Unit 2 Study Guide
... 6. What carries out the process of nitrogen fixation? Bacteria in the roots of legume plants. 7. How is carbon stored in the biosphere? Stored in the form of fossil fuels, underground. 8. How does nitrogen in the soil return back to the atmosphere? A process called denitrification, carried out by a ...
... 6. What carries out the process of nitrogen fixation? Bacteria in the roots of legume plants. 7. How is carbon stored in the biosphere? Stored in the form of fossil fuels, underground. 8. How does nitrogen in the soil return back to the atmosphere? A process called denitrification, carried out by a ...
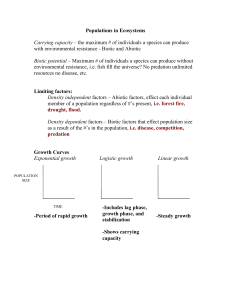
Populations in Ecosystems
... Biotic relationships Predation – organism that eats another organism Scavenger – organism that eats dead organism Competition – Interaction between two organisms for a limited resource Parasitism – Relationship between two organisms where 1 is harmed and one benefits Mutualism – 2 organisms live to ...
... Biotic relationships Predation – organism that eats another organism Scavenger – organism that eats dead organism Competition – Interaction between two organisms for a limited resource Parasitism – Relationship between two organisms where 1 is harmed and one benefits Mutualism – 2 organisms live to ...
Environmental Science
... • Species: different kinds of plants, animals, and microbes in the community • One species: individuals that are similar in appearance and distinct form other individuals. • Biological definition of a species: the entirety of a population that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring in the comm ...
... • Species: different kinds of plants, animals, and microbes in the community • One species: individuals that are similar in appearance and distinct form other individuals. • Biological definition of a species: the entirety of a population that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring in the comm ...
Ecology - Fall River Public Schools
... place ◦ Biome – a group of ecosystems that have the same and similar communities ...
... place ◦ Biome – a group of ecosystems that have the same and similar communities ...
Ecology - Review
... Competition: organisms of the same of different species attempt to use an ecological resource in the same place at the same time. o No two species can occupy the same niche in the same habitat at the same time. Predation: one organism captures and feeds another organism o Predation: the organism t ...
... Competition: organisms of the same of different species attempt to use an ecological resource in the same place at the same time. o No two species can occupy the same niche in the same habitat at the same time. Predation: one organism captures and feeds another organism o Predation: the organism t ...
Natural Selection Review Sheet
... Theories of Beginnings If natural selection results in gradual incremental changes in the genetic composition of populations, why isn't there one continuous spectrum of organisms all the way back to the origin of life? We believe there is but there are a lot of organisms (parts) missing simply becau ...
... Theories of Beginnings If natural selection results in gradual incremental changes in the genetic composition of populations, why isn't there one continuous spectrum of organisms all the way back to the origin of life? We believe there is but there are a lot of organisms (parts) missing simply becau ...
Section 3.3: Cycles of Matter
... Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. ...
... Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. ...
File - Schuette Science
... __________Species __________ __________ _________ Biosphere KEY QUESTON: (Notes and Text) Explain one major difference between the levels of species, populations, and communities versus the levels of ecosystems and biosphere. ...
... __________Species __________ __________ _________ Biosphere KEY QUESTON: (Notes and Text) Explain one major difference between the levels of species, populations, and communities versus the levels of ecosystems and biosphere. ...
Book of abstracts VLIZ Young
... It is illustrated that an integrated multidisciplinary approach is a satisfying strategy to obtain adequate system knowledge so that the complex role of wetlands can be understood. The results of OMES, an integrated research program are presented for this purpose. Mass balances indicated that tidal ...
... It is illustrated that an integrated multidisciplinary approach is a satisfying strategy to obtain adequate system knowledge so that the complex role of wetlands can be understood. The results of OMES, an integrated research program are presented for this purpose. Mass balances indicated that tidal ...
Ecology Test #1 Review
... the predator hunts and Wolf-predator consumes the prey. Moose-prey Type of relationship where Wolves hunt in a organism of the same pack. species or different species work together to improve their odds of survival. Type of relationship where Wolves compete organisms of the same for living space, sp ...
... the predator hunts and Wolf-predator consumes the prey. Moose-prey Type of relationship where Wolves hunt in a organism of the same pack. species or different species work together to improve their odds of survival. Type of relationship where Wolves compete organisms of the same for living space, sp ...
Name: ______ AP Biology Comprehension Check Enduring
... 1.C.1. Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history. 1.C.2. Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other. 1.C.3. Populations of organisms continue to evolve. Enduring Understanding 1.D: The origin of living systems is explained by ...
... 1.C.1. Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history. 1.C.2. Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other. 1.C.3. Populations of organisms continue to evolve. Enduring Understanding 1.D: The origin of living systems is explained by ...
Challenge 1: Biodiversity Crisis and recent
... Genetic diversity (between population, individuals) o Comprises genetic variation within a population and between populations o Important role in the survival and adaptability of a species Species with less genetic variation are at greater risk Vulnerability of a population to disease can increa ...
