Chapter 3: cells
... •An animal cell placed in a hypertonic solution will lose water and shrink (crenation). •Hypotonic solution - a solution that has a lower solute ...
... •An animal cell placed in a hypertonic solution will lose water and shrink (crenation). •Hypotonic solution - a solution that has a lower solute ...
Cell Organelles and Functions – Analogy Project
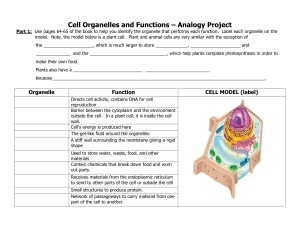
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
Mitochondria
... In tuberculosis, this mechanism is blocked: Mycobacterium tuberculosis secretes a protein that blocks this fusion these bacteria can now survive within the host cells tuberculosis ...
... In tuberculosis, this mechanism is blocked: Mycobacterium tuberculosis secretes a protein that blocks this fusion these bacteria can now survive within the host cells tuberculosis ...
Useful fundamental numbers in molecular biology The numbers
... DG needed to achieve an order of magnitude ratio of concentrations: ~6 kJ/mole = ~2 kT = ~60 meV Energetic contribution of a hydrogen bond: ~6-24 kJ/mole Æ 1-4 orders of magnitude concentration change DG of ATP hydrolysis under physiological conditions ~50 kJ/mole Æ ~20 kT Diffusion and catalysis ra ...
... DG needed to achieve an order of magnitude ratio of concentrations: ~6 kJ/mole = ~2 kT = ~60 meV Energetic contribution of a hydrogen bond: ~6-24 kJ/mole Æ 1-4 orders of magnitude concentration change DG of ATP hydrolysis under physiological conditions ~50 kJ/mole Æ ~20 kT Diffusion and catalysis ra ...
Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet
... Despite their difference in size and shape, all cells are enclosed by a cell membrane that consists of a double layer of phospholipids interspersed with proteins. Its unique structure is described as selectively permeable because it permits some substances to cross it rapidly, while others are unabl ...
... Despite their difference in size and shape, all cells are enclosed by a cell membrane that consists of a double layer of phospholipids interspersed with proteins. Its unique structure is described as selectively permeable because it permits some substances to cross it rapidly, while others are unabl ...
Study Guide
... Packets of proteins made by the ___________________ are then transported through the __________________ and then sent to the _____________________ in order to be sorted and packaged. ...
... Packets of proteins made by the ___________________ are then transported through the __________________ and then sent to the _____________________ in order to be sorted and packaged. ...
Power Plant City Plans Demolition Service City Border Postal
... surrounds the entire cell and holds it together. It separates the cell from everything that is outside of it. It is also controls what is able to pass into and out of the cell. ...
... surrounds the entire cell and holds it together. It separates the cell from everything that is outside of it. It is also controls what is able to pass into and out of the cell. ...
Name
... the surface of some bacteria are structures called pili (pilus-singular) that help bacteria adhere to surfaces. Color and label all the pili LIGHT GREEN. Some bacteria are motile (can move). Many of these bacteria have long, whip like structures called flagella (flagellum-singular). Color and label ...
... the surface of some bacteria are structures called pili (pilus-singular) that help bacteria adhere to surfaces. Color and label all the pili LIGHT GREEN. Some bacteria are motile (can move). Many of these bacteria have long, whip like structures called flagella (flagellum-singular). Color and label ...
Journal of Bacteriology
... composition of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: effect of lipopolysaccharide mutations. J. Bacteriol. 117:406416. Blum, H., H. Beier, and H. J. Gross. 1987. Improved silver staining of plant proteins, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide ...
... composition of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: effect of lipopolysaccharide mutations. J. Bacteriol. 117:406416. Blum, H., H. Beier, and H. J. Gross. 1987. Improved silver staining of plant proteins, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide ...
DOMAIN BACTERIA AND DOMAIN ARCHAEA
... In gram-negative bacteria, a third set of rings lies near the LPS layer. Flagella are located at one or both ends of the cell (polar flagellation) or over the entire surface (peritrichous flagellation). They rotate continuously and permit the bacterium to swim rapidly. Motile bacteria appear to sens ...
... In gram-negative bacteria, a third set of rings lies near the LPS layer. Flagella are located at one or both ends of the cell (polar flagellation) or over the entire surface (peritrichous flagellation). They rotate continuously and permit the bacterium to swim rapidly. Motile bacteria appear to sens ...
Unicellular Organisms 6_2.pub
... Unicellular organisms can use movement or locomotion to move toward or away from things such as food, light, and predators Movement — a change in the shape or figure of all or part of an organism — usually achieved using pseudopods — e.g. amoeba and white blood cells use pseudopods to obtain food ...
... Unicellular organisms can use movement or locomotion to move toward or away from things such as food, light, and predators Movement — a change in the shape or figure of all or part of an organism — usually achieved using pseudopods — e.g. amoeba and white blood cells use pseudopods to obtain food ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... B. cellular respiration. C. resource storage. D. protein synthesis. 6. If the ribosomes stop working in a cell, which cellular process would be most directly affected? A. Photosynthesis B. Aerobic respiration C. Protein synthesis D. Excretion of cellular wastes 2nd Item Specification: Identify the d ...
... B. cellular respiration. C. resource storage. D. protein synthesis. 6. If the ribosomes stop working in a cell, which cellular process would be most directly affected? A. Photosynthesis B. Aerobic respiration C. Protein synthesis D. Excretion of cellular wastes 2nd Item Specification: Identify the d ...
