Cellular Structures
... Usually covers the entire cell or a large section of a cell Function: locomotion of the cell or movement of substances within an organism ...
... Usually covers the entire cell or a large section of a cell Function: locomotion of the cell or movement of substances within an organism ...
Note questions part 4 - Peoria Public Schools
... 117. Digestion is the function of what organelle? 118. Both cilia and flagella function in ___________________ and are made of __________________. 119. What is the microtubule arrangement of cilia? Include a sketch. ...
... 117. Digestion is the function of what organelle? 118. Both cilia and flagella function in ___________________ and are made of __________________. 119. What is the microtubule arrangement of cilia? Include a sketch. ...
Basic Structure of a Cell
... 117. Digestion is the function of what organelle? 118. Both cilia and flagella function in ___________________ and are made of __________________. 119. What is the microtubule arrangement of cilia? Include a sketch. ...
... 117. Digestion is the function of what organelle? 118. Both cilia and flagella function in ___________________ and are made of __________________. 119. What is the microtubule arrangement of cilia? Include a sketch. ...
cell test review 15-16 - Mercer Island School District
... Eggmosis Lab E. Know the structure of the cell membrane and how these terms relate to its function and/or identify them in a picture: Phospholipid Cholesterol ...
... Eggmosis Lab E. Know the structure of the cell membrane and how these terms relate to its function and/or identify them in a picture: Phospholipid Cholesterol ...
Prokaryotic_cells
... for all metabolic reactions, since there are no organelles Ribosomes. The smaller (70 S) type. Nucleoid (or Nuclear Zone). The region of the cytoplasm that contains DNA. It is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. DNA. Always circular, and not associated with any proteins to form chromatin. ...
... for all metabolic reactions, since there are no organelles Ribosomes. The smaller (70 S) type. Nucleoid (or Nuclear Zone). The region of the cytoplasm that contains DNA. It is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. DNA. Always circular, and not associated with any proteins to form chromatin. ...
BIO 105 Summer 2013 Chapter 3 Part I – The Cell Cell Theory
... Objectives: By the end of lecture today you should be able to address the following points: 1. What is cell theory? 2. Identify the cellular organelles and their functions. 3. What is the difference between a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell? 4. What are the major parts of a eukaryotic cell? 5. Descr ...
... Objectives: By the end of lecture today you should be able to address the following points: 1. What is cell theory? 2. Identify the cellular organelles and their functions. 3. What is the difference between a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell? 4. What are the major parts of a eukaryotic cell? 5. Descr ...
Cell Structure & Function BINGO
... This organelle processes, packages, and stores fats and proteins produced by the ER. ...
... This organelle processes, packages, and stores fats and proteins produced by the ER. ...
Document
... Answer: Both bacterial cell walls and cytoskeletons provide structure and maintain shape. Most cell walls contain peptidoglycan, which forms a single molecule that surrounds the entire cell. Another layer, the capsule, may enclose the cell wall and can protect the bacterium from attack and from dryi ...
... Answer: Both bacterial cell walls and cytoskeletons provide structure and maintain shape. Most cell walls contain peptidoglycan, which forms a single molecule that surrounds the entire cell. Another layer, the capsule, may enclose the cell wall and can protect the bacterium from attack and from dryi ...
Cell Structure
... Freely permeable to solutes, the openings in the mesh are large and all types of molecules can pass through them. Lysozyme ( tears and saliva) -attacks peptidoglycan. It hydrolyzes the NAM - NAG linkage. Penicillin inhibits cells wall synthesis. The G+ cell wall is very sensitive to the action of ly ...
... Freely permeable to solutes, the openings in the mesh are large and all types of molecules can pass through them. Lysozyme ( tears and saliva) -attacks peptidoglycan. It hydrolyzes the NAM - NAG linkage. Penicillin inhibits cells wall synthesis. The G+ cell wall is very sensitive to the action of ly ...
4-2: Parts of a Eukaryotic Cell
... Appearance: hair-like organelles Function: assist in movement ...
... Appearance: hair-like organelles Function: assist in movement ...
PPT
... – Plant cells and bacterial cells have cell walls, • Which help protect the cells, maintain their shape, and keep the cells from absorbing too much water. ...
... – Plant cells and bacterial cells have cell walls, • Which help protect the cells, maintain their shape, and keep the cells from absorbing too much water. ...
CHEMISTRY
... Chapter 7 focuses in on the cell membrane and goes into more detail about how this part of the cell functions to control what enters and leaves a cell (= “selective permeability”). The good news is that if you were paying attention in Biology I, this should all be review! ...
... Chapter 7 focuses in on the cell membrane and goes into more detail about how this part of the cell functions to control what enters and leaves a cell (= “selective permeability”). The good news is that if you were paying attention in Biology I, this should all be review! ...
Lab 2- Bacterial cell structures/simple staining
... In this exercise, you will view prepared slides of bacteria that make capsules, spores/endospores, or have unique shapes/structures beyond the standard rods or cocci you have seen so far. Review lecture notes, Chapter 3 about all these microbes and structures. Prepared Slides to View - Work In Pairs ...
