032307-1
... •In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins such as histones to form chromosomes. The genes within these chr ...
... •In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins such as histones to form chromosomes. The genes within these chr ...
Ch 6 Powerpoint - Plain Local Schools
... A. Mitochondria are structures where cellular respiration occurs, a process that most organisms use to access energy B. ATP is the main energy source for the cell and is the end result of cellular respiration C. Mitochondria have many infoldings which allows for a larger surface area which results i ...
... A. Mitochondria are structures where cellular respiration occurs, a process that most organisms use to access energy B. ATP is the main energy source for the cell and is the end result of cellular respiration C. Mitochondria have many infoldings which allows for a larger surface area which results i ...
Plasmolysis DATA SHEET Pre-Lab Questions
... ** Class Copy ** Do not write on! ** Background All cells have a cell membrane, which is described as being “Selectively Permeable”. This means that some materials can move easily in or out of the cell through the cell membrane as though it were a screen. When a substance passes through the membrane ...
... ** Class Copy ** Do not write on! ** Background All cells have a cell membrane, which is described as being “Selectively Permeable”. This means that some materials can move easily in or out of the cell through the cell membrane as though it were a screen. When a substance passes through the membrane ...
10-2
... condenses and the duplicated chromosomes become visible. Outside the nucleus, a spindle starts to form. The duplicated strands of the DNA molecule can be seen to be attached along their length at an area called the centromere. Each DNA strand in the duplicated chromosome is referred to as a chromati ...
... condenses and the duplicated chromosomes become visible. Outside the nucleus, a spindle starts to form. The duplicated strands of the DNA molecule can be seen to be attached along their length at an area called the centromere. Each DNA strand in the duplicated chromosome is referred to as a chromati ...
Chemistry ID Selection - TI E2E Community
... You can find the Mathcad™ program and files at http://www.ti.com/litv/zip/sluc138bg or a link to the program can be found under the Software section on most of the bq device websites. Discharge data will be required for analysis by the tool. ...
... You can find the Mathcad™ program and files at http://www.ti.com/litv/zip/sluc138bg or a link to the program can be found under the Software section on most of the bq device websites. Discharge data will be required for analysis by the tool. ...
Microscope Lab
... 1. Place a drop of water on a clean slide. 2. Place an Elodea leaf in the drop of water, place a coverslip on top. 3. Observe under low power first (4x), then under high power (10x) Draw in Figure 9. Label the following organelles: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell wall, and chloroplasts. ...
... 1. Place a drop of water on a clean slide. 2. Place an Elodea leaf in the drop of water, place a coverslip on top. 3. Observe under low power first (4x), then under high power (10x) Draw in Figure 9. Label the following organelles: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell wall, and chloroplasts. ...
1 The Characteristics of Cells
... cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can perform all the functions needed for life. Most cells are so small you need a microscope to see them. More than 50 human cells can fit on the dot in this letter i. Some living things are made of only one cell. Others are made of millions of cells. Cells fr ...
... cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can perform all the functions needed for life. Most cells are so small you need a microscope to see them. More than 50 human cells can fit on the dot in this letter i. Some living things are made of only one cell. Others are made of millions of cells. Cells fr ...
Cell-a-bration Project
... Breaks down glucose(sugar) to throughout the cell – there make a special type of energy are many of them in a cell called ATP through cellular respiration. Oval/Spherical in shape found Transforms light energy into throughout a plant cell only, chemical energy, does green color photosynthesis, this ...
... Breaks down glucose(sugar) to throughout the cell – there make a special type of energy are many of them in a cell called ATP through cellular respiration. Oval/Spherical in shape found Transforms light energy into throughout a plant cell only, chemical energy, does green color photosynthesis, this ...
DNA Methylation Profiles of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells, a
... unprecedented applications: the creation of hiPSC lines from both healthy and diseased subjects introduces new solutions for disease modelling and translational medicine. In this perspective, we extensively applied the study of the DNAm profiles also on control and disease-specific hiPSC lines in or ...
... unprecedented applications: the creation of hiPSC lines from both healthy and diseased subjects introduces new solutions for disease modelling and translational medicine. In this perspective, we extensively applied the study of the DNAm profiles also on control and disease-specific hiPSC lines in or ...
isotonic
... the cell than the concentration of solute inside the cell. The solution outside the cell is said to be hypertonic. The water will move out of the cell until equilibrium is reached. ...
... the cell than the concentration of solute inside the cell. The solution outside the cell is said to be hypertonic. The water will move out of the cell until equilibrium is reached. ...
Module 2 Exchange and transport
... only occurs in one direction. The thick walls of xylem cells also help support plants. ...
... only occurs in one direction. The thick walls of xylem cells also help support plants. ...
Cell Transport Photosynthesis & Respiration
... D. Fermentation To obtain and use cellular energy, plant cells use which process below? A. Photosynthesis only B. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration C. Cellular respiration only D. Chemosynthesis ...
