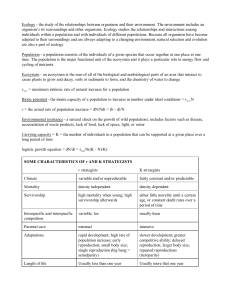
NAME: Dr. Bram AP Biology Ecology Unit Worksheet (Campbell
... 5. (A) Write the equation for logistic growth, and (B) draw a graph showing logistic population growth. ...
... 5. (A) Write the equation for logistic growth, and (B) draw a graph showing logistic population growth. ...
Ecology - the study of the relationships between organisms and their
... Ecology - the study of the relationships between organisms and their environment. The environment includes an organism’s its surroundings and other organisms. Ecology studies the relationships and interactions among individuals within a population and with individuals of different populations. Becau ...
... Ecology - the study of the relationships between organisms and their environment. The environment includes an organism’s its surroundings and other organisms. Ecology studies the relationships and interactions among individuals within a population and with individuals of different populations. Becau ...
Chapter 5, Lesson 1 Interactions in an Ecosystem
... community – all the populations living in an area ...
... community – all the populations living in an area ...
Chapter 4 Summary
... the sun through the biosphere and back into space, matter cycling, and gravity. 4-3 Ecosystem Components Biologists have classified the terrestrial portion of the biosphere into biomes. Marine and freshwater portions of the biosphere are divided into aquatic life zones. Abiotic components of an ecos ...
... the sun through the biosphere and back into space, matter cycling, and gravity. 4-3 Ecosystem Components Biologists have classified the terrestrial portion of the biosphere into biomes. Marine and freshwater portions of the biosphere are divided into aquatic life zones. Abiotic components of an ecos ...
Ch 3-6: Ecology Test Review 1.) What`s another name for
... 5.) ____________ are at the bottom of every energy pyramid. 6.) Where do they get their energy? ____________________ 7.) What’s another name for autotrophs? ...
... 5.) ____________ are at the bottom of every energy pyramid. 6.) Where do they get their energy? ____________________ 7.) What’s another name for autotrophs? ...
*Homeostasis is maintaining a stable internal environment
... *Homeostasis is maintaining a stable internal environment. *Membrane bound structures in cells are called organelles. *Ribosomes make protein. *Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides which include a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogen base. *Carbohydrates are the main energy source for organisms ...
... *Homeostasis is maintaining a stable internal environment. *Membrane bound structures in cells are called organelles. *Ribosomes make protein. *Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides which include a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogen base. *Carbohydrates are the main energy source for organisms ...
Ecology in One Page - Lakewood City School District
... Some organisms have specially defined relationships called symbiosis. This is where one organism lives on or in another. There are three types of symbiosis, including mutualism, where both organisms benefit by the symbiosis. There is also commensalisms, where neither organism benefits or is harmed, ...
... Some organisms have specially defined relationships called symbiosis. This is where one organism lives on or in another. There are three types of symbiosis, including mutualism, where both organisms benefit by the symbiosis. There is also commensalisms, where neither organism benefits or is harmed, ...
Meeting 4: Evolution, Plant and Animal Adaptations
... • Describe the above ground – below ground tissue trade off • Explain key adaptive differences between terrestrial and aquatic plants • Identify key processes common to all animals • Explain why scaling is a fundamental constraint on the evolution of organisms • Explain why positive and negativ ...
... • Describe the above ground – below ground tissue trade off • Explain key adaptive differences between terrestrial and aquatic plants • Identify key processes common to all animals • Explain why scaling is a fundamental constraint on the evolution of organisms • Explain why positive and negativ ...
Chapter 50: An Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere
... evolutionary biology. Environmental ...
... evolutionary biology. Environmental ...
Ecology
... Niche—organism’s role in its environment ~Can’t have 2 species with the same niche in the same area because of the Competitive Exclusion Principle—2 extremely similar species cannot co-exist in the same place because one will be slightly better at getting the resources and reproduce more. ...
... Niche—organism’s role in its environment ~Can’t have 2 species with the same niche in the same area because of the Competitive Exclusion Principle—2 extremely similar species cannot co-exist in the same place because one will be slightly better at getting the resources and reproduce more. ...
