Cell Exam Questions
... You would expect A. the level of water to rise on the left of the membrane. B. the level of water to rise on the right of the membrane. C. the level of water to remain unchanged on both sides of the membrane. D. the concentration of sucrose to increase on the right side of the membrane. ...
... You would expect A. the level of water to rise on the left of the membrane. B. the level of water to rise on the right of the membrane. C. the level of water to remain unchanged on both sides of the membrane. D. the concentration of sucrose to increase on the right side of the membrane. ...
5.4 Asexual Reproduction
... KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. ...
... KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. ...
Prokaryotic cells
... – Describe how the structure of the plasma membrane allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for a cell – Compare the mechanisms that transport materials across the plasma membrane, (i.e., passive transport-diffusion, osmosis, facilitate diffusion; and active ...
... – Describe how the structure of the plasma membrane allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for a cell – Compare the mechanisms that transport materials across the plasma membrane, (i.e., passive transport-diffusion, osmosis, facilitate diffusion; and active ...
1 - Cell Theory
... of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (they are the smallest unit that can perform life functions). 3. Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division). Why is the Cell Theory called a Theory and not a Fact? ...
... of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (they are the smallest unit that can perform life functions). 3. Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division). Why is the Cell Theory called a Theory and not a Fact? ...
Cell Structure and Function description
... enzymes. Vital in embryonic development. Produced by the Rough E.R. and Golgi ...
... enzymes. Vital in embryonic development. Produced by the Rough E.R. and Golgi ...
Uncovering the Unexpected Site of Biosynthesis of a Major Cell Wall
... Pinpointing the site of MLG biosynthesis is no small task, as standard chemical fixation techniques used to visualize the site of enzyme function destroy the integrity of the subcellular ultrastructure. Therefore, the authors subjected various grass tissues to cryofixation using high-pressure freezi ...
... Pinpointing the site of MLG biosynthesis is no small task, as standard chemical fixation techniques used to visualize the site of enzyme function destroy the integrity of the subcellular ultrastructure. Therefore, the authors subjected various grass tissues to cryofixation using high-pressure freezi ...
Prokaryotes
... hair-like structures called flagella (14 – 20 nm diameter) rotate like a ship’s propeller protein called Flagellin, flagellar subunits basal body rotates the flagellum to cause movement of the cell Arrangement of flagella ...
... hair-like structures called flagella (14 – 20 nm diameter) rotate like a ship’s propeller protein called Flagellin, flagellar subunits basal body rotates the flagellum to cause movement of the cell Arrangement of flagella ...
Cells - Miss Gerges
... protection to the cell membrane Found outside the cell membrane in plant cells Is made of cellulose Found in plants, algae, fungi, and most ...
... protection to the cell membrane Found outside the cell membrane in plant cells Is made of cellulose Found in plants, algae, fungi, and most ...
cell parts.pages
... All the cells are enclosed in a protective membrane called the cell membrane however plant cells have an extra addition the cell wall. The cells have certain organelles that are membrane bound within them, these structures are called cellular organelles. These organelles are specified to perform cer ...
... All the cells are enclosed in a protective membrane called the cell membrane however plant cells have an extra addition the cell wall. The cells have certain organelles that are membrane bound within them, these structures are called cellular organelles. These organelles are specified to perform cer ...
Name of Organelle Location Function(s) Plasma membrane Nucleus
... 11.What is the difference between the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum? ...
... 11.What is the difference between the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum? ...
Mystery Organisms
... swim and they eat other things in the water for food. When I found one of these organisms dead on the side of the stream, I took it apart and observed its cells under the microscope. Each of the cells had a very large, darkened circle inside of it as well as other small structures that had lines aro ...
... swim and they eat other things in the water for food. When I found one of these organisms dead on the side of the stream, I took it apart and observed its cells under the microscope. Each of the cells had a very large, darkened circle inside of it as well as other small structures that had lines aro ...
Protoplasts, Spheroplasts, and L Forms The
... Figure(12) Bacterial spore Spores are much more resistant than vegetative forms to disinfectants, drying and heating, ultraviolet light. In fact sterilization procedures are assessed by their ability to kill spores ,so the moist heat (autoclaving)at 100-120co , 10-20 min. kill spores( while heating ...
... Figure(12) Bacterial spore Spores are much more resistant than vegetative forms to disinfectants, drying and heating, ultraviolet light. In fact sterilization procedures are assessed by their ability to kill spores ,so the moist heat (autoclaving)at 100-120co , 10-20 min. kill spores( while heating ...
samplequestex1
... 17. Which of the following statements regarding the Golgi apparatus is false? A) The Golgi apparatus works closely with the endoplasmic reticulum. B) The Golgi apparatus serves as a molecular warehouse and finishing factory. C) The Golgi apparatus decreases in size when a cell increases its protein ...
... 17. Which of the following statements regarding the Golgi apparatus is false? A) The Golgi apparatus works closely with the endoplasmic reticulum. B) The Golgi apparatus serves as a molecular warehouse and finishing factory. C) The Golgi apparatus decreases in size when a cell increases its protein ...