... D. Fermentation To obtain and use cellular energy, plant cells use which process below? A. Photosynthesis only B. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration C. Cellular respiration only D. Chemosynthesis ...
The Molecular Mechanisms of Pterostilbene
... Cigarette smoke is a major risk factor for bladder cancer and contributes to chemoresistance in bladder cancer patients who continue to smoke while receiving chemotherapy. Nicotine has been implicated as a co-carcinogen that promotes lung cancer development through pro-survival pathways and is known ...
... Cigarette smoke is a major risk factor for bladder cancer and contributes to chemoresistance in bladder cancer patients who continue to smoke while receiving chemotherapy. Nicotine has been implicated as a co-carcinogen that promotes lung cancer development through pro-survival pathways and is known ...
Lesson Overview
... A malignant tumor is cancerous. It invades and destroys surrounding healthy tissue and can spread to other parts of the body. The spread of cancer cells is called metastasis. Cancer cells absorb nutrients needed by other cells, block nerve connections, and prevent organs from ...
... A malignant tumor is cancerous. It invades and destroys surrounding healthy tissue and can spread to other parts of the body. The spread of cancer cells is called metastasis. Cancer cells absorb nutrients needed by other cells, block nerve connections, and prevent organs from ...
Biology Keystone Exam Review Packet
... • Part A: Identify the process in the cell membrane that produces this difference in concentration. The process is active transport (needs energy). • Part B: Explain the process that occurs as the cell produces the ion concentration gradient. There are specialized proteins in the cell membrane that ...
... • Part A: Identify the process in the cell membrane that produces this difference in concentration. The process is active transport (needs energy). • Part B: Explain the process that occurs as the cell produces the ion concentration gradient. There are specialized proteins in the cell membrane that ...
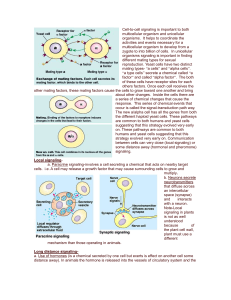
Long distance signaling
... organisms. It helps to coordinate the activities and events necessary for a multicellular organism to develop from a zygote to into billion of cells. In unicellular organisms signaling is important in finding different mating types for sexual reproduction. Yeast cells have two distinct mating types- ...
... organisms. It helps to coordinate the activities and events necessary for a multicellular organism to develop from a zygote to into billion of cells. In unicellular organisms signaling is important in finding different mating types for sexual reproduction. Yeast cells have two distinct mating types- ...
Chapter 4 Cells and Their Environment
... 9. What do plant cells have that prevent the cell from expanding too much? ___________________________________ III. Crossing the Cell Membrane 1. __________________________________ can pass across the cell membrane when aided by transport proteins. 2. Transport proteins called ____________ for ions ...
... 9. What do plant cells have that prevent the cell from expanding too much? ___________________________________ III. Crossing the Cell Membrane 1. __________________________________ can pass across the cell membrane when aided by transport proteins. 2. Transport proteins called ____________ for ions ...
10-3
... Experiments show that normal cells will reproduce until they come into contact with other cells. When cells come into contact with other cells, they respond by not growing. This demonstrates that controls on cell growth and division can be turned on and off. ...
... Experiments show that normal cells will reproduce until they come into contact with other cells. When cells come into contact with other cells, they respond by not growing. This demonstrates that controls on cell growth and division can be turned on and off. ...
Cells - Tuckahoe Common School District
... What is Active Transport? • Active transport is the process by which the cell “carries” a substance in or out. • This requires the cell to use its energy. • When does active transport occur? – If the cell membrane is not permeable for the substance. – If the concentration levels inside and outside ...
... What is Active Transport? • Active transport is the process by which the cell “carries” a substance in or out. • This requires the cell to use its energy. • When does active transport occur? – If the cell membrane is not permeable for the substance. – If the concentration levels inside and outside ...
Classification Lecture
... is misleading. Descriptions are too long to be a name. ex: Mountain Lion or Puma or Cougar ex: Starfish, dragonfly ex:“Oak with deeply divided leaves that have no hairs on their undersides and no teeth around their edges.” ...
... is misleading. Descriptions are too long to be a name. ex: Mountain Lion or Puma or Cougar ex: Starfish, dragonfly ex:“Oak with deeply divided leaves that have no hairs on their undersides and no teeth around their edges.” ...
Feb14-08
... – Heterokontous - having flagella of different length, ornamentation, position or behavior – There are approximately 100 species from fresh water and 100 species from saltwater – All tend to be in high latitude and high altitude places – They are small and uncommon 3-50µm in length Readily eaten ...
... – Heterokontous - having flagella of different length, ornamentation, position or behavior – There are approximately 100 species from fresh water and 100 species from saltwater – All tend to be in high latitude and high altitude places – They are small and uncommon 3-50µm in length Readily eaten ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.