a whole. Our experiments led to a hypothetical model of the structure of the primary cell walls of plants. The model was sketchy but useful, and the chemical data presented have, for the most part, stood the test of time. It is the model and the underlying chemistry that led to such frequen ...
... cells as a whole. Our experiments led to a hypothetical model of the structure of the primary cell walls of plants. The model was sketchy but useful, and the chemical data presented have, for the most part, stood the test of time. It is the model and the underlying chemistry that led to such frequen ...
Biology
... water and shrinks. Water moves in: if the solution is hypotonic, water moves into the cell. The cell gains water and expands in size. No net change in water movement: if the solution is isotonic, water diffuses into and out of the cell at equal rates. The cell stays the ...
... water and shrinks. Water moves in: if the solution is hypotonic, water moves into the cell. The cell gains water and expands in size. No net change in water movement: if the solution is isotonic, water diffuses into and out of the cell at equal rates. The cell stays the ...
PDF
... genes At a certain point in the development of most animal embryos, the mid-blastula transition (MBT), cell cycle progression slows down, and developmental control switches from maternal factors to zygotic transcripts. How are these two concurrent events controlled? Here, Eric Wieschaus and colleagu ...
... genes At a certain point in the development of most animal embryos, the mid-blastula transition (MBT), cell cycle progression slows down, and developmental control switches from maternal factors to zygotic transcripts. How are these two concurrent events controlled? Here, Eric Wieschaus and colleagu ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.