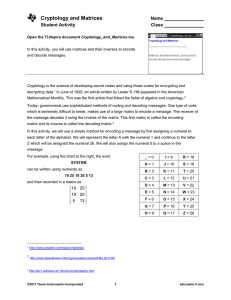
Show that when the unit vector j is multiplied by the following
... Instructions: 60-min time limit. You can use Maple to do the problems and check your answers, but clearly show your setup and solution for each problem on the test pages – read each problem to see what we want specifically. 1 (10 points) i and j are the unit vectors along x and y axes. Write the vec ...
... Instructions: 60-min time limit. You can use Maple to do the problems and check your answers, but clearly show your setup and solution for each problem on the test pages – read each problem to see what we want specifically. 1 (10 points) i and j are the unit vectors along x and y axes. Write the vec ...
EC220 - Web del Profesor
... two equations, there are two unknown variables (Price and Quantity) and each equation has variables that we assumed are exogenous. Another example is the SavingInvestment model. Saving and investment depend on the real interest rate. The equilibrium condition requires that Saving=Investment (loanabl ...
... two equations, there are two unknown variables (Price and Quantity) and each equation has variables that we assumed are exogenous. Another example is the SavingInvestment model. Saving and investment depend on the real interest rate. The equilibrium condition requires that Saving=Investment (loanabl ...
Elimination with Matrices
... The elimination matrix used to eliminate the entry in row m column n is denoted Emn . The calculation above took us from A to E21 A. The three elimination steps leading to U were: E32 ( E31 ( E21 A)) = U, where E31 = I. Thus E32 ( E21 A) = U. Matrix multiplication is associative, so we can also writ ...
... The elimination matrix used to eliminate the entry in row m column n is denoted Emn . The calculation above took us from A to E21 A. The three elimination steps leading to U were: E32 ( E31 ( E21 A)) = U, where E31 = I. Thus E32 ( E21 A) = U. Matrix multiplication is associative, so we can also writ ...
Linear Transformations 3.1 Linear Transformations
... notation and ideas are common to all applications (trickier are issues of interpretation and existence). In the end, the first object of study, the wave function in position space, can be represented by a vector in Hilbert space (the vector space of square integrable functions). Operations like “mea ...
... notation and ideas are common to all applications (trickier are issues of interpretation and existence). In the end, the first object of study, the wave function in position space, can be represented by a vector in Hilbert space (the vector space of square integrable functions). Operations like “mea ...
Oct. 3
... We define an operation that produces a matrix C by concatenating horizontally a given matrix A times the successive columns of another matrix B. We define such a concatenation involving A and B the product A times B, usually denoted AB. The operation that produces such a concatenation is called matr ...
... We define an operation that produces a matrix C by concatenating horizontally a given matrix A times the successive columns of another matrix B. We define such a concatenation involving A and B the product A times B, usually denoted AB. The operation that produces such a concatenation is called matr ...
determinants
... The focus before was to determine information about the solution set of the linear system of equations given as the matrix equation Ax = b. We saw that in general, both the coefficient matrix A and right side b contributed to the specific nature of the solution set. This followed since the linear sy ...
... The focus before was to determine information about the solution set of the linear system of equations given as the matrix equation Ax = b. We saw that in general, both the coefficient matrix A and right side b contributed to the specific nature of the solution set. This followed since the linear sy ...
2 Sequence of transformations
... The analysis required is that the translation parameters have to be scaled (multiplied) by the scaling parameters, because in the rst case, the scaling matrix is applied before the translation, and the translation gets scaled. This change in the parameters corrects for that. (2 points for the right ...
... The analysis required is that the translation parameters have to be scaled (multiplied) by the scaling parameters, because in the rst case, the scaling matrix is applied before the translation, and the translation gets scaled. This change in the parameters corrects for that. (2 points for the right ...
Proposition 7.3 If α : V → V is self-adjoint, then 1) Every eigenvalue
... Theorem 7.6 (Spectral Theorem) Let α : V → V be a self-adjoint linear operator on an ndimensional inner product space. Then there is an orthonormal basis v1 , . . . , vn of eigenvectors of α. Proof (Not examinable). We first prove by induction on n that we can find a orthonormal basis of eigenvecto ...
... Theorem 7.6 (Spectral Theorem) Let α : V → V be a self-adjoint linear operator on an ndimensional inner product space. Then there is an orthonormal basis v1 , . . . , vn of eigenvectors of α. Proof (Not examinable). We first prove by induction on n that we can find a orthonormal basis of eigenvecto ...
LINEAR ALGEBRA (1) True or False? (No explanation required
... Every nonzero matrix A has an inverse A−1 The inverse of a product AB of square matrices A, B is equal to A−1 B −1 Homogeneous linear systems of equations always have a solution The rank of an m × n-matrix is always ≤ n The set of polynomials of degree = 2 is a vector space The product of an m × n- ...
... Every nonzero matrix A has an inverse A−1 The inverse of a product AB of square matrices A, B is equal to A−1 B −1 Homogeneous linear systems of equations always have a solution The rank of an m × n-matrix is always ≤ n The set of polynomials of degree = 2 is a vector space The product of an m × n- ...