Succession
... Ecological Succession Ecosystems constantly change. A tree falling in a forest affects the forest ecosystem. A fire might alter the forest habitat so much that some species cannot survive and others can thrive. The process of one community replacing another as a result of changing abiotic and biotic ...
... Ecological Succession Ecosystems constantly change. A tree falling in a forest affects the forest ecosystem. A fire might alter the forest habitat so much that some species cannot survive and others can thrive. The process of one community replacing another as a result of changing abiotic and biotic ...
Instructor`s Manual to accompany Principles of Life
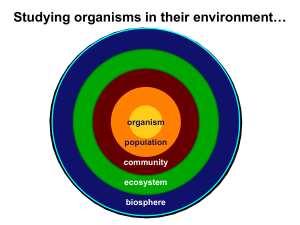
... Abiotic components of the environment—nonliving Biotic component—living organisms An ecological system—one or more organisms plus the external environment with which they interact Ecology—term coined by Ernst Haeckel in 1866; made it a legitimate scientific subject and emphasized its relevance to ev ...
... Abiotic components of the environment—nonliving Biotic component—living organisms An ecological system—one or more organisms plus the external environment with which they interact Ecology—term coined by Ernst Haeckel in 1866; made it a legitimate scientific subject and emphasized its relevance to ev ...
ECOSYSTEMS ARE ALWAYS CHANGNING
... • Primary succession: establishment of a new biological community (plants starting to grow where a glacier retreated & left a barren area) • Pioneer Species: the first living things to move into a barren environment (moss & lichen are common when no topsoil is available- have tiny rootlike anchors) ...
... • Primary succession: establishment of a new biological community (plants starting to grow where a glacier retreated & left a barren area) • Pioneer Species: the first living things to move into a barren environment (moss & lichen are common when no topsoil is available- have tiny rootlike anchors) ...
Page 1 of 9 Biology-Ecology Notes and Questions I.What is Ecology
... 8)What is logistic growth and how does that differ from exponential growth? As resources become less available,the growth slows or stops….This generally is an s-shaped curve….and occurs following a time of exponential growth---Exponential growth occurs @ ideal ...
... 8)What is logistic growth and how does that differ from exponential growth? As resources become less available,the growth slows or stops….This generally is an s-shaped curve….and occurs following a time of exponential growth---Exponential growth occurs @ ideal ...
Ecological Relationships and Succession
... These tadpoles are confined to a limited environment. What are they all competing for in that environment? Propose an explanation for why the population size affects the number of weeks before metamorphosis of the tadpoles occurs. What is different about this compared to the competition seen in grap ...
... These tadpoles are confined to a limited environment. What are they all competing for in that environment? Propose an explanation for why the population size affects the number of weeks before metamorphosis of the tadpoles occurs. What is different about this compared to the competition seen in grap ...
Unit 1 Section 2.5 Ecological Niche
... and inside of niche of the Blackburnian warbler. The principle of competition exclusion states that evolutionary forces pull the niches of similar organisms apart so that the organisms adapt differently giving rise to niche differentiation. As such, two species cannot occupy the same ecological nich ...
... and inside of niche of the Blackburnian warbler. The principle of competition exclusion states that evolutionary forces pull the niches of similar organisms apart so that the organisms adapt differently giving rise to niche differentiation. As such, two species cannot occupy the same ecological nich ...
Study of the Global Ecosystem
... community. – Ecologists investigate interactions among the organisms in a community. • How do different species of algae eating fish compete for food? • How do desert plants compete for limited water resources? ...
... community. – Ecologists investigate interactions among the organisms in a community. • How do different species of algae eating fish compete for food? • How do desert plants compete for limited water resources? ...
Descent With Modification
... collected, analyzing data and reading an essay by Thomas Malthus, Darwin formulated a theory that explained how different species originated. ...
... collected, analyzing data and reading an essay by Thomas Malthus, Darwin formulated a theory that explained how different species originated. ...
Ecosystems - Mr Goldbaum`s Biology CLass Page
... is the study of Ecosystems Ecosystems consist of both biological and physical factors interacting, known as biotic and abiotic factors. Examples of ecosystems – marine, alpine, desert Ecosystems are largely self-sustaining they can continue into the future largely without inputs from outside t ...
... is the study of Ecosystems Ecosystems consist of both biological and physical factors interacting, known as biotic and abiotic factors. Examples of ecosystems – marine, alpine, desert Ecosystems are largely self-sustaining they can continue into the future largely without inputs from outside t ...
ECOLOGY AND POPULATION BIOLOGY (BIOL 314) What is this
... interactions between species. We will emphasize a knowledge of natural history and biological diversity, as well as an appreciation of the technological, statistical and mathematical aspects of research in ecology. The outcomes for this course include: 1) You will be able to “explain how science rel ...
... interactions between species. We will emphasize a knowledge of natural history and biological diversity, as well as an appreciation of the technological, statistical and mathematical aspects of research in ecology. The outcomes for this course include: 1) You will be able to “explain how science rel ...
File
... 28. Inherited Trait – a characteristic that is passed down from parents to offspring through genes. Example: blue eyes. 29. Acquired Trait – characteristics that are not passed down but instead "acquired" after birth. Example of this is: scars, pierced ears, the length of your hair, the loss of a l ...
... 28. Inherited Trait – a characteristic that is passed down from parents to offspring through genes. Example: blue eyes. 29. Acquired Trait – characteristics that are not passed down but instead "acquired" after birth. Example of this is: scars, pierced ears, the length of your hair, the loss of a l ...