... In this exercise, you will view prepared slides of bacteria that make capsules, spores/endospores, or have unique shapes/structures beyond the standard rods or cocci you have seen so far. Review lecture notes, Chapter 3 about all these microbes and structures. Prepared Slides to View - Work In Pairs ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Notes
... Comparing Prokaryotic Cells with Eukaryotic Cells • Cells in our world come in two basic types, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. ...
... Comparing Prokaryotic Cells with Eukaryotic Cells • Cells in our world come in two basic types, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. ...
Centrosome - English at the Shore Spot
... Animal or Plant Cell? • Centrosomes are found in both • Centrioles are only in animal cells • Plants still perform • Why? Cilia and flagella for cells are surface features used for cell movement, cells in plants aren’t required to move around like those in animal cells ...
... Animal or Plant Cell? • Centrosomes are found in both • Centrioles are only in animal cells • Plants still perform • Why? Cilia and flagella for cells are surface features used for cell movement, cells in plants aren’t required to move around like those in animal cells ...
Cell Model Foldable
... a. List and define the 3 organelles that are only found or look significantly different in plant cells: Cell Wall, Chloroplasts, and Vacuole. Right Side Label Animal Cells Only a. List and define the 5 organelles that are only found or look significantly different in animal cells: Lysosome, Cent ...
... a. List and define the 3 organelles that are only found or look significantly different in plant cells: Cell Wall, Chloroplasts, and Vacuole. Right Side Label Animal Cells Only a. List and define the 5 organelles that are only found or look significantly different in animal cells: Lysosome, Cent ...
Cytology
... Cytoplasm : is the area of space outside the nucleus but which is contained within the cell membrane. It contains the organelles and fluid. The organelles are tiny structures in the cytoplasm which perform various jobs for the cell. The fluid part of the cytoplasm is called the cytosol. Cell ...
... Cytoplasm : is the area of space outside the nucleus but which is contained within the cell membrane. It contains the organelles and fluid. The organelles are tiny structures in the cytoplasm which perform various jobs for the cell. The fluid part of the cytoplasm is called the cytosol. Cell ...
10 E all qs
... A4: When the extracellular solution is higher. Q5: What is an isotonic solution? A5: When the solution inside and outside the cell are the same. DIFFICULT Q1: List three differences between a plant cell and an animal cell. A1: Animal cells don’t have a cell wall, but plant cells do. Animal cells don ...
... A4: When the extracellular solution is higher. Q5: What is an isotonic solution? A5: When the solution inside and outside the cell are the same. DIFFICULT Q1: List three differences between a plant cell and an animal cell. A1: Animal cells don’t have a cell wall, but plant cells do. Animal cells don ...
PreAssessment
... True/False. Please indicate by writing True or False on the line provided that corresponds to each statement below. 1.__________The transport of specific particles through a membrane by carrier proteins is known as facilitated diffusion. ...
... True/False. Please indicate by writing True or False on the line provided that corresponds to each statement below. 1.__________The transport of specific particles through a membrane by carrier proteins is known as facilitated diffusion. ...
Parts of the Cell
... iii. Fluid Mosaic Model: Lipid bilayers behaves more like a fluid than a solid. Organelles: internal structures that form special functions for the cell. a. Cytoplasm: material between cell membrane and nucleus that contains the organelles. b. Mitochondria: “Powerhouse” of the cell. Produce ATP whic ...
... iii. Fluid Mosaic Model: Lipid bilayers behaves more like a fluid than a solid. Organelles: internal structures that form special functions for the cell. a. Cytoplasm: material between cell membrane and nucleus that contains the organelles. b. Mitochondria: “Powerhouse” of the cell. Produce ATP whic ...
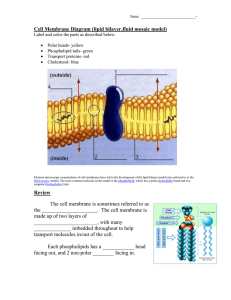
Cell Membrane Diagram (lipid bilayer,fluid mosaic model)
... Label and color the parts as described below. ...
... Label and color the parts as described below. ...
Vocabulary Flip Chart - Effingham County Schools
... a coiled structure of DNA and protein that forms in the cell nucleus during cell division ...
... a coiled structure of DNA and protein that forms in the cell nucleus during cell division ...
Flagellum
A flagellum (/fləˈdʒɛləm/; plural: flagella) is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. Flagella are organelles defined by function rather than structure. There are large differences between different types of flagella; the prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella differ greatly in protein composition, structure, and mechanism of propulsion. However, both are used for swimming.An example of a flagellate bacterium is the ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, which uses multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium. An example of a eukaryotic flagellate cell is the mammalian sperm cell, which uses its flagellum to propel itself through the female reproductive tract. Eukaryotic flagella are structurally identical to eukaryotic cilia, although distinctions are sometimes made according to function and/or length.