Science Understandings - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... Although species my look very different, the similarities become apparent when analyzing the internal structures of organisms Although species my look very different, the similarities become apparent when analyzing their common ancestry (fossil record) Diversity of species develops gradually over ma ...
... Although species my look very different, the similarities become apparent when analyzing the internal structures of organisms Although species my look very different, the similarities become apparent when analyzing their common ancestry (fossil record) Diversity of species develops gradually over ma ...
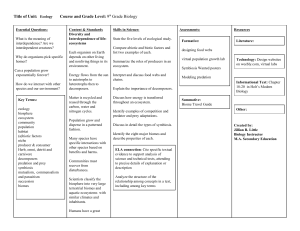
Title of Unit: Ecology Course and Grade Level: 9th Grade Biology
... Interdependence of life: ecosystems Each organism on Earth depends on other living and nonliving things in its environment. ...
... Interdependence of life: ecosystems Each organism on Earth depends on other living and nonliving things in its environment. ...
An Introduction to Ecology and Evolution
... Definitions Ecology • The word first came into use in 1869 by Ernest Haeckel • He based ecology on the Greek word oikos, meaning home or house • Ecology is the study of the relationships of organisms to their environment and to one another ...
... Definitions Ecology • The word first came into use in 1869 by Ernest Haeckel • He based ecology on the Greek word oikos, meaning home or house • Ecology is the study of the relationships of organisms to their environment and to one another ...
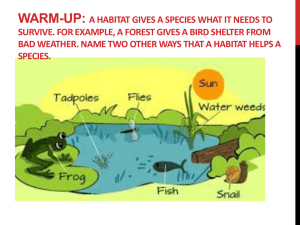
Warm-UP: A habitat gives a species what it needs to survive. For
... The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that supports life. This includes the top of Earths’s crust (lithosphere), the water on Earth’s surface (hydrosphere), and the atmosphere. ...
... The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that supports life. This includes the top of Earths’s crust (lithosphere), the water on Earth’s surface (hydrosphere), and the atmosphere. ...
Biology Lab CCR Notes Chapter 3 The Biosphere
... Biology Lab CCR Notes: Chapter 3 The Biosphere The branch of biology dealing with interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment is called ecology. The following is a correct description about the organization of an ecosystem: species make up populations, which make up comm ...
... Biology Lab CCR Notes: Chapter 3 The Biosphere The branch of biology dealing with interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment is called ecology. The following is a correct description about the organization of an ecosystem: species make up populations, which make up comm ...
Marine Ecosystems Test - Easy Peasy All-in
... 7. Plants absorb ______ from the air, and with the sun’s light energy they make highenergy carbon molecules called _______. (2) ...
... 7. Plants absorb ______ from the air, and with the sun’s light energy they make highenergy carbon molecules called _______. (2) ...
Module code SB-4323 Module Title Population, Community and
... Lower order : 10% - Describe concepts and current knowledge in population and community ecology Middle order : 10% - Analyse data from field practicals and interpret the results in written reports Higher order: 80% - Prepare and conduct oral presentations on ecological concepts - Appraise ...
... Lower order : 10% - Describe concepts and current knowledge in population and community ecology Middle order : 10% - Analyse data from field practicals and interpret the results in written reports Higher order: 80% - Prepare and conduct oral presentations on ecological concepts - Appraise ...
Evolution, Ecology, and Biodiversity
... 1. Describe the processes involved in population growth and regulation and how these can be applied to the management of natural populations 2. Describe the fundamental processes that promote species coexistence and lead to the maintenance of species diversity 3. Apply and integrate knowledge of spe ...
... 1. Describe the processes involved in population growth and regulation and how these can be applied to the management of natural populations 2. Describe the fundamental processes that promote species coexistence and lead to the maintenance of species diversity 3. Apply and integrate knowledge of spe ...
Answers to the Chapter 4 and 5 test (AP Environmental Science)
... 4. Water. Lack of water can cause a population to decline. Also, fire can cause the same effect, by destroying habitats and organisms. 5. An endangered species has a declining population like a threatened species but it is heading for extinction, unlike the other. 6. If a keystone species is removed ...
... 4. Water. Lack of water can cause a population to decline. Also, fire can cause the same effect, by destroying habitats and organisms. 5. An endangered species has a declining population like a threatened species but it is heading for extinction, unlike the other. 6. If a keystone species is removed ...
