
[2011 question paper]
... Entrance Examination, 2011 Part A For each of the statements given below, state whether it is True or False and give brief reasons in the sheets provided. Marks will be given only when reasons are provided. 1. (k!)2 is a factor of (2k + 2)! for any positive integer k. 2. Let p(x) be a polynomial of ...
... Entrance Examination, 2011 Part A For each of the statements given below, state whether it is True or False and give brief reasons in the sheets provided. Marks will be given only when reasons are provided. 1. (k!)2 is a factor of (2k + 2)! for any positive integer k. 2. Let p(x) be a polynomial of ...
Assignment1
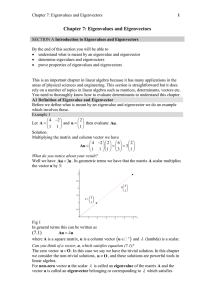
... Inverse of square matrix is defined as a matrix which when multiplied by matrix gives an identity matrix of same size. A * A-1 = I ...
... Inverse of square matrix is defined as a matrix which when multiplied by matrix gives an identity matrix of same size. A * A-1 = I ...
Matrix Theory Review for Final Exam The final exam is Wednesday
... there exists an orthogonal matrix Q and a diagonal matrix D so that QT AQ = D. That is, A is orthogonally similar to a diagonal matrix. In essence, this says that the way A acts on Rn is to stretch it in n orthogonal directions. One can find Q as follows: (a) find the eigenvalues of A; (b) for each ...
... there exists an orthogonal matrix Q and a diagonal matrix D so that QT AQ = D. That is, A is orthogonally similar to a diagonal matrix. In essence, this says that the way A acts on Rn is to stretch it in n orthogonal directions. One can find Q as follows: (a) find the eigenvalues of A; (b) for each ...
Jordan normal form
In linear algebra, a Jordan normal form (often called Jordan canonical form)of a linear operator on a finite-dimensional vector space is an upper triangular matrix of a particular form called a Jordan matrix, representing the operator with respect to some basis. Such matrix has each non-zero off-diagonal entry equal to 1, immediately above the main diagonal (on the superdiagonal), and with identical diagonal entries to the left and below them. If the vector space is over a field K, then a basis with respect to which the matrix has the required form exists if and only if all eigenvalues of the matrix lie in K, or equivalently if the characteristic polynomial of the operator splits into linear factors over K. This condition is always satisfied if K is the field of complex numbers. The diagonal entries of the normal form are the eigenvalues of the operator, with the number of times each one occurs being given by its algebraic multiplicity.If the operator is originally given by a square matrix M, then its Jordan normal form is also called the Jordan normal form of M. Any square matrix has a Jordan normal form if the field of coefficients is extended to one containing all the eigenvalues of the matrix. In spite of its name, the normal form for a given M is not entirely unique, as it is a block diagonal matrix formed of Jordan blocks, the order of which is not fixed; it is conventional to group blocks for the same eigenvalue together, but no ordering is imposed among the eigenvalues, nor among the blocks for a given eigenvalue, although the latter could for instance be ordered by weakly decreasing size.The Jordan–Chevalley decomposition is particularly simple with respect to a basis for which the operator takes its Jordan normal form. The diagonal form for diagonalizable matrices, for instance normal matrices, is a special case of the Jordan normal form.The Jordan normal form is named after Camille Jordan.









![[2011 question paper]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008843345_1-9a0802372adf6384e8c1e5127a999f79-300x300.png)









![perA= ]TY[aMi)` « P^X = ^ = xW - American Mathematical Society](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014142501_1-23faff90adae754bbfcc6088c2128850-300x300.png)

