Chloroplasts
... Bacteria evolved into different cell types • Some bacteria evolved into protists. • There are three types of protists which later evolved into more complex organisms. – Protozoa animal-like – Algae plant-like – Slime molds fungi-like ...
... Bacteria evolved into different cell types • Some bacteria evolved into protists. • There are three types of protists which later evolved into more complex organisms. – Protozoa animal-like – Algae plant-like – Slime molds fungi-like ...
Folie 1
... Most highly organized life form among protozoa. Characteristic cilia Lokomotion via cilia beating Nuclear duality, i.e. one large nucleus (macronucleus, metabolism), one small nucleus (micronucleus, reproduction) ...
... Most highly organized life form among protozoa. Characteristic cilia Lokomotion via cilia beating Nuclear duality, i.e. one large nucleus (macronucleus, metabolism), one small nucleus (micronucleus, reproduction) ...
Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes - Duncanville Middle School
... excess or worn-out organelles and food particles. They also digest bacteria and viruses that enter the cell. Why do the digestive enzymes inside a lysosome not destroy the cell? ...
... excess or worn-out organelles and food particles. They also digest bacteria and viruses that enter the cell. Why do the digestive enzymes inside a lysosome not destroy the cell? ...
Cell structure and function
... mediate attachment to surfaces some (type IV fimbriae) required for twitching motility or gliding motility that occurs in some bacteria ...
... mediate attachment to surfaces some (type IV fimbriae) required for twitching motility or gliding motility that occurs in some bacteria ...
Cell Anatomy
... • Internal cellular material • Contains three elements – Cytosol • Fluid that suspends the other elements ...
... • Internal cellular material • Contains three elements – Cytosol • Fluid that suspends the other elements ...
Assessment
... _____ 7. Which of these includes the main parts of an organ system? a. leaves on a tree c. heart and blood vessels b. stem of a flower d. large mass of amoebas _____ 8. In which of these does true multicellularity occur? a. eukaryotes c. colonial organisms b. prokaryotes d. All of the above _____ 9. ...
... _____ 7. Which of these includes the main parts of an organ system? a. leaves on a tree c. heart and blood vessels b. stem of a flower d. large mass of amoebas _____ 8. In which of these does true multicellularity occur? a. eukaryotes c. colonial organisms b. prokaryotes d. All of the above _____ 9. ...
MICROBIOLOGY
... • They are photosynthetic – make carbohydrates – passed on to other marine organisms when they are eaten • Cell walls are impregnated with silicon dioxide ...
... • They are photosynthetic – make carbohydrates – passed on to other marine organisms when they are eaten • Cell walls are impregnated with silicon dioxide ...
Cell Power Point Questions
... 12) The __________________ regulates movement of materials into and out of the cell. 13) The ________________ contains DNA and chromosomes. 14) The ________________ is the energy powerhouse of the eukaryotic cell. 15) The cell wall is absent in _________________. 16) Chloroplasts are found in ______ ...
... 12) The __________________ regulates movement of materials into and out of the cell. 13) The ________________ contains DNA and chromosomes. 14) The ________________ is the energy powerhouse of the eukaryotic cell. 15) The cell wall is absent in _________________. 16) Chloroplasts are found in ______ ...
Cellular Structures and Organelles
... Cell Membrane HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID Bilayer (two layers) with POLAR heads facing the water and NON-POLAR tails facing away from the water ...
... Cell Membrane HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID Bilayer (two layers) with POLAR heads facing the water and NON-POLAR tails facing away from the water ...
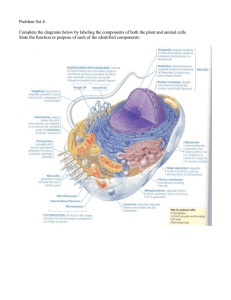
Problem Set 4:
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
Lesson 2 Bacteria.notebook
... 459 will help). peptidoglycan in 1. Eubacteria largest group, live almost everywhere, * have their cells (a protein/sugar mixture) 2. Archabacteria very similar but lack the peptidoglycan in their cell walls ...
... 459 will help). peptidoglycan in 1. Eubacteria largest group, live almost everywhere, * have their cells (a protein/sugar mixture) 2. Archabacteria very similar but lack the peptidoglycan in their cell walls ...