Movement through the Membrane
... – Provides a tough, flexible barrier between the cell and its surroundings ...
... – Provides a tough, flexible barrier between the cell and its surroundings ...
Viruses & Bacteria
... Do not cause disease Archaebacteria can live in extremely harsh environments They do not require oxygen (anaerobic) and can live in extremely salty (halophiles) environments, as well as extremely hot (thermophiles)or cold (psychrophiles) ...
... Do not cause disease Archaebacteria can live in extremely harsh environments They do not require oxygen (anaerobic) and can live in extremely salty (halophiles) environments, as well as extremely hot (thermophiles)or cold (psychrophiles) ...
7.3 Cell Structures
... • Ribosomes- protein factories that build the proteins for the cell • Plasmid- packets of DNA that the bacteria can swap with other bacteria to make it more resistant to medicine • Cell membrane- regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell • Cell wall- rigid outer structure that pro ...
... • Ribosomes- protein factories that build the proteins for the cell • Plasmid- packets of DNA that the bacteria can swap with other bacteria to make it more resistant to medicine • Cell membrane- regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell • Cell wall- rigid outer structure that pro ...
3-1
... The water will flow from inside cell to outside cell at equal rate and visa versa. This happens because concentration is equal on both sides. The state of equilibrium of extracellular fluid is ISOTONIC to intracellular fluid. (iso means ...
... The water will flow from inside cell to outside cell at equal rate and visa versa. This happens because concentration is equal on both sides. The state of equilibrium of extracellular fluid is ISOTONIC to intracellular fluid. (iso means ...
NUCLEATED CELLS…EUKARYOTES The Eukaryota is a domain of
... There are a number of depictions of the tree of life. Most modern Trees of Life have 3 domains: 1) Eubacteria (sometimes called just Bacteria). This first domain is where most of the common bacteria belong...all its members are single celled organisms with no nuclei. The most famous bacteria E. Coli ...
... There are a number of depictions of the tree of life. Most modern Trees of Life have 3 domains: 1) Eubacteria (sometimes called just Bacteria). This first domain is where most of the common bacteria belong...all its members are single celled organisms with no nuclei. The most famous bacteria E. Coli ...
Ch 6 Chapter summary - OHS General Biology
... ○ Each tubulin molecule is a dimer consisting of two subunits. ...
... ○ Each tubulin molecule is a dimer consisting of two subunits. ...
ws-cell_city - High School Biology
... might represent companies, places, or parts of the city because they each have similar jobs. PART A DIRECTIONS: In #1-14, complete each description below with the correct organelle name. 1. The _______________is a large, round/oval structure usually located near the center of the cell. It is the con ...
... might represent companies, places, or parts of the city because they each have similar jobs. PART A DIRECTIONS: In #1-14, complete each description below with the correct organelle name. 1. The _______________is a large, round/oval structure usually located near the center of the cell. It is the con ...
3-20
... • Process where mRNA, rRNA & tRNA are used to form a specific protein – sequence of nucleotides on mRNA is “read” by rRNA to construct a protein (with its specific sequence of ...
... • Process where mRNA, rRNA & tRNA are used to form a specific protein – sequence of nucleotides on mRNA is “read” by rRNA to construct a protein (with its specific sequence of ...
Cell Theory
... -protect cell & maintain cell shape Bacterial cell walls -may be composed of peptidoglycan -may be Gram positive or Gram negative Archaean cell walls lack peptidoglycan. ...
... -protect cell & maintain cell shape Bacterial cell walls -may be composed of peptidoglycan -may be Gram positive or Gram negative Archaean cell walls lack peptidoglycan. ...
Chapter 3 The Cell
... molecules and a higher concentration of solutes than the inside. water will diffuse out of the cell the cell will shrink plasmolysis- a collapse of the cell’s cytoplasm. IV. Transport across membranes A. Passive Transport 1. diffusion – process by which molecules tend to scatter themselves thr ...
... molecules and a higher concentration of solutes than the inside. water will diffuse out of the cell the cell will shrink plasmolysis- a collapse of the cell’s cytoplasm. IV. Transport across membranes A. Passive Transport 1. diffusion – process by which molecules tend to scatter themselves thr ...
Chapter 3 Study Guide
... 6) List two examples of eukaryotic cells. 7) List an example of a prokaryotic cell. 8) What organelle stores the cell’s genetic (DNA & RNA) information? 9) How would you best describe the rough ER? 10) What organelle is responsible for energy? 11) What organelle contains enzymes to break down old ce ...
... 6) List two examples of eukaryotic cells. 7) List an example of a prokaryotic cell. 8) What organelle stores the cell’s genetic (DNA & RNA) information? 9) How would you best describe the rough ER? 10) What organelle is responsible for energy? 11) What organelle contains enzymes to break down old ce ...
The Cell - Education Service Center, Region 2
... function – used to store water, food or waste. In plant cells, they help keep the plant from wilting. ...
... function – used to store water, food or waste. In plant cells, they help keep the plant from wilting. ...
Flagellum
A flagellum (/fləˈdʒɛləm/; plural: flagella) is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. Flagella are organelles defined by function rather than structure. There are large differences between different types of flagella; the prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella differ greatly in protein composition, structure, and mechanism of propulsion. However, both are used for swimming.An example of a flagellate bacterium is the ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, which uses multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium. An example of a eukaryotic flagellate cell is the mammalian sperm cell, which uses its flagellum to propel itself through the female reproductive tract. Eukaryotic flagella are structurally identical to eukaryotic cilia, although distinctions are sometimes made according to function and/or length.