T______ 1. An adaptation is an inherited trait that helps an organism
... 7. The process of how organisms acquire adaptations over time is called evolution. 8. An organism from others have descended is an ancestor. 9. Scientists believe the Earth is about 4.6 billion years old. 10. Another word for a branching diagram is a cladogram. 11. The rock layers from which most fo ...
... 7. The process of how organisms acquire adaptations over time is called evolution. 8. An organism from others have descended is an ancestor. 9. Scientists believe the Earth is about 4.6 billion years old. 10. Another word for a branching diagram is a cladogram. 11. The rock layers from which most fo ...
answers ap essays evolution
... 1. Evolution is one of the major unifying concepts of modern biology. A) Explain the mechanisms that lead to evolutionary change. B) Describe how scientists use each of the following as evidence for evolution. 1. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics 2. Comparative biochemistry 3. The fossil record ...
... 1. Evolution is one of the major unifying concepts of modern biology. A) Explain the mechanisms that lead to evolutionary change. B) Describe how scientists use each of the following as evidence for evolution. 1. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics 2. Comparative biochemistry 3. The fossil record ...
The ecosystem: the function of near waterways
... To identify species of living organisms and make conclusions about observations To illustrate them and compare them to other sources of information To understand the significance of the ecosystem and how it functions as well as the basic principles of environmental protection To value the diversity ...
... To identify species of living organisms and make conclusions about observations To illustrate them and compare them to other sources of information To understand the significance of the ecosystem and how it functions as well as the basic principles of environmental protection To value the diversity ...
Chapter 5
... A gradual process of change and replacement of the types of species in a community can take hundreds or thousands of years each new community that arises often makes it harder for the previous community to survive or the new community will not survive at all ...
... A gradual process of change and replacement of the types of species in a community can take hundreds or thousands of years each new community that arises often makes it harder for the previous community to survive or the new community will not survive at all ...
The Organization of Life
... • Over many generations natural selection causes the characteristics of populations to change. • Darwin and Fossils --remains of extinct species from which modern species evolved. ...
... • Over many generations natural selection causes the characteristics of populations to change. • Darwin and Fossils --remains of extinct species from which modern species evolved. ...
BIODIVERSITY: WHY IT MATTERS Should it matter to humans that
... Should it matter to humans that other life forms are disappearing? Many people think so. Human populations depend on plants and animals for much of their food, medicines, clothing, and shelter. Perhaps even more important, intact ecosystems perform many vital functions, like purifying the air, filte ...
... Should it matter to humans that other life forms are disappearing? Many people think so. Human populations depend on plants and animals for much of their food, medicines, clothing, and shelter. Perhaps even more important, intact ecosystems perform many vital functions, like purifying the air, filte ...
Evolution by Natural Selection NOTES
... supported by the environment. MANY of these individuals, therefore, will die. 3. Individuals whose INHERITED TRAITS give them a higher probability to SURVIVE AND REPRODUCE IN A GIVEN ENVIRONMENT, will leave more offspring. Those individuals without such advantageous inherited traits are more likely ...
... supported by the environment. MANY of these individuals, therefore, will die. 3. Individuals whose INHERITED TRAITS give them a higher probability to SURVIVE AND REPRODUCE IN A GIVEN ENVIRONMENT, will leave more offspring. Those individuals without such advantageous inherited traits are more likely ...
UNIT 6 – SYLLABUS and Parent Letter
... and utilize them by going to www.quizlet.com , type 2. abiotic 13. food web in cdurden3131 in your search 3. herbivore 14. mutualism 4. carnivore 15. commensalism 5. omnivore 16. parasitism 6. natural selection 17. generation time 7. scavengers 18. extinct 8. adaptation 19. biome 9. speciation 20. p ...
... and utilize them by going to www.quizlet.com , type 2. abiotic 13. food web in cdurden3131 in your search 3. herbivore 14. mutualism 4. carnivore 15. commensalism 5. omnivore 16. parasitism 6. natural selection 17. generation time 7. scavengers 18. extinct 8. adaptation 19. biome 9. speciation 20. p ...
Lecture 054 - Ecosystems
... Community of organisms plus the abiotic factors that exist in a certain area ...
... Community of organisms plus the abiotic factors that exist in a certain area ...
Ecology

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, ""house""; -λογία, ""study of"") is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment. It is an interdisciplinary field that includes biology and Earth science. Ecology includes the study of interactions organisms have with each other, other organisms, and with abiotic components of their environment. Topics of interest to ecologists include the diversity, distribution, amount (biomass), and number (population) of particular organisms; as well as cooperation and competition between organisms, both within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are composed of dynamically interacting parts including organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, pedogenesis, nutrient cycling, and various niche construction activities, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. These processes are sustained by organisms with specific life history traits, and the variety of organisms is called biodiversity. Biodiversity, which refers to the varieties of species, genes, and ecosystems, enhances certain ecosystem services.Ecology is not synonymous with environment, environmentalism, natural history, or environmental science. It is closely related to evolutionary biology, genetics, and ethology. An important focus for ecologists is to improve the understanding of how biodiversity affects ecological function. Ecologists seek to explain: Life processes, interactions and adaptations The movement of materials and energy through living communities The successional development of ecosystems The abundance and distribution of organisms and biodiversity in the context of the environment.Ecology is a human science as well. There are many practical applications of ecology in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries), city planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). For example, the Circles of Sustainability approach treats ecology as more than the environment 'out there'. It is not treated as separate from humans. Organisms (including humans) and resources compose ecosystems which, in turn, maintain biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and produce natural capital like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value.The word ""ecology"" (""Ökologie"") was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919). Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle laid the foundations of ecology in their studies on natural history. Modern ecology became a much more rigorous science in the late 19th century. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection became the cornerstones of modern ecological theory.