Ecosystem: Stability and Change
... Replacement of Organisms Ecological Succession- the natural replacement of one community in particular area with a different, and usually more complex community, over a period of time ...
... Replacement of Organisms Ecological Succession- the natural replacement of one community in particular area with a different, and usually more complex community, over a period of time ...
Ecosystem Notes - Alvin Independent School District
... growing, metabolizing nutrients, and usually reproducing. ...
... growing, metabolizing nutrients, and usually reproducing. ...
2. Biodiversity in Ecosystems Notes word
... • Within ecosystems are ____________. A habitat is where an organism ______. Abiotic Interactions in Ecosystems • The ________________________ are what ______ the ________________________to ____________ in an ecosystem. Abiotic factors include oxygen, water, nutrients, light and soil. ...
... • Within ecosystems are ____________. A habitat is where an organism ______. Abiotic Interactions in Ecosystems • The ________________________ are what ______ the ________________________to ____________ in an ecosystem. Abiotic factors include oxygen, water, nutrients, light and soil. ...
Ch 2 Principles of Ecology
... _____________ (-) orbit the nucleus. D. Organisms in Ecosystems 1. ____________________ – the ____________________ where an organism lives out its life. Ex: an earthworm feeds on organic material from the soil it moves through 2. ____________________ – the ____________________ and position a species ...
... _____________ (-) orbit the nucleus. D. Organisms in Ecosystems 1. ____________________ – the ____________________ where an organism lives out its life. Ex: an earthworm feeds on organic material from the soil it moves through 2. ____________________ – the ____________________ and position a species ...
1.1 Safety in the Science Classroom
... • A niche refers to the role an organism has within an ecosystem. How an organism fits into its environment physically, chemically and biologically. ...
... • A niche refers to the role an organism has within an ecosystem. How an organism fits into its environment physically, chemically and biologically. ...
Ch 37 HW - TeacherWeb
... there are 2 words (vs.) be sure to distinguish differences between them. Indent on the line below and write an example or sentence or draw a picture of the vocabulary. 1. community 2. interspecific 3. mutualism vs. parasitism 4. commensalisms vs. predation 5. ecological niche ...
... there are 2 words (vs.) be sure to distinguish differences between them. Indent on the line below and write an example or sentence or draw a picture of the vocabulary. 1. community 2. interspecific 3. mutualism vs. parasitism 4. commensalisms vs. predation 5. ecological niche ...
Ecology

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, ""house""; -λογία, ""study of"") is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment. It is an interdisciplinary field that includes biology and Earth science. Ecology includes the study of interactions organisms have with each other, other organisms, and with abiotic components of their environment. Topics of interest to ecologists include the diversity, distribution, amount (biomass), and number (population) of particular organisms; as well as cooperation and competition between organisms, both within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are composed of dynamically interacting parts including organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, pedogenesis, nutrient cycling, and various niche construction activities, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. These processes are sustained by organisms with specific life history traits, and the variety of organisms is called biodiversity. Biodiversity, which refers to the varieties of species, genes, and ecosystems, enhances certain ecosystem services.Ecology is not synonymous with environment, environmentalism, natural history, or environmental science. It is closely related to evolutionary biology, genetics, and ethology. An important focus for ecologists is to improve the understanding of how biodiversity affects ecological function. Ecologists seek to explain: Life processes, interactions and adaptations The movement of materials and energy through living communities The successional development of ecosystems The abundance and distribution of organisms and biodiversity in the context of the environment.Ecology is a human science as well. There are many practical applications of ecology in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries), city planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). For example, the Circles of Sustainability approach treats ecology as more than the environment 'out there'. It is not treated as separate from humans. Organisms (including humans) and resources compose ecosystems which, in turn, maintain biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and produce natural capital like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value.The word ""ecology"" (""Ökologie"") was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919). Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle laid the foundations of ecology in their studies on natural history. Modern ecology became a much more rigorous science in the late 19th century. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection became the cornerstones of modern ecological theory.