Eukaryotic Cell Analogy Project
... So what is a cell? The most basic characteristics of a cell involve DNA and ribosomes enclosed within a semipermeable cell membrane. So what is a eukaryotic cell? The most basic characteristics of a eukaryotic cell involve the nucleus (DNA enclosed within a nuclear envelope), ribosomes, and organell ...
... So what is a cell? The most basic characteristics of a cell involve DNA and ribosomes enclosed within a semipermeable cell membrane. So what is a eukaryotic cell? The most basic characteristics of a eukaryotic cell involve the nucleus (DNA enclosed within a nuclear envelope), ribosomes, and organell ...
Unit planner 8 Term 3 2015
... examining a variety of cells using a light microscope, by digital technology or by viewing a simulation distinguishing plant cells from animal or fungal cells identifying structures within cells and describing their function recognising that some organisms consist of a single cell recognising that c ...
... examining a variety of cells using a light microscope, by digital technology or by viewing a simulation distinguishing plant cells from animal or fungal cells identifying structures within cells and describing their function recognising that some organisms consist of a single cell recognising that c ...
What do Cells Look Like? Introduction Points: |230
... 7. Was the color in the plant sample particularly concentrated in any internal structure? Why might this be? What was that structure? (10pt) ...
... 7. Was the color in the plant sample particularly concentrated in any internal structure? Why might this be? What was that structure? (10pt) ...
Chapter 4 2015 - Franklin College
... The Emerald Sea Slug is capable of stealing both the genes and cell organelles that are responsible for photosynthesis from the algae • allows the slug to temporarily give up its life as an animal and instead "live like a plant,“ • first known example of horizontal gene transfer in multicellular or ...
... The Emerald Sea Slug is capable of stealing both the genes and cell organelles that are responsible for photosynthesis from the algae • allows the slug to temporarily give up its life as an animal and instead "live like a plant,“ • first known example of horizontal gene transfer in multicellular or ...
Apceth Initiates Phase II Clinical Trial for Pioneering
... Successfully Completed Phase I Clinical Study and Regulatory Approval Enable World’s First GeneticallyEngineered Cell Therapy to Enter Phase II Munich, Germany, March 26, 2015 / B3C newswire / -- apceth, a global leader in engineered cell therapies, today announced the successful completion of the P ...
... Successfully Completed Phase I Clinical Study and Regulatory Approval Enable World’s First GeneticallyEngineered Cell Therapy to Enter Phase II Munich, Germany, March 26, 2015 / B3C newswire / -- apceth, a global leader in engineered cell therapies, today announced the successful completion of the P ...
7th Grade Science Marking Period 2 Cell Organelle Project The
... The purpose of this project is for the students to strengthen their knowledge of a cell and its many structures by making a physical model. First, students are to choose between the two types of eukaryotic cells, an animal cell and a plant cell. Then students are to represent their cell and its vari ...
... The purpose of this project is for the students to strengthen their knowledge of a cell and its many structures by making a physical model. First, students are to choose between the two types of eukaryotic cells, an animal cell and a plant cell. Then students are to represent their cell and its vari ...
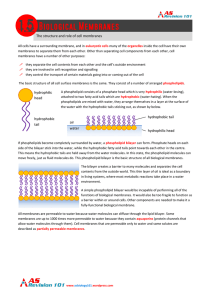
The structure and role of cell membranes hydrophilic head
... side of the bilayer stick into the water, while the hydrophobic fatty acid tails point towards each other in the centre. This means the hydrophobic tails are held away from the water molecules. In this state, the phospholipid molecules can move freely, just as fluid molecules do. This phospholipid b ...
... side of the bilayer stick into the water, while the hydrophobic fatty acid tails point towards each other in the centre. This means the hydrophobic tails are held away from the water molecules. In this state, the phospholipid molecules can move freely, just as fluid molecules do. This phospholipid b ...
Key idea 1 notes
... May be specialized to digest food or pump excess water out of the cell Larger in plant cells than in animal cells Contractile Vacuole: A specialized organelle designed to pump out excess water. Useful only ...
... May be specialized to digest food or pump excess water out of the cell Larger in plant cells than in animal cells Contractile Vacuole: A specialized organelle designed to pump out excess water. Useful only ...
Viral cultivation by cell culture
... The cell culture is the method routinely employed nowadays for identification and cultivation of viruses. Cells of various types of tissues of animals may be cultivated. But more commonly, fibroblast and muscle epithelial cells are used for the propagation of virus. The tissue is first removed from ...
... The cell culture is the method routinely employed nowadays for identification and cultivation of viruses. Cells of various types of tissues of animals may be cultivated. But more commonly, fibroblast and muscle epithelial cells are used for the propagation of virus. The tissue is first removed from ...
cells - Plain Local Schools
... A. Mitochondria are structures where cellular respiration occurs, a process that most organisms use to access energy B. ATP is the main energy source for the cell and is the end result of cellular respiration C. Mitochondria have many infoldings which allows for a larger surface area which results i ...
... A. Mitochondria are structures where cellular respiration occurs, a process that most organisms use to access energy B. ATP is the main energy source for the cell and is the end result of cellular respiration C. Mitochondria have many infoldings which allows for a larger surface area which results i ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.