... Genetic diversity (between population, individuals) o Comprises genetic variation within a population and between populations o Important role in the survival and adaptability of a species Species with less genetic variation are at greater risk Vulnerability of a population to disease can increa ...
Science Chapter 7 Notes - msgreenshomepage
... of community changes which take place on a previously colonized, but disturbed or damaged habitat. Examples include areas which have been cleared of existing vegetation (such as after tree-felling in a woodland) and ...
... of community changes which take place on a previously colonized, but disturbed or damaged habitat. Examples include areas which have been cleared of existing vegetation (such as after tree-felling in a woodland) and ...
Evolution - GEOCITIES.ws
... • Darwin suspected that all species present on earth had begun as one species, and through a series of adaptations over millions of years, had diverged into all the species present today. • Descent with Modification: through a series of adaptations, each new species arises from another. ...
... • Darwin suspected that all species present on earth had begun as one species, and through a series of adaptations over millions of years, had diverged into all the species present today. • Descent with Modification: through a series of adaptations, each new species arises from another. ...
Name Period ____ Date ______ CLASSIFICATION AND ECOLOGY
... physical differences. What are these differences most likely caused by? ...
... physical differences. What are these differences most likely caused by? ...
Evolution - Valhalla High School
... others in their struggle for survival. Any trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce under a given set of environmental conditions is said to have adaptive value. For example, a deer that can run just a little bit faster than another will have a greater chance of escaping a predator. This w ...
... others in their struggle for survival. Any trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce under a given set of environmental conditions is said to have adaptive value. For example, a deer that can run just a little bit faster than another will have a greater chance of escaping a predator. This w ...
The overfishing debate: an eco-evolutionary perspective
... Administration has pointed to evidence that the USA is emerging from decades of overfishing onto a track of sustainability (http://www.legislative.noaa.gov/Testimony/ Schwaab030811.pdf). Others have asserted that overfishing remains a serious problem in the USA and elsewhere around the world [1]. Th ...
... Administration has pointed to evidence that the USA is emerging from decades of overfishing onto a track of sustainability (http://www.legislative.noaa.gov/Testimony/ Schwaab030811.pdf). Others have asserted that overfishing remains a serious problem in the USA and elsewhere around the world [1]. Th ...
ecosystem relationships
... into Yellowstone Park changed the niche of the Elk. • Compare and contrast the niche of two populations in ...
... into Yellowstone Park changed the niche of the Elk. • Compare and contrast the niche of two populations in ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... As well, as one population within the ecosystem changes, those populations that interact with them will also change Populations are also able to change their environment over time, particularly after a major change to that environment ...
... As well, as one population within the ecosystem changes, those populations that interact with them will also change Populations are also able to change their environment over time, particularly after a major change to that environment ...
KGA172_L2.3_final
... 1. Define ecosystem. Explain its etymology. In terms of helping us understand nature, why might it matter that ecosystem has the same origins [derivation] as household – from the Greek oikos? 2. How does Eugene Odum specifically describe ecology and in what ways is the idea of exchange important in ...
... 1. Define ecosystem. Explain its etymology. In terms of helping us understand nature, why might it matter that ecosystem has the same origins [derivation] as household – from the Greek oikos? 2. How does Eugene Odum specifically describe ecology and in what ways is the idea of exchange important in ...
AGROECOSYSTEM CONCEPT
... 1. Numbers of individuals in a population 2. Population dynamics: how and why those numbers increase or decrease over time 3. Population ecologists try to determine the processes common to all populations ...
... 1. Numbers of individuals in a population 2. Population dynamics: how and why those numbers increase or decrease over time 3. Population ecologists try to determine the processes common to all populations ...
Ecology

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, ""house""; -λογία, ""study of"") is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment. It is an interdisciplinary field that includes biology and Earth science. Ecology includes the study of interactions organisms have with each other, other organisms, and with abiotic components of their environment. Topics of interest to ecologists include the diversity, distribution, amount (biomass), and number (population) of particular organisms; as well as cooperation and competition between organisms, both within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are composed of dynamically interacting parts including organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, pedogenesis, nutrient cycling, and various niche construction activities, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. These processes are sustained by organisms with specific life history traits, and the variety of organisms is called biodiversity. Biodiversity, which refers to the varieties of species, genes, and ecosystems, enhances certain ecosystem services.Ecology is not synonymous with environment, environmentalism, natural history, or environmental science. It is closely related to evolutionary biology, genetics, and ethology. An important focus for ecologists is to improve the understanding of how biodiversity affects ecological function. Ecologists seek to explain: Life processes, interactions and adaptations The movement of materials and energy through living communities The successional development of ecosystems The abundance and distribution of organisms and biodiversity in the context of the environment.Ecology is a human science as well. There are many practical applications of ecology in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries), city planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). For example, the Circles of Sustainability approach treats ecology as more than the environment 'out there'. It is not treated as separate from humans. Organisms (including humans) and resources compose ecosystems which, in turn, maintain biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and produce natural capital like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value.The word ""ecology"" (""Ökologie"") was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919). Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle laid the foundations of ecology in their studies on natural history. Modern ecology became a much more rigorous science in the late 19th century. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection became the cornerstones of modern ecological theory.