What is Ecology
... Scientists will study life at many different levels from the cellular to the entire planet – the biosphere. The Biosphere consists of the entire planet and everything in it (from about 8 km above the Earth to about 11 km below the ...
... Scientists will study life at many different levels from the cellular to the entire planet – the biosphere. The Biosphere consists of the entire planet and everything in it (from about 8 km above the Earth to about 11 km below the ...
Ecology Video Guide Sheet
... 6. Explain the following organisms interactions a. Competition b. Predation c. Symbiosis i. Mutualism ii. Commensalism iii. Parasitism 7. _____________________ species are those that are naturally found in a location, while _______________ species are accidentally or purposefully introduced to a new ...
... 6. Explain the following organisms interactions a. Competition b. Predation c. Symbiosis i. Mutualism ii. Commensalism iii. Parasitism 7. _____________________ species are those that are naturally found in a location, while _______________ species are accidentally or purposefully introduced to a new ...
AP Study Guide for Behavior/Ecology Unit Test
... Herbivores and carnivores. Their roles/niches Matter and Energy movement through ecosystems and their differences Photosynthesis vs. Cell Respiration: reactants, products, organisms that do these Importance of Cyanobacteria Effect of nutrient enrichment and Eutrophication Meaning of gross and net pr ...
... Herbivores and carnivores. Their roles/niches Matter and Energy movement through ecosystems and their differences Photosynthesis vs. Cell Respiration: reactants, products, organisms that do these Importance of Cyanobacteria Effect of nutrient enrichment and Eutrophication Meaning of gross and net pr ...
Study Guide Lesson 2
... Define Levels of Ecosystem organization: species, habitats, populations, community, ecosystems and ecology. ...
... Define Levels of Ecosystem organization: species, habitats, populations, community, ecosystems and ecology. ...
3-1 Handout
... A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area ...
... A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area ...
39-Ecology
... • Toxins in the Environment (↑ concentration in successive trophic levels of food webs) • Greenhouse Gases + Global Warming (↑CO2) • Depletion of Atmospheric Ozone (chlorinecontaining pollutants → the penetration of UV) ...
... • Toxins in the Environment (↑ concentration in successive trophic levels of food webs) • Greenhouse Gases + Global Warming (↑CO2) • Depletion of Atmospheric Ozone (chlorinecontaining pollutants → the penetration of UV) ...
Biosphere Study Guide (from GVL) - Easy Peasy All-in
... 3. Why do ecologists ask questions about events and organisms that range in complexity from an individual to the biosphere? ...
... 3. Why do ecologists ask questions about events and organisms that range in complexity from an individual to the biosphere? ...
Ecology

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, ""house""; -λογία, ""study of"") is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment. It is an interdisciplinary field that includes biology and Earth science. Ecology includes the study of interactions organisms have with each other, other organisms, and with abiotic components of their environment. Topics of interest to ecologists include the diversity, distribution, amount (biomass), and number (population) of particular organisms; as well as cooperation and competition between organisms, both within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are composed of dynamically interacting parts including organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, pedogenesis, nutrient cycling, and various niche construction activities, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. These processes are sustained by organisms with specific life history traits, and the variety of organisms is called biodiversity. Biodiversity, which refers to the varieties of species, genes, and ecosystems, enhances certain ecosystem services.Ecology is not synonymous with environment, environmentalism, natural history, or environmental science. It is closely related to evolutionary biology, genetics, and ethology. An important focus for ecologists is to improve the understanding of how biodiversity affects ecological function. Ecologists seek to explain: Life processes, interactions and adaptations The movement of materials and energy through living communities The successional development of ecosystems The abundance and distribution of organisms and biodiversity in the context of the environment.Ecology is a human science as well. There are many practical applications of ecology in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries), city planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). For example, the Circles of Sustainability approach treats ecology as more than the environment 'out there'. It is not treated as separate from humans. Organisms (including humans) and resources compose ecosystems which, in turn, maintain biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and produce natural capital like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value.The word ""ecology"" (""Ökologie"") was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919). Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle laid the foundations of ecology in their studies on natural history. Modern ecology became a much more rigorous science in the late 19th century. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection became the cornerstones of modern ecological theory.