nutrient-cycle ppt
... and their conversion under pressure into coal and petroleum (fossil fuels), store carbon underground. 4. Human activities, such as mining, cutting and burning forests, and burning fossil fuels, release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere ...
... and their conversion under pressure into coal and petroleum (fossil fuels), store carbon underground. 4. Human activities, such as mining, cutting and burning forests, and burning fossil fuels, release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere ...
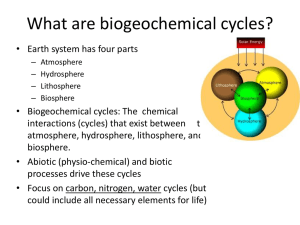
Biogeochemical Cycles
... Carbon is a key ingredient in living tissues. It forms animal skeletons, is an important component of the atmosphere, and is taken up by plants in photosynthesis. In the atmosphere, carbon is present as carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide is released into the air by volcanic activity, burning o ...
... Carbon is a key ingredient in living tissues. It forms animal skeletons, is an important component of the atmosphere, and is taken up by plants in photosynthesis. In the atmosphere, carbon is present as carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide is released into the air by volcanic activity, burning o ...
Test File - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... Direction: Carefully read the test questions and apply Reading and test taking strategies on each one of them. ...
... Direction: Carefully read the test questions and apply Reading and test taking strategies on each one of them. ...
Document
... fertilisers to the soil. farmers using natural fertilisers such as compost and manure. the decay of deal plants and animals. farmers planting peas and beans in their fields every 2 or 3 years. fa ...
... fertilisers to the soil. farmers using natural fertilisers such as compost and manure. the decay of deal plants and animals. farmers planting peas and beans in their fields every 2 or 3 years. fa ...
Nitrogen is essential to living things for the production of amino
... called algae to grow rapidly. When they die, they are broken down by ...
... called algae to grow rapidly. When they die, they are broken down by ...
Core Worksheet – Option E - Cambridge Resources for the IB Diploma
... Organic matter is removed in the secondary stage. Describe the activated sludge process for removal of organic matter. ...
... Organic matter is removed in the secondary stage. Describe the activated sludge process for removal of organic matter. ...
I Must Have That Formula
... of oxygen gas. The resulting reactions produce a potentially dangerous mixture that include other nitrogen oxides, ozone, and irritating organic compounds, as well as carbon dioxide and water vapor. Air Pollution Control and Prevention SO2 Ca(OH )2 CaSO3 H 2O : Formula that represents the proc ...
... of oxygen gas. The resulting reactions produce a potentially dangerous mixture that include other nitrogen oxides, ozone, and irritating organic compounds, as well as carbon dioxide and water vapor. Air Pollution Control and Prevention SO2 Ca(OH )2 CaSO3 H 2O : Formula that represents the proc ...
I Must Have That Formula
... CO2 H 2O H 2CO3 : The pH of rainwater is normally slightly acidic, at about 5.6, due mainly to reaction of carbon dioxide with water to form carbonic acid. SO2 H 2O H 2 SO3 SO3 H 2O H 2 SO4 2 NO2 H 2O HNO3 HNO2 Other natural events can contribute to the acidity of precipitation. Vo ...
... CO2 H 2O H 2CO3 : The pH of rainwater is normally slightly acidic, at about 5.6, due mainly to reaction of carbon dioxide with water to form carbonic acid. SO2 H 2O H 2 SO3 SO3 H 2O H 2 SO4 2 NO2 H 2O HNO3 HNO2 Other natural events can contribute to the acidity of precipitation. Vo ...
Document
... gas molecules, splitting them into individual oxygen atoms. These highly reactive oxygen atoms are examples of free radicals; they quickly enter into chemical reactions that allow them to attain stable arrangements of electrons. In the stratosphere free radicals can combine with oxygen molecules to ...
... gas molecules, splitting them into individual oxygen atoms. These highly reactive oxygen atoms are examples of free radicals; they quickly enter into chemical reactions that allow them to attain stable arrangements of electrons. In the stratosphere free radicals can combine with oxygen molecules to ...
I Must Have That Formula APES Chemistry Review From Kelly A
... fires, and lightning produce sulfur dioxide, sulfur trioxide, and nitrogen dioxide. These gases can react with atmospheric water in much the same way that carbon dioxide does to produce sulfurous acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid and nitrous acid. Ozone Formation and Destruction O2 high-energy UVph ...
