CELL CYCLE
... Cells are in this phase most of the time Can see nucleus DNA spread out as chromatin Can’t see chromosomes DNA gets copied (S) Cell gets ready to divide ...
... Cells are in this phase most of the time Can see nucleus DNA spread out as chromatin Can’t see chromosomes DNA gets copied (S) Cell gets ready to divide ...
Cell Theory and Basic Structures - CGW-Life-Science
... 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells (cells make cells). a. Cell division = mitosis ...
... 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells (cells make cells). a. Cell division = mitosis ...
Mitosis/Meiosis Jeopardy!
... b) Cells containing a haploid number of cells are created c) 2 genetically identical daughter cells are created d) 4 genetically different daughter cells are created ...
... b) Cells containing a haploid number of cells are created c) 2 genetically identical daughter cells are created d) 4 genetically different daughter cells are created ...
Plant and Animal cells by: Cody Mills
... They contain enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen. Mitochondria are the organelles that convert energy to forms that cells can use for work. The energy factory of the cell. Nonmembrane organelles within the cells include microtubules and microfilaments. They form a framew ...
... They contain enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen. Mitochondria are the organelles that convert energy to forms that cells can use for work. The energy factory of the cell. Nonmembrane organelles within the cells include microtubules and microfilaments. They form a framew ...
Cell Division Jeopardy
... offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parents. What type of cell division do you think they use? ...
... offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parents. What type of cell division do you think they use? ...
BIOLOGY EXAM REVIEW
... b) Explain what is happening in the diagram above and use the following terms in your explanation: Red blood cell, bronchioles, alveoli, bronchi, mouth, trachea, oxygen, carbon dioxide, ...
... b) Explain what is happening in the diagram above and use the following terms in your explanation: Red blood cell, bronchioles, alveoli, bronchi, mouth, trachea, oxygen, carbon dioxide, ...
Cellular Repro genetics to post
... Cells begin split Cell membrane between cells Four gametes are formed ...
... Cells begin split Cell membrane between cells Four gametes are formed ...
cell division
... Each of the trillions of cells in your body, except reproductive cells, has a copy of the same heredity material. Cell division allows growth and replaces warn out or damaged cells We are larger and have more cells than a baby because of cell division. ...
... Each of the trillions of cells in your body, except reproductive cells, has a copy of the same heredity material. Cell division allows growth and replaces warn out or damaged cells We are larger and have more cells than a baby because of cell division. ...
3 The cell as the basic unit of life
... (d) Mitochondria. Respiration occurs in mitochondria to release energy. ...
... (d) Mitochondria. Respiration occurs in mitochondria to release energy. ...
Cell Cycle Lab Instructions
... The cell will now enter what is known as the M phase of the cell cycle, or mitosis. During mitosis, the nucleus and its contents will be divided into two nuclei with equal amounts of chromosomes (DNA) in each. The cell itself will not actually divide until later. Mitosis consists of 4 stages: propha ...
... The cell will now enter what is known as the M phase of the cell cycle, or mitosis. During mitosis, the nucleus and its contents will be divided into two nuclei with equal amounts of chromosomes (DNA) in each. The cell itself will not actually divide until later. Mitosis consists of 4 stages: propha ...
Cell Reproduction
... which is when DNA synthesis occurs The third subphase is called G2, which is a time of metabolic activity; proteins needed for cell division are produced ...
... which is when DNA synthesis occurs The third subphase is called G2, which is a time of metabolic activity; proteins needed for cell division are produced ...
Ch 12 - MsBabbey
... • The mitotic spindle is made of microtubules and proteins which help move the chromosomes around. • It is made in the centrosome (an organelle) • Asters are short microtubules that extend out from the ...
... • The mitotic spindle is made of microtubules and proteins which help move the chromosomes around. • It is made in the centrosome (an organelle) • Asters are short microtubules that extend out from the ...
013368718X_CH04_047
... 16. The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. 17. THINK VISUALLY The four circles below represent the nucleus of a cell going through mitosis. Draw four chromosomes as they go through each phase. Label each phase and describe what is happening to the DNA. ...
... 16. The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. 17. THINK VISUALLY The four circles below represent the nucleus of a cell going through mitosis. Draw four chromosomes as they go through each phase. Label each phase and describe what is happening to the DNA. ...
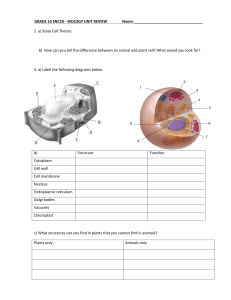
Biology 2201 Name: Organelle Assignment
... Be brief, point form is best You may only get a couple of organelles described per page! You must include the following organelles: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. ...
... Be brief, point form is best You may only get a couple of organelles described per page! You must include the following organelles: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. ...
The cell cycle Mitosis
... phases (G1 and G2); an S (for synthesis) phase, in which the genetic material is duplicated; and an M phase, in which mitosis partitions the genetic material and the cell divides. ...
... phases (G1 and G2); an S (for synthesis) phase, in which the genetic material is duplicated; and an M phase, in which mitosis partitions the genetic material and the cell divides. ...
You Light Up My Life
... Henrietta’s Immortal Cells • HeLa cells • Derived from cervical cancer that killed Henrietta Lacks • First human cells to grow and divide in culture • Used in research throughout the world ...
... Henrietta’s Immortal Cells • HeLa cells • Derived from cervical cancer that killed Henrietta Lacks • First human cells to grow and divide in culture • Used in research throughout the world ...
Mitosis and Meiosis Webquest
... 12. What is the genetic relationship between the cells in mitosis? Are the same or different? ____________ 13. Some cells divide rapidly. Some not at all after maturity. Examples? ___________________________ 14. How is binary fission a similar process? _______________________________________________ ...
... 12. What is the genetic relationship between the cells in mitosis? Are the same or different? ____________ 13. Some cells divide rapidly. Some not at all after maturity. Examples? ___________________________ 14. How is binary fission a similar process? _______________________________________________ ...
Cell Divison Mitosis and Meiosis
... Some Methods of Asexual Reproduction 1. Binary fission - equal division of both the organism cytoplasm and nucleus to form two identical organisms ex: Protist, amoeba ...
... Some Methods of Asexual Reproduction 1. Binary fission - equal division of both the organism cytoplasm and nucleus to form two identical organisms ex: Protist, amoeba ...
Meiosisorder
... CytokinesisThe cell membrane(and cell wall in plant cells) divides the cytoplasm and its contents to and create new cells. ...
... CytokinesisThe cell membrane(and cell wall in plant cells) divides the cytoplasm and its contents to and create new cells. ...
Cell Divison Mitosis and Meiosis
... Some Methods of Asexual Reproduction 1. Binary fission - equal division of both the organism cytoplasm and nucleus to form two identical organisms ex: Protist, amoeba ...
... Some Methods of Asexual Reproduction 1. Binary fission - equal division of both the organism cytoplasm and nucleus to form two identical organisms ex: Protist, amoeba ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.