Cell Theory
... cells • Contain a nucleus and many other organelles • Some move using cilia, flagella or pseudopodia (false feet) • May be part of a unicellular or multicellular organism – Plants, animals, fungi, ...
... cells • Contain a nucleus and many other organelles • Some move using cilia, flagella or pseudopodia (false feet) • May be part of a unicellular or multicellular organism – Plants, animals, fungi, ...
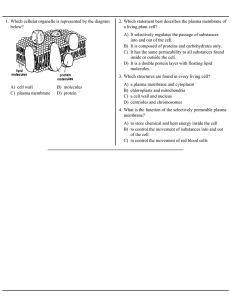
A) cell wall B) molecules C) plasma membrane D) protein 1. Which
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
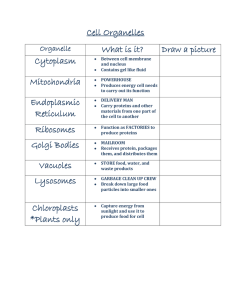
Cell Organelles
... • This is a storage organelle. Plant cells generally have one large one that takes up most of the space within the cell and is used for storage of all sorts of molecules. ...
... • This is a storage organelle. Plant cells generally have one large one that takes up most of the space within the cell and is used for storage of all sorts of molecules. ...
Cell Organelles Review Package
... 23. Why are many membranes that are present in cells interchangeable? Give an example in your explanation. __________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 24. Which organelles will probably be more abundant than others in an active eukary ...
... 23. Why are many membranes that are present in cells interchangeable? Give an example in your explanation. __________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 24. Which organelles will probably be more abundant than others in an active eukary ...
Bacteria
... 1. Bacteria are classified as prokaryotes. The genetic material in their cells is not contained in a nucleus. 2. List three characteristics of living things that bacteria possess. a. reproduce b. use energy c. cellular organization 3. What cell structure helps a bacterium move? flagellum 4. Draw the ...
... 1. Bacteria are classified as prokaryotes. The genetic material in their cells is not contained in a nucleus. 2. List three characteristics of living things that bacteria possess. a. reproduce b. use energy c. cellular organization 3. What cell structure helps a bacterium move? flagellum 4. Draw the ...
Name_________________________ KEY Ch 4 Quiz How is the
... 4. Name 2 of the 3 types of fibers that make up the cytoskeleton (1) Microfilament Intermediate filament Microtubule 5. Name 2 of the 3 types of intercellular junctions and what function they serve (2) • Tight junctions can bind cells together into leakproof sheets • Anchoring junctions link animal ...
... 4. Name 2 of the 3 types of fibers that make up the cytoskeleton (1) Microfilament Intermediate filament Microtubule 5. Name 2 of the 3 types of intercellular junctions and what function they serve (2) • Tight junctions can bind cells together into leakproof sheets • Anchoring junctions link animal ...
Centriole organelles made of microtubules involved in cell division
... Captures light energy and converts to sugar ...
... Captures light energy and converts to sugar ...
Marine Biology Cell Assessment 1) Cyanide is a poison that
... 2) Use the information and the figure below to answer the following. The diagram below shows a colony of prokaryotes and a single-celled eukaryote. The eukaryote contains organelles that resemble the three types of bacteria found in the colony of prokaryotes. More than a billion years ago, bacteria ...
... 2) Use the information and the figure below to answer the following. The diagram below shows a colony of prokaryotes and a single-celled eukaryote. The eukaryote contains organelles that resemble the three types of bacteria found in the colony of prokaryotes. More than a billion years ago, bacteria ...
Flagellum
A flagellum (/fləˈdʒɛləm/; plural: flagella) is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. Flagella are organelles defined by function rather than structure. There are large differences between different types of flagella; the prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella differ greatly in protein composition, structure, and mechanism of propulsion. However, both are used for swimming.An example of a flagellate bacterium is the ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, which uses multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium. An example of a eukaryotic flagellate cell is the mammalian sperm cell, which uses its flagellum to propel itself through the female reproductive tract. Eukaryotic flagella are structurally identical to eukaryotic cilia, although distinctions are sometimes made according to function and/or length.