... fires, and lightning produce sulfur dioxide, sulfur trioxide, and nitrogen dioxide. These gases can react with atmospheric water in much the same way that carbon dioxide does to produce sulfurous acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid and nitrous acid. Ozone Formation and Destruction O2 high-energy UVph ...
I_Must_Have_That_Formula[1]
... equation represents the key ingredients and products of photochemical smog. Hydrocarbons (including VOC’s), carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides from vehicle exhausts are irradiated by sunlight in the presence of oxygen gas. The resulting reactions produce a potentially dangerous mixture that includ ...
... equation represents the key ingredients and products of photochemical smog. Hydrocarbons (including VOC’s), carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides from vehicle exhausts are irradiated by sunlight in the presence of oxygen gas. The resulting reactions produce a potentially dangerous mixture that includ ...
Nutrient Recycling Poster
... ensures that there is no real longterm drain on the Earth’s nutrients, despite millions of years of plant and animal activity. ...
... ensures that there is no real longterm drain on the Earth’s nutrients, despite millions of years of plant and animal activity. ...
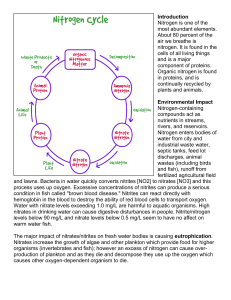
the nitrogen cycle: what a gas
... THE NITROGEN CYCLE: WHAT A GAS!! Although nitrogen gas makes up 79% of the Earth’s ___________________, it cannot be used in that form. Nitrogen is needed so cells can make ____________________ and genetic material like ____________________. For this to happen, the nitrogen gas must first be convert ...
... THE NITROGEN CYCLE: WHAT A GAS!! Although nitrogen gas makes up 79% of the Earth’s ___________________, it cannot be used in that form. Nitrogen is needed so cells can make ____________________ and genetic material like ____________________. For this to happen, the nitrogen gas must first be convert ...
Nitrogen dioxide poisoning
Nitrogen dioxide poisoning is the illness resulting from the toxic effect of Nitrogen (II) oxide. It usually occurs after the inhalation of the gas beyond the threshold limit value.Nitrogen (II) oxide is reddish-brown with very a sharp, harsh smell at high concentrations. It is colourless and odourless at lower concentration but yet harmful. Nitrogen dioxide poisoning depends on the duration, frequency and intensity of exposure.Nitrogen (II) oxide is an irritant of the mucous membrane linked with other air pollutant that causes pulmonary diseases such as OLD, asthma, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sometimes Acute exacerbation of COPD and in fatal cases, deaths.Its poor solubility in water enhances its passage and its ability to pass through the moist oral mucosa of the respiratory tract.Like most toxic gases, the dose inhaled determines the toxicity on the respiratory tract. Occupational exposures constitute the highest risk of toxicity and domestic exposure is uncommon. Prolonged exposure to low concentration of the gas may have lethal effects, as can short-term exposure to high concentrations like Chlorine gas poisoning. It is one of the major air pollutant capable of causing severe heath hazards such as Coronary artery disease as well as Stroke.Nitrogen (II) oxide is often released into the environment as a byproduct of fuel combustion but rarely released by Spontaneous combustion. Known sources of Nitrogen gas poisoning includes automobile exhaust, Power stations, The toxicity may also results from non-combustible sources such as the one released from anaerobic fermentation of food grains and Anaerobic digestion of Biodegradable waste.The WHO developed a global recommendation limiting exposures less than 20 part per billion for chronic exposure and value less 100ppb for one hour for acute exposure, using Nitrogen (II)oxide as a marker for other pollutant from fuel combustions. The standardss also based on the concentration of Nitrogen (II) oxide that show a significant and profound effects on the function of the pulmonary of asthmatic patients.Historically, some states in the U.S including Chicago and L.A have high levels of Nitrogen (II) oxide but the EPA set a standard values less than 100 ppb for one hour exposure and less than 53 ppb for chronic exposure.
















![I_Must_Have_That_Formula[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000170703_1-9524811e6570bb070018bb76b27ae172-300x300.png)